In certain physical models, the nonhomogeneous term, or forcing term, g(t) in the equation ay" + by' + cy = g(t) may not be continuous, but have a jump discontinuity. If this occurs, a reasonable solution can still be obtained using the following procedure. Consider the following initial value problem. 240 if 0sts 7x/6 y" + 4y' + 40y = g(t); y(0) = 0, y'(0) = 0, where g(t) = . if t> 7x/6 Complete parts (a) through (c) below. (a) Find a solution to the initial value problem for 0sts7r/6. The solution for 0sts 7/6 is y(t) = - 6 e cos 6t - 2 e 21 sin 6t + 6 (Type an equation.) (b) Find a general solution for t> 7a /6. The general solution for t> 7n/6 is y(t) = C, e -21 cos 6t + C2 e -21 sin 6t. (Type an equation. Do not use d, D, e, E, i, or I as arbitrary constants since these letters already have defined meanings.) (c) Now choose the constants in the general solution from part (b) so that the solution from part (a) and the solution from part (b) agree, together with their first derivatives, at t= 7x/6. This gives a piecewise continuously differentiable function that satisfies the differential equation except at t= 7x/6. if 0st< 7x/6 The solution to the differential equation is y(t) = if t> 7x/6
In certain physical models, the nonhomogeneous term, or forcing term, g(t) in the equation ay" + by' + cy = g(t) may not be continuous, but have a jump discontinuity. If this occurs, a reasonable solution can still be obtained using the following procedure. Consider the following initial value problem. 240 if 0sts 7x/6 y" + 4y' + 40y = g(t); y(0) = 0, y'(0) = 0, where g(t) = . if t> 7x/6 Complete parts (a) through (c) below. (a) Find a solution to the initial value problem for 0sts7r/6. The solution for 0sts 7/6 is y(t) = - 6 e cos 6t - 2 e 21 sin 6t + 6 (Type an equation.) (b) Find a general solution for t> 7a /6. The general solution for t> 7n/6 is y(t) = C, e -21 cos 6t + C2 e -21 sin 6t. (Type an equation. Do not use d, D, e, E, i, or I as arbitrary constants since these letters already have defined meanings.) (c) Now choose the constants in the general solution from part (b) so that the solution from part (a) and the solution from part (b) agree, together with their first derivatives, at t= 7x/6. This gives a piecewise continuously differentiable function that satisfies the differential equation except at t= 7x/6. if 0st< 7x/6 The solution to the differential equation is y(t) = if t> 7x/6
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter39: Relativity
Section39.2: Special Case: Galilean Relativity
Problem 39.2CE: Suppose the primed and laboratory observers want to measure the length of a rod that rests on the...
Related questions
Question
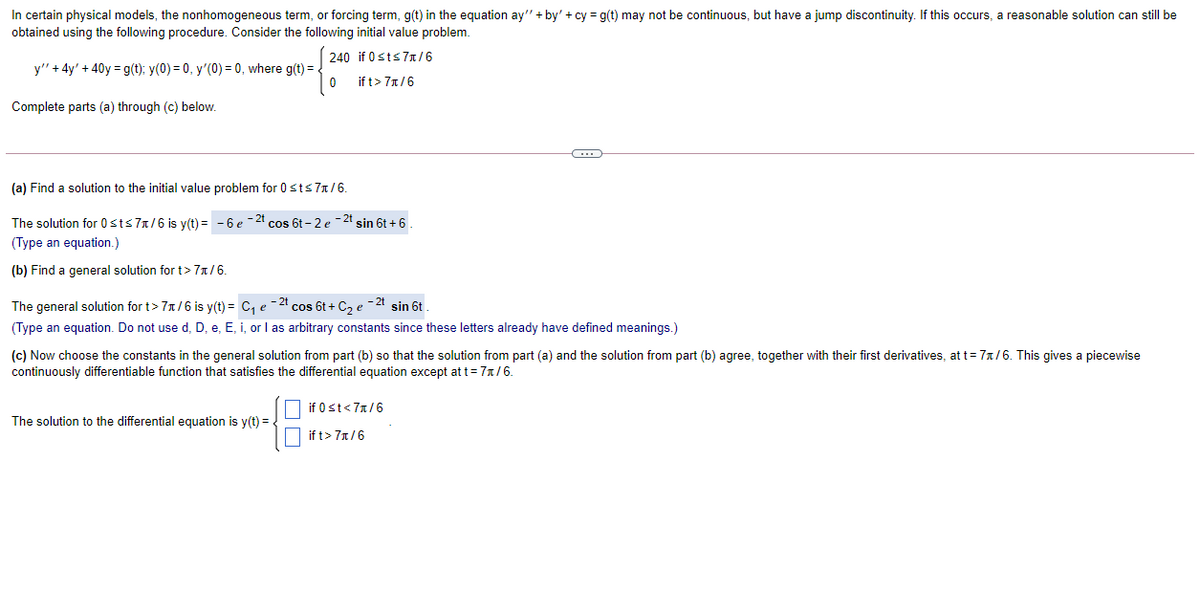
Transcribed Image Text:In certain physical models, the nonhomogeneous term, or forcing term, g(t) in the equation ay" + by' + cy = g(t) may not be continuous, but have a jump discontinuity. If this occurs, a reasonable solution can still be
obtained using the following procedure. Consider the following initial value problem.
240 if 0sts7T/6
y" + 4y' + 40y = g(t); y(0) = 0, y'(0) = 0, where g(t) = .
if t> 7x/6
Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
(a) Find a solution to the initial value problem for 0 sts 71/6.
The solution for 0sts 7n/6 is y(t) = - 6 e -21
*cos 6t - 2 e - 2t
sin 6t + 6
(Type an equation.)
(b) Find a general solution for t> 71/6.
The general solution for t> 7x/6 is y(t) = C, e-2 cos 6t + C, e -2t sin 6t
(Type an equation. Do not use d. D. e, E, i, or I as arbitrary constants since these letters already have defined meanings.)
(c) Now choose the constants in the general solution from part (b) so that the solution from part (a) and the solution from part (b) agree, together with their first derivatives, at t= 71/6. This gives a piecewise
continuously differentiable function that satisfies the differential equation except at t= 7x/6.
if 0st<7x/6
The solution to the differential equation is y(t) = .
if t> 7x/6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill