In microbiology, dilutions are critical for getting a countable number of microbes to grow on a petri dish. If you suspect your culture of bacteria has 50 x 106 cells per mL, what would you want the final dilution to be in order to end up with 50 colonies of bacteria on a petri dish? Express your answer as an exponent rounded to two decimal places. Eg. 10.01e-3, not 0.00101. Treat colonies of bacteria (cells / mL) the way you would treat concentration (Moles / L) The formula M1V1 = M2V2 can still be used. The final concentration is the number of colonies on the petri dish. Solve %3D for V2. A 0.00000001 dilution is performed on a culture of bacteria in order to perform viable plate counts. From the dilution, *0.1 mL* of solution is plated on solid media, and 150 colonies of bacteria grow on the petri dish. Assuming each colony came from a single bacterium, how many bacteria are in a single mL of the original culture? Express your answer to two decimal places using exponential notation. • Since only 0.1 mL is put on the plate, this counts as an extra dilution!!! Any time less than 1 mL is transfered, a dilution is being performed. Any time more than 1 mL is transfered, a concentration is being performed.
In microbiology, dilutions are critical for getting a countable number of microbes to grow on a petri dish. If you suspect your culture of bacteria has 50 x 106 cells per mL, what would you want the final dilution to be in order to end up with 50 colonies of bacteria on a petri dish? Express your answer as an exponent rounded to two decimal places. Eg. 10.01e-3, not 0.00101. Treat colonies of bacteria (cells / mL) the way you would treat concentration (Moles / L) The formula M1V1 = M2V2 can still be used. The final concentration is the number of colonies on the petri dish. Solve %3D for V2. A 0.00000001 dilution is performed on a culture of bacteria in order to perform viable plate counts. From the dilution, *0.1 mL* of solution is plated on solid media, and 150 colonies of bacteria grow on the petri dish. Assuming each colony came from a single bacterium, how many bacteria are in a single mL of the original culture? Express your answer to two decimal places using exponential notation. • Since only 0.1 mL is put on the plate, this counts as an extra dilution!!! Any time less than 1 mL is transfered, a dilution is being performed. Any time more than 1 mL is transfered, a concentration is being performed.
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter1: Chemistry And Measurement
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.153QP
Related questions
Question
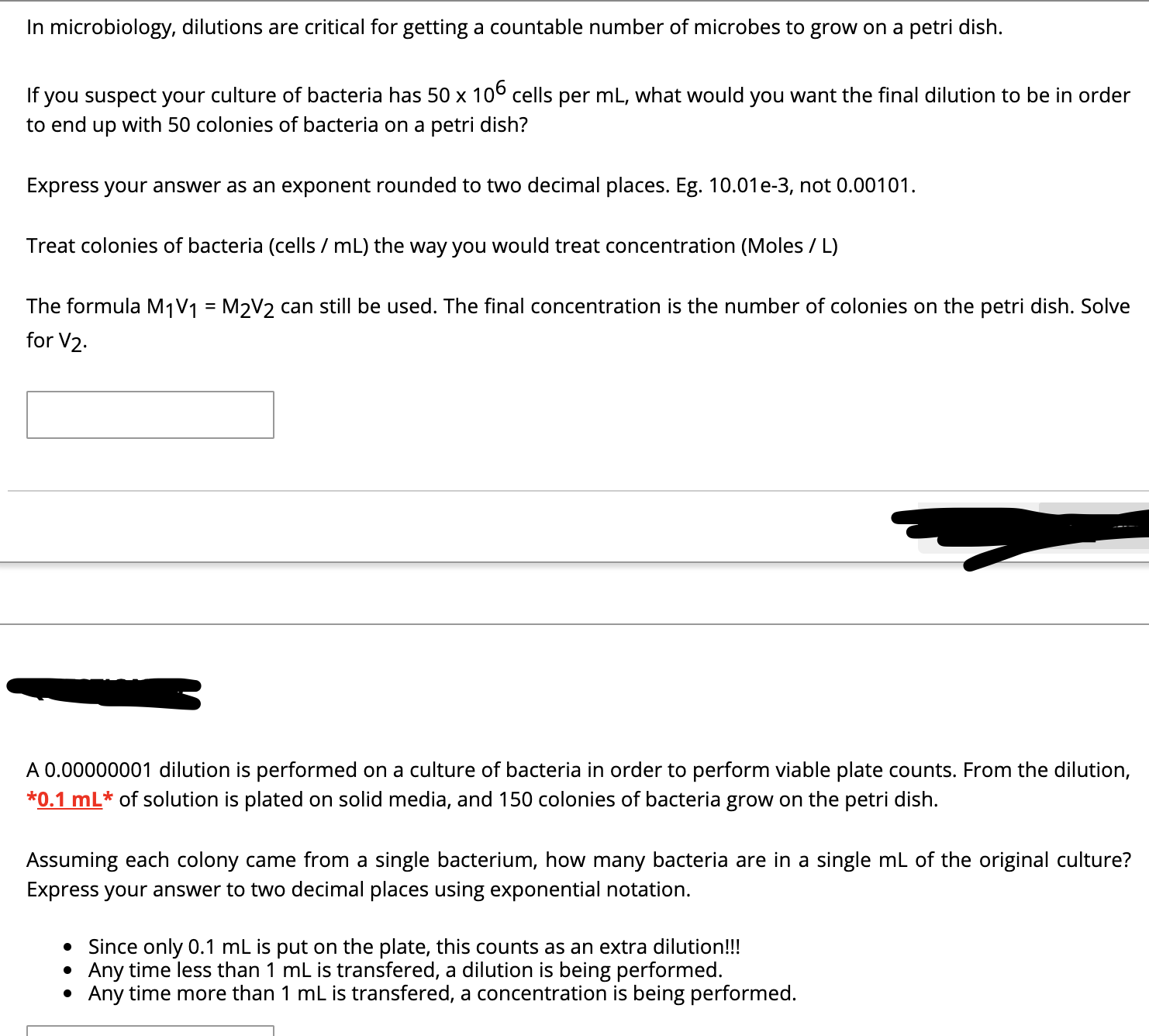
Transcribed Image Text:In microbiology, dilutions are critical for getting a countable number of microbes to grow on a petri dish.
If you suspect your culture of bacteria has 50 x 106 cells per mL, what would you want the final dilution to be in order
to end up with 50 colonies of bacteria on a petri dish?
Express your answer as an exponent rounded to two decimal places. Eg. 10.01e-3, not 0.00101.
Treat colonies of bacteria (cells / mL) the way you would treat concentration (Moles / L)
The formula M1V1 = M2V2 can still be used. The final concentration is the number of colonies on the petri dish. Solve
%3D
for V2.
A 0.00000001 dilution is performed on a culture of bacteria in order to perform viable plate counts. From the dilution,
*0.1 mL* of solution is plated on solid media, and 150 colonies of bacteria grow on the petri dish.
Assuming each colony came from a single bacterium, how many bacteria are in a single mL of the original culture?
Express your answer to two decimal places using exponential notation.
• Since only 0.1 mL is put on the plate, this counts as an extra dilution!!!
Any time less than 1 mL is transfered, a dilution is being performed.
Any time more than 1 mL is transfered, a concentration is being performed.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning