In the laboratory a student burns a 0.596-g sample of acetylsalicylic acid (C,H§O4) in a bomb calorimeter containing 1090. g of water. The temperature increases from 24.40 °C to 26.80 °C. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J g-l°C" 1 The molar heat of combustion is -3869 kJ per mole of acetylsalicylic acid.
In the laboratory a student burns a 0.596-g sample of acetylsalicylic acid (C,H§O4) in a bomb calorimeter containing 1090. g of water. The temperature increases from 24.40 °C to 26.80 °C. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J g-l°C" 1 The molar heat of combustion is -3869 kJ per mole of acetylsalicylic acid.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter6: Thermochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 112AE: In a bomb calorimeter, the reaction vessel is surrounded by water that must be added for each...
Related questions
Question
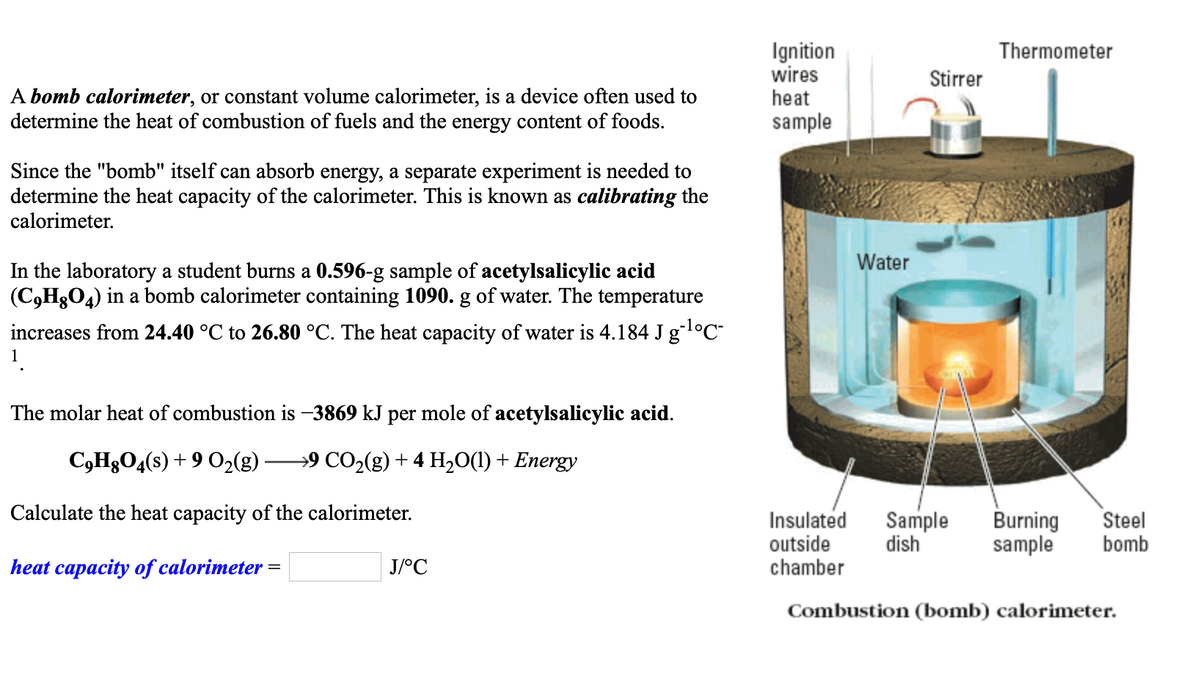
Transcribed Image Text:Ignition
wires
heat
Thermometer
Stirrer
A bomb calorimeter, or constant volume calorimeter, is a device often used to
determine the heat of combustion of fuels and the energy content of foods.
sample
Since the "bomb" itself can absorb energy, a separate experiment is needed to
determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. This is known as calibrating the
calorimeter.
%3D
Water
In the laboratory a student burns a 0.596-g sample of acetylsalicylic acid
(C,H3O4) in a bomb calorimeter containing 1090. g of water. The temperature
increases from 24.40 °C to 26.80 °C. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J gl°C
1
The molar heat of combustion is -3869 kJ per mole of acetylsalicylic acid.
C,H3O4(s) + 9 O2(g) -
→9 CO2(g) + 4 H20(1) + Energy
Calculate the heat capacity of the calorimeter.
Burning
sample
Insulated
Sample
dish
Steel
outside
chamber
bomb
heat capacity of calorimeter =
J/°C
Combustion (bomb) calorimeter.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning