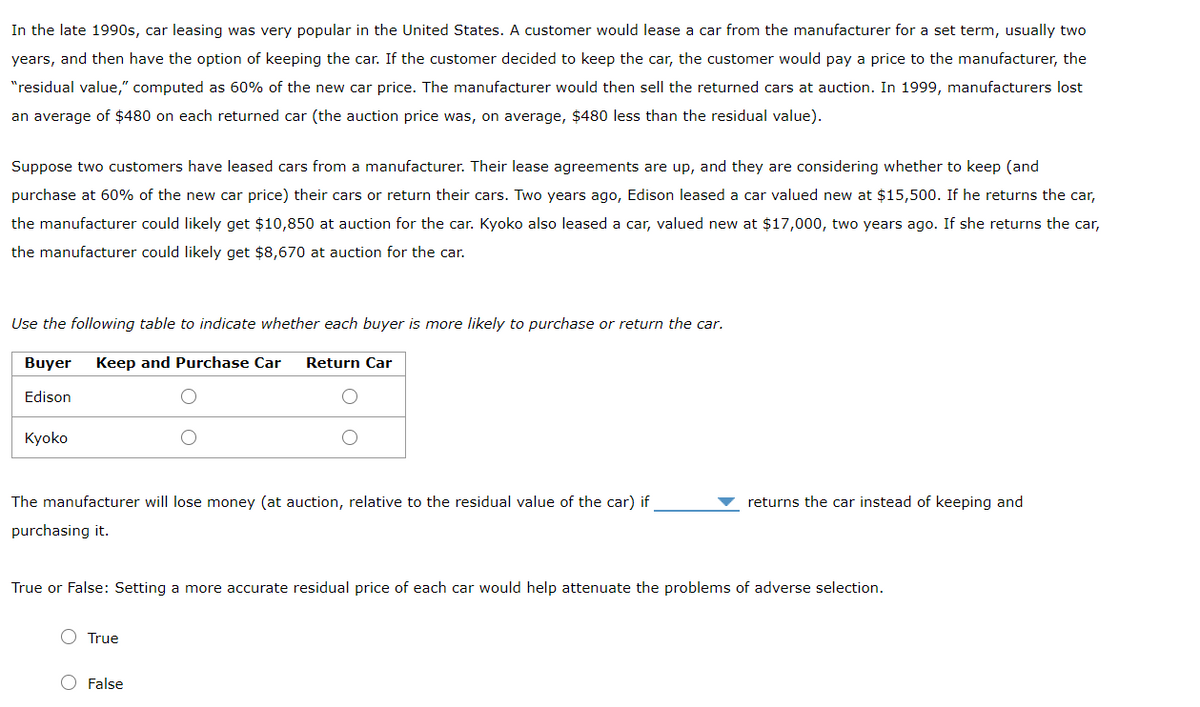
In the late 1990s, car leasing was very popular in the United States. A customer would lease a car from the manufacturer for a set term, usually two years, and then have the option of keeping the car. If the customer decided to keep the car, the customer would pay a price to the manufacturer, the "residual value," computed as 60% of the new car price. The manufacturer would then sell the returned cars at auction. In 1999, manufacturers lost an average of $480 on each returned car (the auction price was, on average, $480 less than the residual value). Suppose two customers have leased cars from a manufacturer. Their lease agreements are up, and they are considering whether to keep (and purchase at 60% of the new car price) their cars or return their cars. Two years ago, Edison leased a car valued new at $15,500. If he returns the car, the manufacturer could likely get $10,850 at auction for the car. Kyoko also leased a car, valued new at $17,000, two years ago. If she returns the car, the manufacturer could likely get $8,670 at auction for the car. Use the following table to indicate whether each buyer is more likely to purchase or return the car. Buyer Keep and Purchase Car Return Car Edison Kyoko The manufacturer will lose money (at auction, relative to the residual value of the car) if returns the car instead of keeping and purchasing it. True or False: Setting a more accurate residual price of each car would help attenuate the problems of adverse selection. True O False
Net Present Value
Net present value is the most important concept of finance. It is used to evaluate the investment and financing decisions that involve cash flows occurring over multiple periods. The difference between the present value of cash inflow and cash outflow is termed as net present value (NPV). It is used for capital budgeting and investment planning. It is also used to compare similar investment alternatives.
Investment Decision
The term investment refers to allocating money with the intention of getting positive returns in the future period. For example, an asset would be acquired with the motive of generating income by selling the asset when there is a price increase.
Factors That Complicate Capital Investment Analysis
Capital investment analysis is a way of the budgeting process that companies and the government use to evaluate the profitability of the investment that has been done for the long term. This can include the evaluation of fixed assets such as machinery, equipment, etc.
Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting is a decision-making process whereby long-term investments is evaluated and selected based on whether such investment is worth pursuing in future or not. It plays an important role in financial decision-making as it impacts the profitability of the business in the long term. The benefits of capital budgeting may be in the form of increased revenue or reduction in cost. The capital budgeting decisions include replacing or rebuilding of the fixed assets, addition of an asset. These long-term investment decisions involve a large number of funds and are irreversible because the market for the second-hand asset may be difficult to find and will have an effect over long-time spam. A right decision can yield favorable returns on the other hand a wrong decision may have an effect on the sustainability of the firm. Capital budgeting helps businesses to understand risks that are involved in undertaking capital investment. It also enables them to choose the option which generates the best return by applying the various capital budgeting techniques.
In the late 1990s, car leasing was very popular in the United States. A customer would lease a car from the manufacturer for a set term, usually two years, and then have the option of keeping the car. If the customer decided to keep the car, the customer would pay a price to the manufacturer, the “residual value,” computed as 60% of the new car price. The manufacturer would then sell the returned cars at auction. In 1999, manufacturers lost an average of $480 on each returned car (the auction price was, on average, $480 less than the residual value).
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images








