In the long-run, the amount of economic profits: O for firms under monopolistic competition tend to diminish so that no more than normal profits can be earned, because entry barriers are fairly low, unless they can successfully and continuously differentiate their product or service. for (unregulated) monopoly firms always tends downward toward zero because consumers easily find close substitute goods or services. O for firms under perfect competition will tend to get ever higher because free entry of new firms adds to the profits of the existing firms in the market. for firms under perfect competition will tend to get higher over time because small-sized firms are constantly investing large sums of money in the latest production technologies and in innovations through research and development (R&D).
In the long-run, the amount of economic profits: O for firms under monopolistic competition tend to diminish so that no more than normal profits can be earned, because entry barriers are fairly low, unless they can successfully and continuously differentiate their product or service. for (unregulated) monopoly firms always tends downward toward zero because consumers easily find close substitute goods or services. O for firms under perfect competition will tend to get ever higher because free entry of new firms adds to the profits of the existing firms in the market. for firms under perfect competition will tend to get higher over time because small-sized firms are constantly investing large sums of money in the latest production technologies and in innovations through research and development (R&D).
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter9: Monopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 28CTQ: Intellectual property laws are intended to promote innovation, but some economists, such as Milton...
Related questions
Question
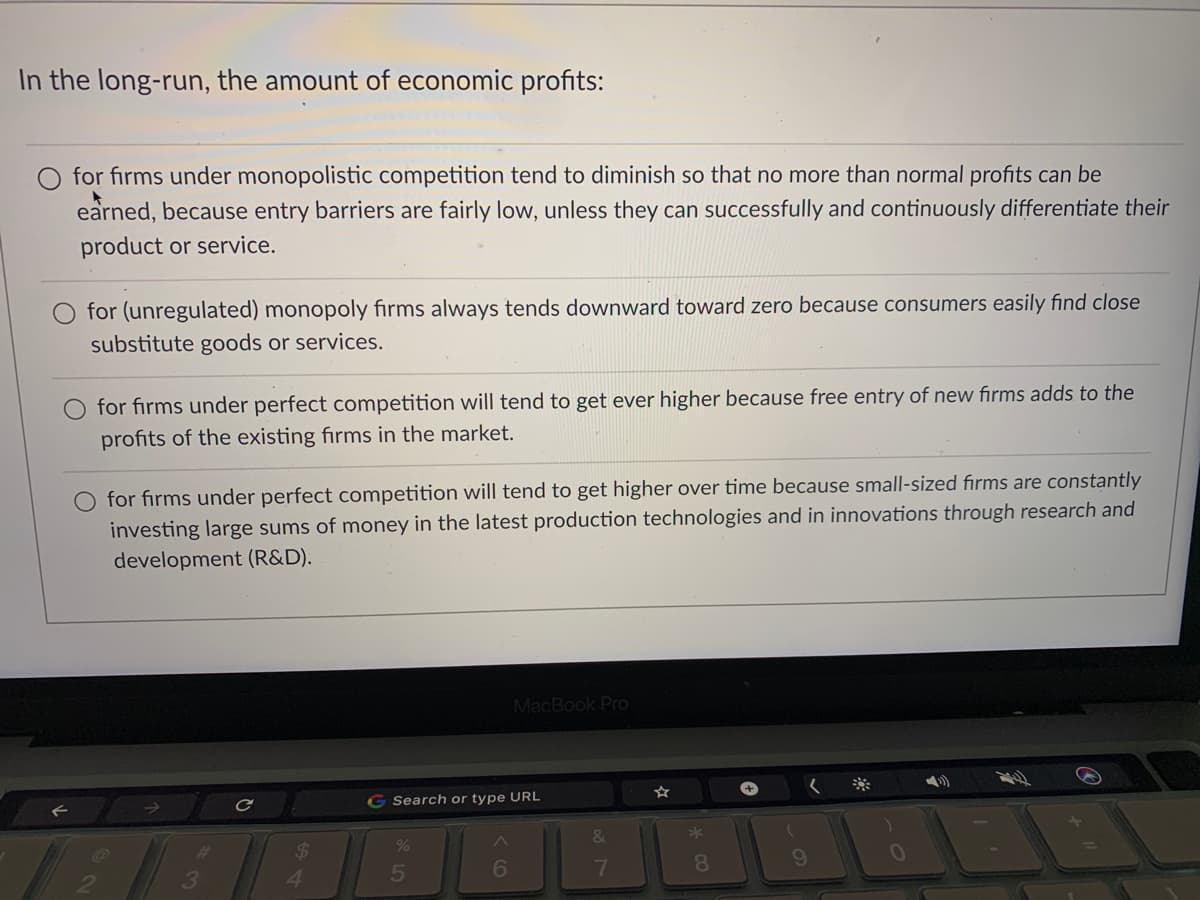
Transcribed Image Text:In the long-run, the amount of economic profits:
for firms under monopolistic competition tend to diminish so that no more than normal profits can be
earned, because entry barriers are fairly low, unless they can successfully and continuously differentiate their
product or service.
for (unregulated) monopoly firms always tends downward toward zero because consumers easily find close
substitute goods or services.
for firms under perfect competition will tend to get ever higher because free entry of new firms adds to the
profits of the existing firms in the market.
O for firms under perfect competition will tend to get higher over time because small-sized firms are constantly
investing large sums of money in the latest production technologies and in innovations through research and
development (R&D).
MacBook Pro
G Search or type URL
24
5
7

Transcribed Image Text:What is a feature common to both Monopolistic-Competition and Oligopoly type of markets?
productive efficiency will occur in both the short run and long run, a desirable economic property of markets.
many smaller sized fırms can produce the good or service at lower cost per unit than larger sized firms, thus
large firms fail in the long run.
the demand curve for each fırm is not going to be purely elastic, because products are at least slightly
different than potential rival fırms' product and/or there may be some consumer brand loyalty.
Firms in both types of markets eventually will be broken up by government anti-trust laws and regulations.
MacBook Pro
G Search or type URL
+,
%23
&
*
3
5
8.
9.
W
E
01
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning