inal illness that is accompanied by intense pain. As a first atter thesis, he conducts an experiment in which 16 rats are randomly ps of eight each. Animals in the experimental group receive a small l e thalamus thought to be involved with pain perception. Animals in th ive a comparable lesion in a brain area believed to be unrelated to p furgon gach animal is given a brief electrical shock to the nawe
inal illness that is accompanied by intense pain. As a first atter thesis, he conducts an experiment in which 16 rats are randomly ps of eight each. Animals in the experimental group receive a small l e thalamus thought to be involved with pain perception. Animals in th ive a comparable lesion in a brain area believed to be unrelated to p furgon gach animal is given a brief electrical shock to the nawe
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
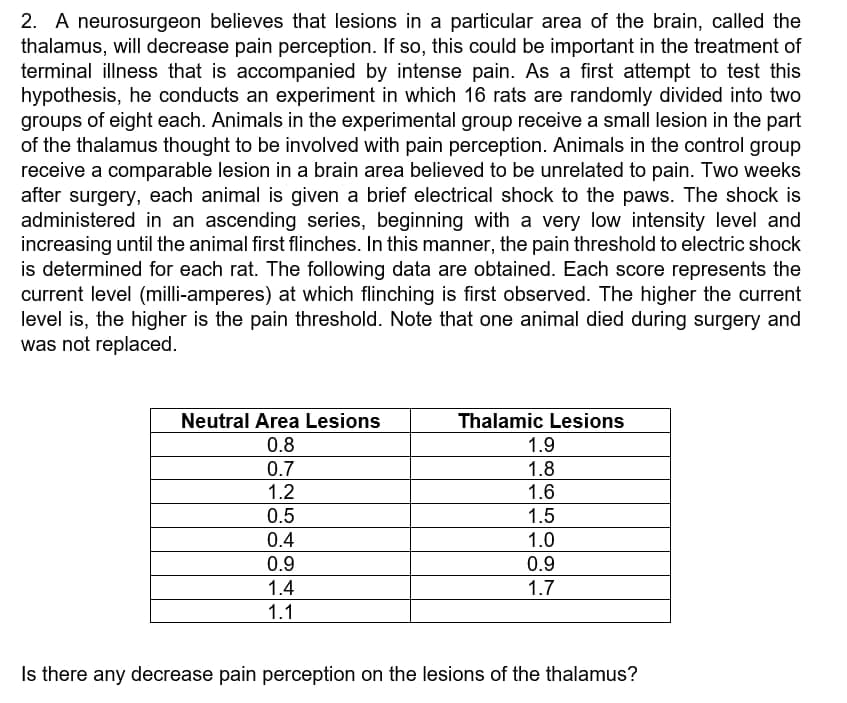
Transcribed Image Text:2. A neurosurgeon believes that lesions in a particular area of the brain, called the
thalamus, will decrease pain perception. If so, this could be important in the treatment of
terminal illness that is accompanied by intense pain. As a first attempt to test this
hypothesis, he conducts an experiment in which 16 rats are randomly divided into two
groups of eight each. Animals in the experimental group receive a small lesion in the part
of the thalamus thought to be involved with pain perception. Animals in the control group
receive a comparable lesion in a brain area believed to be unrelated to pain. Two weeks
after surgery, each animal is given a brief electrical shock to the paws. The shock is
administered in an ascending series, beginning with a very low intensity level and
increasing until the animal first flinches. In this manner, the pain threshold to electric shock
is determined for each rat. The following data are obtained. Each score represents the
current level (milli-amperes) at which flinching is first observed. The higher the current
level is, the higher is the pain threshold. Note that one animal died during surgery and
was not replaced.
Neutral Area Lesions
Thalamic Lesions
1.9
0.8
0.7
1.8
1.2
1.6
0.5
1.5
0.4
1.0
0.9
0.9
1.4
1.7
1.1
Is there any decrease pain perception on the lesions of the thalamus?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL