-Incomplete manufacturing costs, expenses, and selling data for two different cases follows. Case Direct materials used Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Total manufacturing costs Beginning work in process inventory Ending work in process inventory Sales revenue Sales discounts $ 9,600 5,000 8,000 (a) 1,000 (b) 24,500 2,500 17,000 (c) 20,000 $ (g) 8,000 4,000 16,000 (h) 3,000 (i) 1,400 22,000 3,300 Cost of goods manufactured Beginning finished goods inventory Goods available for sale Cost of goods sold Ending finished goods inventory Gross profit Operating expenses (d) 3,400 (e) 2,500 (f) () (k) 2,500 7,000 (1) 5,000 Net income
-Incomplete manufacturing costs, expenses, and selling data for two different cases follows. Case Direct materials used Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Total manufacturing costs Beginning work in process inventory Ending work in process inventory Sales revenue Sales discounts $ 9,600 5,000 8,000 (a) 1,000 (b) 24,500 2,500 17,000 (c) 20,000 $ (g) 8,000 4,000 16,000 (h) 3,000 (i) 1,400 22,000 3,300 Cost of goods manufactured Beginning finished goods inventory Goods available for sale Cost of goods sold Ending finished goods inventory Gross profit Operating expenses (d) 3,400 (e) 2,500 (f) () (k) 2,500 7,000 (1) 5,000 Net income
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Chapter1: Introduction To Cost Accounting
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9P: Glasson Manufacturing Co. produces only one product. You have obtained the following information...
Related questions
Question
100%
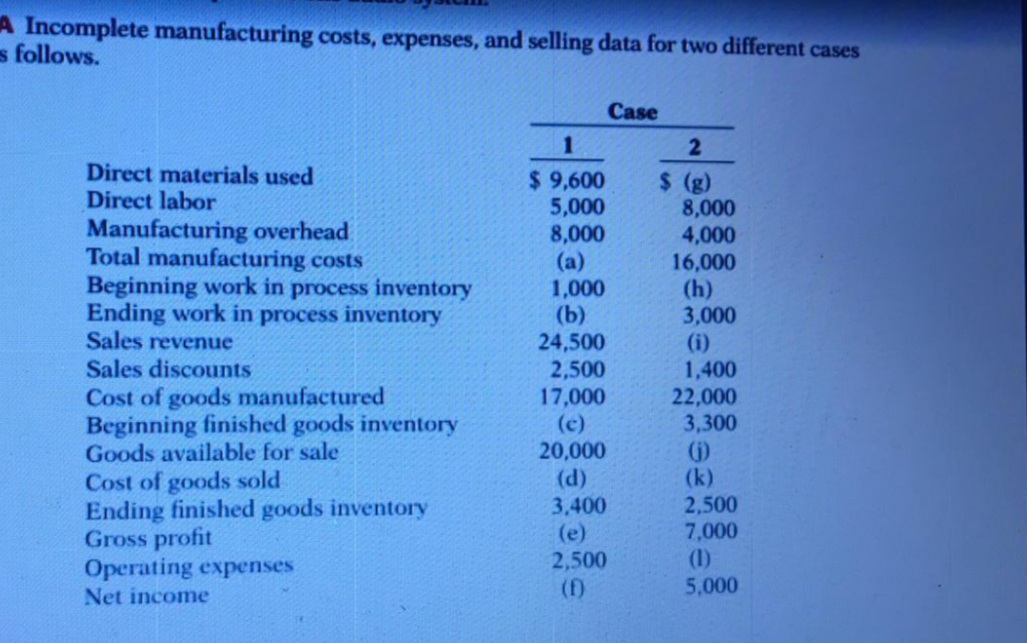
Transcribed Image Text:A Incomplete manufacturing costs, expenses, and selling data for two different cases
s follows.
Case
Direct materials used
Direct labor
$ 9,600
5,000
8,000
(a)
1,000
(b)
24,500
2,500
17,000
(c)
20,000
(d)
3,400
(e)
$ (g)
8,000
4,000
16,000
(h)
3,000
(i)
1,400
22,000
3,300
Manufacturing overhead
Total manufacturing costs
Beginning work in process inventory
Ending work in process inventory
Sales revenue
Sales discounts
Cost of goods manufactured
Beginning finished goods inventory
Goods available for sale
Cost of goods sold
Ending finished goods inventory
Gross profit
Operating expenses
()
(k)
2,500
7,000
(1)
5,000
2,500
(f)
Net income
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning