Individual Problems 18-2 eserve price is a minimum price set by the auctioneer. If no bidder is willing to pay the reserve price, the item is unsold at a profit of $0 for the ctioneer. If only one bidder values the item at or above the reserve price, that bidder pays the reserve price. An auctioneer faces two bidders, each th a value of either $6 or $16, with both values equally probable. Without a reserve price, the second highest bid will be the price paid by the ning bidder. e following table lists the four possible combinations of bidder values. Each combination is equally likely to occur. the following table, indicate the price paid by the winning bidder with and without the stated reserve price. Bidder 1 Value Bidder 2 Value ($) ($) $6 $6 $6 $16 $16 $6 $16 $16 Probability 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 thout a reserve price, the expected price is $ pected price is larger_ the reserve price. Price Without Reserve ($) Price with $16 Reserve Price . With a reserve price of $16, the expected price is $ Thus, the
Individual Problems 18-2 eserve price is a minimum price set by the auctioneer. If no bidder is willing to pay the reserve price, the item is unsold at a profit of $0 for the ctioneer. If only one bidder values the item at or above the reserve price, that bidder pays the reserve price. An auctioneer faces two bidders, each th a value of either $6 or $16, with both values equally probable. Without a reserve price, the second highest bid will be the price paid by the ning bidder. e following table lists the four possible combinations of bidder values. Each combination is equally likely to occur. the following table, indicate the price paid by the winning bidder with and without the stated reserve price. Bidder 1 Value Bidder 2 Value ($) ($) $6 $6 $6 $16 $16 $6 $16 $16 Probability 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 thout a reserve price, the expected price is $ pected price is larger_ the reserve price. Price Without Reserve ($) Price with $16 Reserve Price . With a reserve price of $16, the expected price is $ Thus, the
Chapter17: Capital And Time
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17.11P
Related questions
Question
Sub : Economics
Pls answer fast.I ll upvote. Thank You
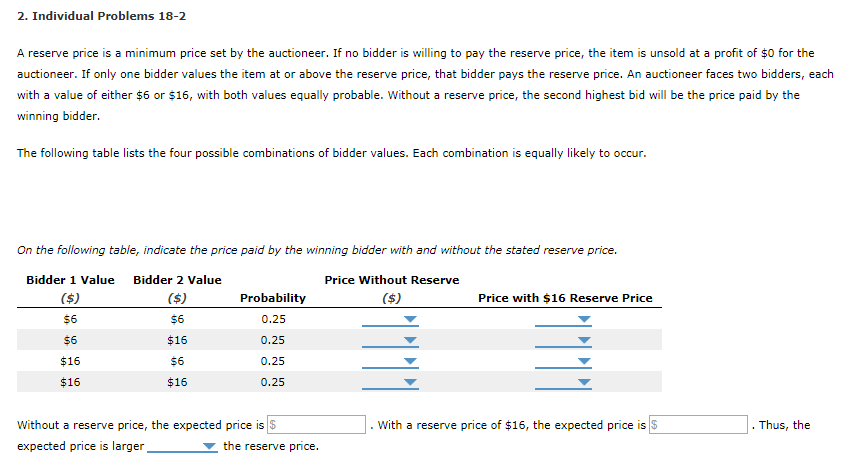
Transcribed Image Text:2. Individual Problems 18-2
A reserve price is a minimum price set by the auctioneer. If no bidder is willing to pay the reserve price, the item is unsold at a profit of $0 for the
auctioneer. If only one bidder values the item at or above the reserve price, that bidder pays the reserve price. An auctioneer faces two bidders, each
with a value of either $6 or $16, with both values equally probable. Without a reserve price, the second highest bid will be the price paid by the
winning bidder.
The following table lists the four possible combinations of bidder values. Each combination is equally likely to occur.
On the following table, indicate the price paid by the winning bidder with and without the stated reserve price.
Bidder 1 Value Bidder 2 Value
($)
Price Without Reserve
($)
($)
$6
$6
$16
$16
$6
$16
$6
$16
Probability
0.25
0.25
0.25
0.25
Without a reserve price, the expected price is $
expected price is larger
the reserve price.
Price with $16 Reserve Price
With a reserve price of $16, the expected price is
.
Thus, the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax