Individuals A, B and C have the following individual demand curves: QA-7-.5P Q-10-P Qc=18-3P Make a price quantity chart for each consumer. Then add a column showing the total quantity demanded for a private good. Next show the quantity price chart showing the total demand for a public good. Graph and label all 5 demand curves on the same graph (see provided graph sheet). If the marginal cost is $4 a unit how many units should be bought if the good is a private good? How many units would each individual buy? If the marginal cost is $6 a unit, to the nearest .1 how many units should be bought if the good is a public good? To the nearest S 0.01 what are the Lindahl prices each person is willing to pay? Do consumers of public goods have the same incentives to reveal their true valuations of Public goods as they do of Private goods? Why or why not?
Individuals A, B and C have the following individual demand curves: QA-7-.5P Q-10-P Qc=18-3P Make a price quantity chart for each consumer. Then add a column showing the total quantity demanded for a private good. Next show the quantity price chart showing the total demand for a public good. Graph and label all 5 demand curves on the same graph (see provided graph sheet). If the marginal cost is $4 a unit how many units should be bought if the good is a private good? How many units would each individual buy? If the marginal cost is $6 a unit, to the nearest .1 how many units should be bought if the good is a public good? To the nearest S 0.01 what are the Lindahl prices each person is willing to pay? Do consumers of public goods have the same incentives to reveal their true valuations of Public goods as they do of Private goods? Why or why not?
Economics (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Roger A. Arnold
Chapter30: Market Failure: Externalities, Public Goods, And Asymmetric Information
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10QP
Related questions
Question
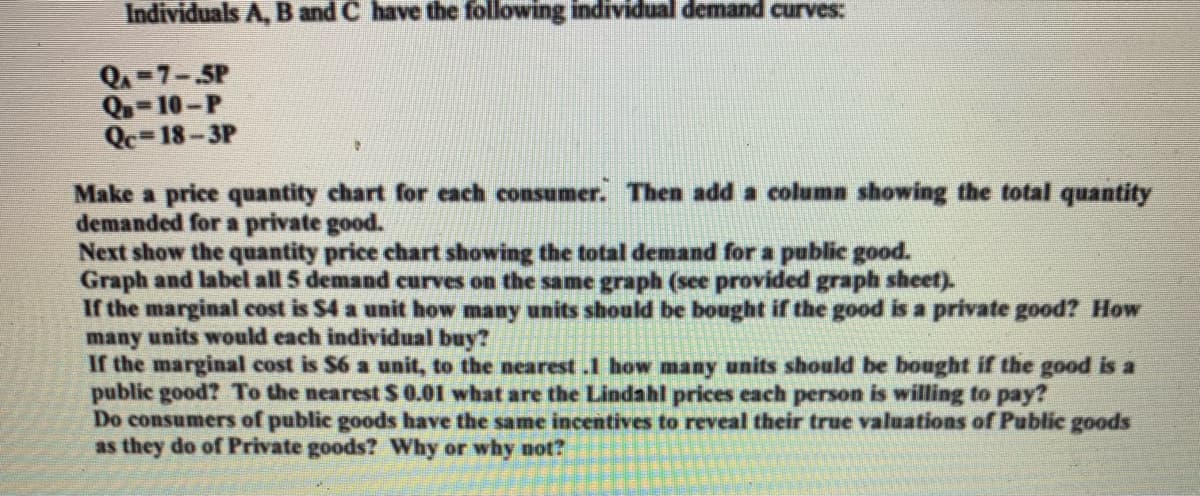
Transcribed Image Text:Individuals A, B and C have the following individual demand curves:
Q=7-5P
Q=10-P
Qc=18-3P
Make a price quantity chart for each consumer. Then add a column showing the total quantity
demanded for a private good.
Next show the quantity price chart showing the total demand for a public good.
Graph and label all 5 demand curves on the same graph (see provided graph sheet).
If the marginal cost is $4 a unit how many units should be bought if the good is a private good? How
many units would each individual buy?
If the marginal cost is $6 a unit, to the nearest .1 how many units should be bought if the good is a
public good? To the nearest S 0.01 what are the Lindahl prices each person is willing to pay?
Do consumers of public goods have the same incentives to reveal their true valuations of Public goods
as they do of Private goods? Why or why not?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning




