Infrared Interpretation – interpret all absorptions in the 4000-1400 cm-1 region of the IR spectra of 2-methyl-4-heptanol. Label the recorded IR spectra and provide an indication of the impurities present, if any.
Infrared Interpretation – interpret all absorptions in the 4000-1400 cm-1 region of the IR spectra of 2-methyl-4-heptanol. Label the recorded IR spectra and provide an indication of the impurities present, if any.
Chapter28: Atomic Spectroscopy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 28.2QAP
Related questions
Question
Infrared Interpretation – interpret all absorptions in the 4000-1400 cm-1 region of the IR spectra of 2-methyl-4-heptanol. Label the recorded IR spectra and provide an indication of the impurities present, if any.
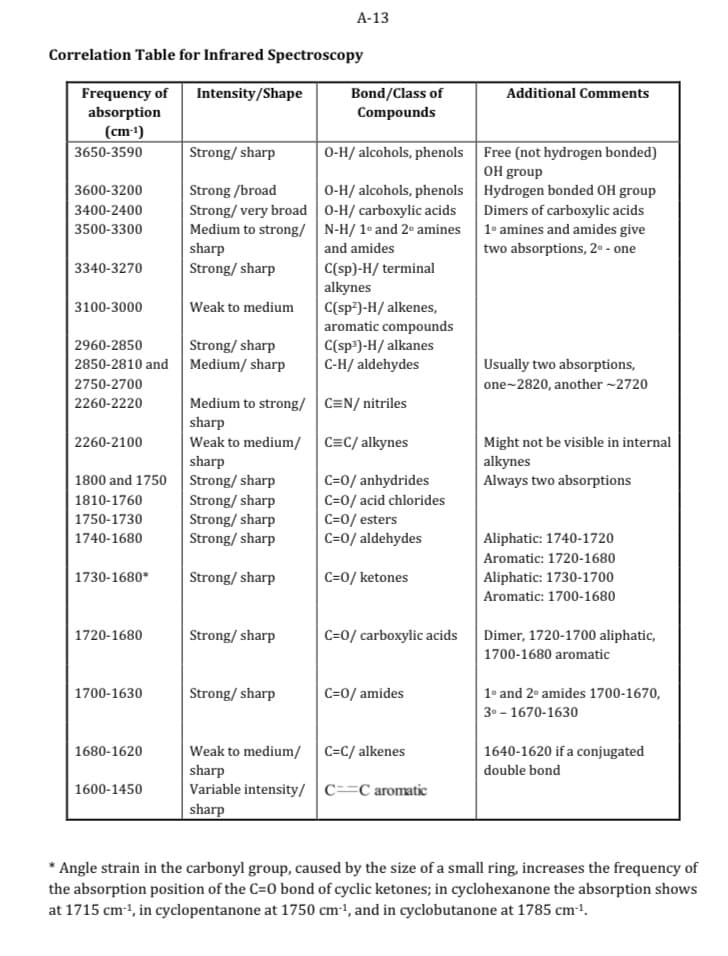
Transcribed Image Text:Correlation Table for Infrared Spectroscopy
Frequency of Intensity/Shape
absorption
(cm-1)
3650-3590
3600-3200
3400-2400
3500-3300
3340-3270
3100-3000
2260-2100
1800 and 1750
1810-1760
1750-1730
1740-1680
2960-2850
Strong/sharp
2850-2810 and Medium/sharp
2750-2700
2260-2220
1730-1680*
1720-1680
1700-1630
1680-1620
Strong/sharp
1600-1450
Strong/broad
Strong/ very broad
Medium to strong/
sharp
Strong/sharp
Weak to medium
Medium to strong/
sharp
Weak to medium/
sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
A-13
Weak to medium/
sharp
Variable intensity/
sharp
Bond/Class of
Compounds
O-H/ alcohols, phenols
O-H/ alcohols, phenols
O-H/ carboxylic acids
N-H/ 1° and 2° amines
and amides
C(sp)-H/ terminal
alkynes
C(sp²)-H/ alkenes,
aromatic compounds
C(sp³)-H/ alkanes
C-H/ aldehydes
C=N/nitriles
C=C/ alkynes
C=0/anhydrides
C=0/ acid chlorides
C=0/esters
C=0/ aldehydes
C=0/ ketones
C=0/ carboxylic acids
C=0/amides
C=C/ alkenes
CC aromatic
Additional Comments
Free (not hydrogen bonded)
OH group
Hydrogen bonded OH group
Dimers of carboxylic acids
1° amines and amides give
two absorptions, 2⁰ - one
Usually two absorptions,
one-2820, another -2720
Might not be visible in internal
alkynes
Always two absorptions
Aliphatic: 1740-1720
Aromatic: 1720-1680
Aliphatic: 1730-1700
Aromatic: 1700-1680
Dimer, 1720-1700 aliphatic,
1700-1680 aromatic
1 and 2 amides 1700-1670,
3⁰-1670-1630
1640-1620 if a conjugated
double bond
*Angle strain in the carbonyl group, caused by the size of a small ring, increases the frequency of
the absorption position of the C=0 bond of cyclic ketones; in cyclohexanone the absorption shows
at 1715 cm-¹, in cyclopentanone at 1750 cm-¹, and in cyclobutanone at 1785 cm-¹.
![3500
3000
2500
Wavenumber cm-1
2000
1500
1000
500
3345.51
2955.65
2927.88
2870.43
1466.22
382.51
1148.31
1121.83
1025.62
944.75
900.2
838.72
606.96
591.02
571.07
554.66
544.06
499.62
472.28
459.78
450.11
441.82
418.52
65 70
Transmittance [%]
75 80 85
95
90
humhy
100
BRUKER
2-methyl-4-heptanol](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F4187eb67-fab6-4738-a29b-fa11c290df86%2F512b9b4e-f2de-4257-8dc7-1a0f7d0f2751%2Fbqefh2e_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:3500
3000
2500
Wavenumber cm-1
2000
1500
1000
500
3345.51
2955.65
2927.88
2870.43
1466.22
382.51
1148.31
1121.83
1025.62
944.75
900.2
838.72
606.96
591.02
571.07
554.66
544.06
499.62
472.28
459.78
450.11
441.82
418.52
65 70
Transmittance [%]
75 80 85
95
90
humhy
100
BRUKER
2-methyl-4-heptanol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning