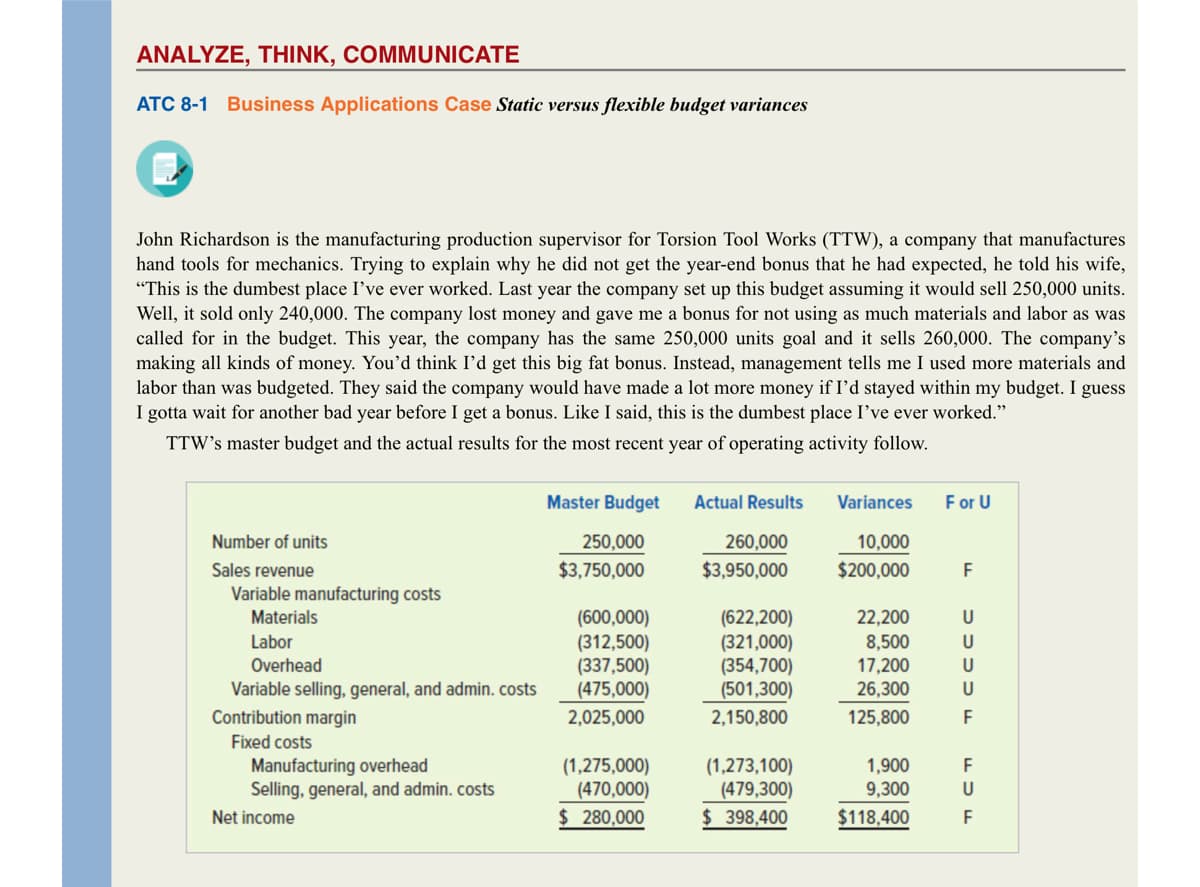
John Richardson is the manufacturing production supervisor for Torsion Tool Works (TTW), a company that manufacture hand tools for mechanics. Trying to explain why he did not get the year-end bonus that he had expected, he told his wife "This is the dumbest place I've ever worked. Last year the company set up this budget assuming it would sell 250,000 units
Master Budget
A master budget can be defined as an estimation of the revenue earned or expenses incurred over a specified period of time in the future and it is generally prepared on a periodic basis which can be either monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or annually. It helps a business, an organization, or even an individual to manage the money effectively. A budget also helps in monitoring the performance of the people in the organization and helps in better decision-making.
Sales Budget and Selling
A budget is a financial plan designed by an undertaking for a definite period in future which acts as a major contributor towards enhancing the financial success of the business undertaking. The budget generally takes into account both current and future income and expenses.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









