Junglebooks needs to manage inventory strategically to compete effectively. Ben Barnesworth is considering decentralizing from a single centralized distribution center (CDC) to six smaller decentralized distribution centers (DCs). With a strategic decision of this importance, Ben hopes to be assured of its profitability. In this assignment you will consider the inventory implications of the decentralization decision. You will likely need to make several assumptions in the process of performing calculations, indicate and defend your assumptions as required. 1. First consider the decentralized analysis. Estimate the optimal decisions for a (Q, R) inventory policy for each of the four SKU types detailed in the case (page 7) for each proposed DC. The data is reproduced here for ease of reference: Number of Titles Unit Cost Lead Time Mean Demand Std Dev Fed Ex Charges Soft Cover I Soft Cover II HardCover I HardCover II 70,000 10,000 20,000 $2.50 $10.00 $10.00 3 3 2 50 100 10 50 20 12 $6.00 $11.00 $11.00 50,000 $2.00 2 25 5 $6.00 The demand at each DC distributed according to the above table; e.g. each of the six DCs sees a mean demand of 25 units for each title of SKU type SoftCover I. Calculate the optimal strategy Q, R) for each decentralized DC. Estimate the annual inventory holding and ordering costs across all DC's for managing the inventory of SKU type SoftCover I. 2. Now consider a centralized analysis (their current system) using the same service level derived for the decentralized system. Determine the optimal decisions of a (Q, R) inventory policy SKU type SoftCover I for a centralized DC. Estimate the annual inventory holding plus ordering costs for managing inventory of SKU type SoftCover I.
Junglebooks needs to manage inventory strategically to compete effectively. Ben Barnesworth is considering decentralizing from a single centralized distribution center (CDC) to six smaller decentralized distribution centers (DCs). With a strategic decision of this importance, Ben hopes to be assured of its profitability. In this assignment you will consider the inventory implications of the decentralization decision. You will likely need to make several assumptions in the process of performing calculations, indicate and defend your assumptions as required. 1. First consider the decentralized analysis. Estimate the optimal decisions for a (Q, R) inventory policy for each of the four SKU types detailed in the case (page 7) for each proposed DC. The data is reproduced here for ease of reference: Number of Titles Unit Cost Lead Time Mean Demand Std Dev Fed Ex Charges Soft Cover I Soft Cover II HardCover I HardCover II 70,000 10,000 20,000 $2.50 $10.00 $10.00 3 3 2 50 100 10 50 20 12 $6.00 $11.00 $11.00 50,000 $2.00 2 25 5 $6.00 The demand at each DC distributed according to the above table; e.g. each of the six DCs sees a mean demand of 25 units for each title of SKU type SoftCover I. Calculate the optimal strategy Q, R) for each decentralized DC. Estimate the annual inventory holding and ordering costs across all DC's for managing the inventory of SKU type SoftCover I. 2. Now consider a centralized analysis (their current system) using the same service level derived for the decentralized system. Determine the optimal decisions of a (Q, R) inventory policy SKU type SoftCover I for a centralized DC. Estimate the annual inventory holding plus ordering costs for managing inventory of SKU type SoftCover I.
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Chapter11: Strategic Cost Management
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9E
Related questions
Question
Hi, previously I had asked questions one at a time so I'm sending all 4 since they all relate together but I'd appreiciate it if you could focus on #1 and 2. *These are not graded questions*
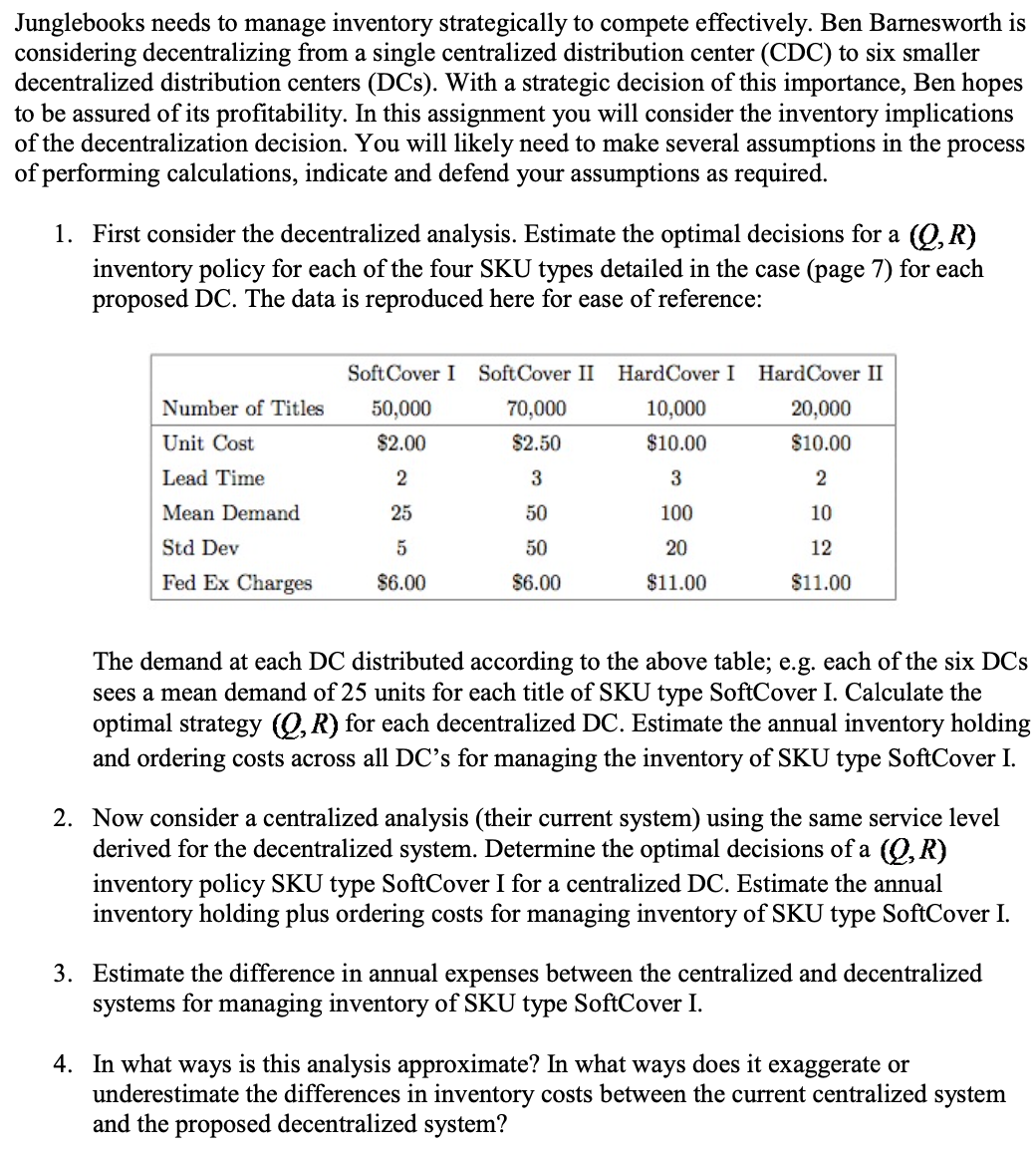
Transcribed Image Text:Junglebooks needs to manage inventory strategically to compete effectively. Ben Barnesworth is
considering decentralizing from a single centralized distribution center (CDC) to six smaller
decentralized distribution centers (DCs). With a strategic decision of this importance, Ben hopes
to be assured of its profitability. In this assignment you will consider the inventory implications
of the decentralization decision. You will likely need to make several assumptions in the
of performing calculations, indicate and defend your assumptions as required.
process
1. First consider the decentralized analysis. Estimate the optimal decisions for a (Q, R)
inventory policy for each of the four SKU types detailed in the case (page 7) for each
proposed DC. The data is reproduced here for ease of reference:
EITIT
Soft Cover I SoftCover II HardCover I HardCover II
Number of Titles
50,000
70,000
10,000
20,000
Unit Cost
$2.00
$2.50
$10.00
$10.00
Lead Time
2
3
3
2
Mean Demand
25
50
100
10
Std Dev
5
50
20
12
Fed Ex Charges
$6.00
$6.00
$11.00
$11.00
The demand at each DC distributed according to the above table; e.g. each of the six DCs
sees a mean demand of 25 units for each title of SKU type SoftCover I. Calculate the
optimal strategy (Q, R) for each decentralized DC. Estimate the annual inventory holding
and ordering costs across all DC's for managing the inventory of SKU type SoftCover I.
2. Now consider a centralized analysis (their current system) using the same service level
derived for the decentralized system. Determine the optimal decisions of a (Q, R)
inventory policy SKU type SoftCover I for a centralized DC. Estimate the annual
inventory holding plus ordering costs for managing inventory of SKU type SoftCover I.
3. Estimate the difference in annual expenses between the centralized and decentralized
systems for managing inventory of SKU type SoftCover I.
4. In what ways is this analysis approximate? In what ways does it exaggerate or
underestimate the differences in inventory costs between the current centralized system
and the proposed decentralized system?

Transcribed Image Text:One week later
BB: Mark, here is a chart that Lee came up with, with all the data you
asked for. In fact, Lee came up with three different charts. The first breaks
our SKUS up into 10 categories, the second into 20, and the third into 50.
MC: Excellent. Let's look at a few of the larger categories from the first
chart.
SoftCover I
SoftCover II
HardCover I
HardCover II
Number of Titles
50,000
70,000
10,000
20,000
Unit Cost
$2.00
$2.50
$10.00
$10.00
Lead Time
2
3
3
2
Mean Demand
25
50
100
10
Std Dev
50
20
12
Fed Ex Charges
$6.00
$6.00
$11.00
$11.00
The chart shows categories which cover about 150,000 of their 500,000
titles. The lead time, in weeks, is the time required to receive a shipment
to a DC after an order is placed. The mean and standard deviation given
in the chart is for the weekly demand projected for one of the proposed
decentralized DCs. Assume 52 weeks/year. The Unit Cost, Lead Time,
Mean Demand, Std Dev and Fed Ex charges are for a single title in a given
category.
MC: The service levels that you should use at each DC is based on
estimates of costs of excess and costs of shortages. We can assume that the
cost of being short a unit at a DC is based on the extra expense to Fed Ex a
unit from another DC when the closest DC is out of stock. The chart gives
representative Fed Ex charges.
Eisenstein
7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning