ldentify the valvetrain components in the drawings. Place the identifying letter next to the name of the component. N- Valve Port Guide Valve Head A Stem Valve Seat Keeper Groove M Margin Stem Tip EFace Pushrod tifter Spring Valve Rocker Arm G Cam Lobe SANMA
ldentify the valvetrain components in the drawings. Place the identifying letter next to the name of the component. N- Valve Port Guide Valve Head A Stem Valve Seat Keeper Groove M Margin Stem Tip EFace Pushrod tifter Spring Valve Rocker Arm G Cam Lobe SANMA
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Chapter37: Clutches
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14RQ: The surface of the pressure plate contacts the. a. transmission main shaft b. throwout bearing c....
Related questions
Question
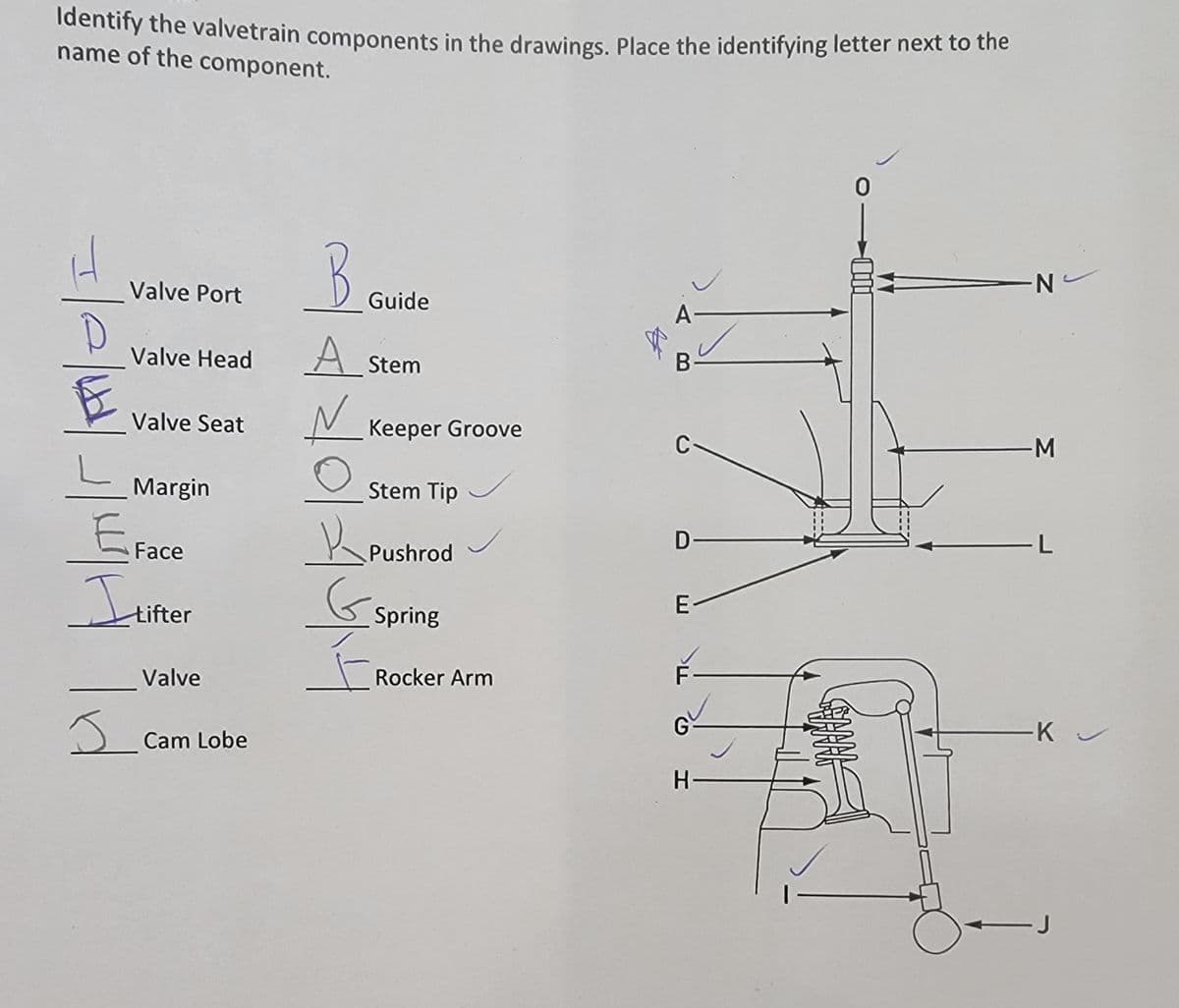
Transcribed Image Text:Identify the valvetrain components in the drawings. Place the identifying letter next to the
name of the component.
B
-N
Valve Port
Guide
Valve Head
A Stem
Valve Seat
Keeper Groove
C-
Margin
Stem Tip
EFace
D-
Pushrod
6.
トリ
E-
tifter
Spring
F-
Valve
Rocker Arm
ーKu
Cam Lobe
H-

Transcribed Image Text:Match the words on the left to the descriptions on the right. Write the letter for the correct
ns:
Match the words on the left to the descriptions on the right. Write the letter for the correct
word on the line provided. For the terms that you are not certain of, use the glossary in your
textbook.
A. Bore
Measurement of work in which 1 pound is moved for a distance of 1 foot
B. Stroke
The volume displaced by the piston
C. Oversquare
Cylinder volume at BDC compared to volume at TDC
Measurement comparing the volume of airflow actually entering the
engine with the maximum that theoretically could enter
D. Cylinder displacement
E. Engine displacement
F. Compression ratio
Ability to do work
L The tendency of a body to keep its state of rest or motion .
G. Compression pressure
A The diameter of the cylinder
H. Force
Usable crankshaft horsepower
I. Work
Metric horsepower equivalent
J. Foot-pound
The measurement of an engine's ability to perform work
K. Energy V
E Cylinder displacement times number of cylinders
Typical gasoline engine compression pressure
L. Inertia
Cylinder bore larger than stroke
M. Momentum
Any action that changes, or tends to change, the position of something
N. Power V
The turning force exerted by the crankshaft
O. Torque
Pressure in the cylinder as the piston moves up when the valves are closed
P. BTU
When an object is moved against resistance or opposing force
Q.1 ВTU
X Name of equipment used to test an engine's power-
R. Horsepower
The heat required to heat a pound of water by 1°F
S. Watts
Piston travel from TDC to BDC
T. Brake horsepower
How fast work is done
U. Road horsepower
British thermal units
V. Volumetric efficiency
Body going in a straight line will keep going the same direction at the same
speed if no other forces act on it
W. 125-175 psi
I WAR Horsepower available at the car's drive wheels
X. Dynamometer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781133612315
Author:
Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285444543
Author:
Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781133612315
Author:
Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285444543
Author:
Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning