Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Chapter34: Particle Size Determination
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 34.2QAP
Related questions
Question
100%
For the table that follows, write which orbital goes with the
quantum numbers. Don’t worry about x, y, z subscripts. If the
quantum numbers are not allowed, write “not allowed.”
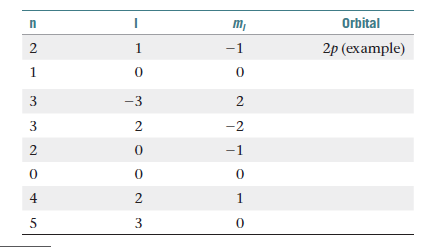
Transcribed Image Text:m,
Orbital
1
-1
2p (example)
1
-3
2
3
-2
-1
4
1.
3
2.
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
