Match the stage of meiosis to its description. Watch for "cell" versus "cells". Singular versus plural is a clue that will help you pick the right roman numeral. homologous chromosomes line up next to each other as tetrads along the mid-line of the cell DNA condenses, tetrads form as homologous chromosomes come together and exchange DNA parts in crossing over, nuclear membrane disintegrates A Early Interphase B. Late Interphase one of each homologous pair reaches the end of the cell, new nuclear membranes form, and the cell membrane begins to pinch in C. Prophase I v DNA condenses in two cells, nuclear membranes disintegrate D. Metaphase I the copies of the chromosomes (daughter chromosomes formerly known as sister chromatids) split apart and move towards the ends of two cells E Anaphase I F. Telophase I v the cell divides into two cells, chromosomes decondense G. Interkinesis tetrads separate and homologous chromosomes begin to move in opposite directions in a cell H. Prophase II v DNA is replicated and decondensed in one cell | Metaphase I two cells begin pinching in, daughter chromosomes reach the ends of the cells and new nuclear membranes form around them J. Anaphase II K. Telophase || four cells, all different from each other and each containing half of the DNA of the original cell are made L. Cytokinesis v DNA is single strands of chromatin in one cell v chromosomes line up across the middle of two cells
Match the stage of meiosis to its description. Watch for "cell" versus "cells". Singular versus plural is a clue that will help you pick the right roman numeral. homologous chromosomes line up next to each other as tetrads along the mid-line of the cell DNA condenses, tetrads form as homologous chromosomes come together and exchange DNA parts in crossing over, nuclear membrane disintegrates A Early Interphase B. Late Interphase one of each homologous pair reaches the end of the cell, new nuclear membranes form, and the cell membrane begins to pinch in C. Prophase I v DNA condenses in two cells, nuclear membranes disintegrate D. Metaphase I the copies of the chromosomes (daughter chromosomes formerly known as sister chromatids) split apart and move towards the ends of two cells E Anaphase I F. Telophase I v the cell divides into two cells, chromosomes decondense G. Interkinesis tetrads separate and homologous chromosomes begin to move in opposite directions in a cell H. Prophase II v DNA is replicated and decondensed in one cell | Metaphase I two cells begin pinching in, daughter chromosomes reach the ends of the cells and new nuclear membranes form around them J. Anaphase II K. Telophase || four cells, all different from each other and each containing half of the DNA of the original cell are made L. Cytokinesis v DNA is single strands of chromatin in one cell v chromosomes line up across the middle of two cells
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter3: Transmission Of Genes From Generation To Generation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24QP: Meiosis Explains Mendels Results: Genes Are on Chromosomes The following diagram shows a...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
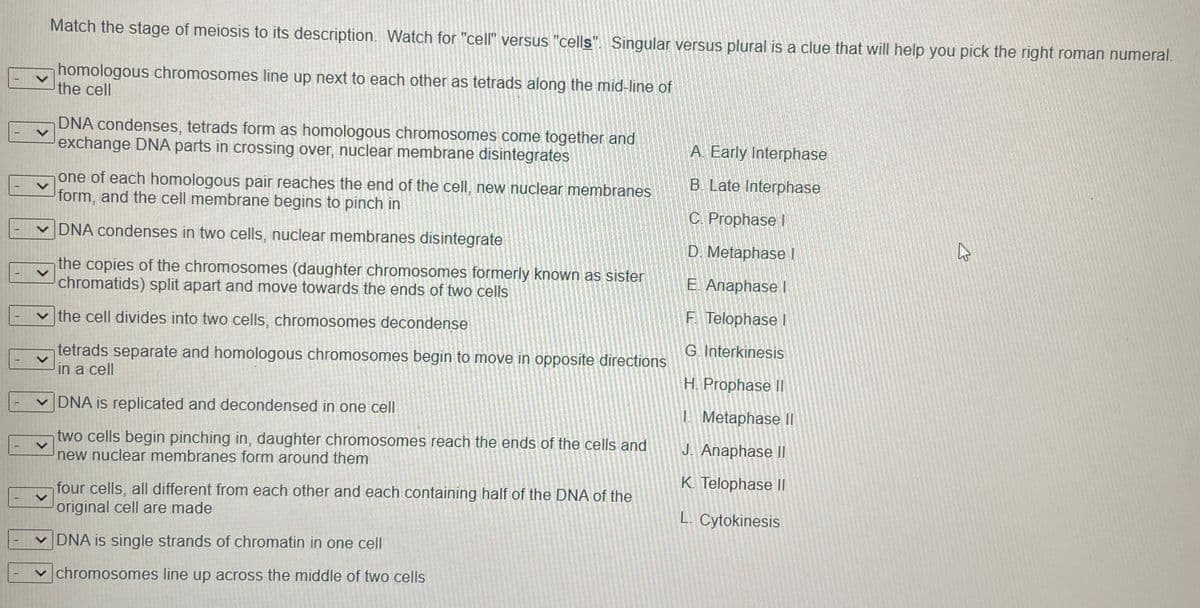
Transcribed Image Text:Match the stage of meiosis to its description. Watch for "cell" versus "cells". Singular versus plural is a clue that will help you pick the right roman numeral.
homologous chromosomes line up next to each other as tetrads along the mid-line of
the cell
DNA condenses, tetrads form as homologous chromosomes come together and
exchange DNA parts in crossing over, nuclear membrane disintegrates
A. Early Interphase
B. Late Interphase
one of each homologous pair reaches the end of the cell, new nuclear membranes
form, and the cell membrane begins to pinch in
C. Prophase I
v DNA condenses in two cells, nuclear membranes disintegrate
D. Metaphase I
the copies of the chromosomes (daughter chromosomes formerly known as sister
chromatids) split apart and move towards the ends of two cells
E. Anaphase I
F Telophase I
the cell divides into two cells, chromosomes decondense
G. Interkinesis
tetrads separate and homologous chromosomes begin to move in opposite directions
in a cell
H. Prophase II
v DNA is replicated and decondensed in one cell
| Metaphase II
two cells begin pinching in, daughter chromosomes reach the ends of the cells and
new nuclear membranes form around them
J. Anaphase Il
K. Telophase II
four cells, all different from each other and each containing half of the DNA of the
original cell are made
L. Cytokinesis
v DNA is single strands of chromatin in one cell
chromosomes line up across the middle of two cells
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning