mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in Part B a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom. It successfully accounts for or predicts certain chemical and physical properties more accurately than other bonding theories. The bond energy, bond length, bond order, and magnetism of a molecule can be predicted from its molecular orbital configuration. The electrons Which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? A blank molecular o diagram (Figure 2) has been provided to help you. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. available in a molecular species are placed in molecular orbitals following the same rules used in electron configurations: the aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle. • View Available Hint(s) Reset Help C2+ Liz C,++ Figure <) 2 of 2> MO Diagram for Period 2 Elements from Li to N Diamagnetic Paramagnetic 2p 2p 2p 2s 2s Energy
mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in Part B a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom. It successfully accounts for or predicts certain chemical and physical properties more accurately than other bonding theories. The bond energy, bond length, bond order, and magnetism of a molecule can be predicted from its molecular orbital configuration. The electrons Which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? A blank molecular o diagram (Figure 2) has been provided to help you. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. available in a molecular species are placed in molecular orbitals following the same rules used in electron configurations: the aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle. • View Available Hint(s) Reset Help C2+ Liz C,++ Figure <) 2 of 2> MO Diagram for Period 2 Elements from Li to N Diamagnetic Paramagnetic 2p 2p 2p 2s 2s Energy
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter10: Molecular Structure And Bonding Theories
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.100QE: The molecular orbital diagram of NO shown in Figure 10.47 also applies to the following species....
Related questions
Question
Please answer question 14 Part A and B
Transcribed Image Text:Molecular orbital (MO) theory is based in quantum
mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in
Part B
a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom. It
successfully accounts for or predicts certain chemical
and physical properties more accurately than other
bonding theories. The bond energy, bond length, bond
order, and magnetism of a molecule can be predicted
from its molecular orbital configuration. The electrons
available in a molecular species are placed in molecular
orbitals following the same rules used in electron
configurations: the aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the
Pauli exclusion principle.
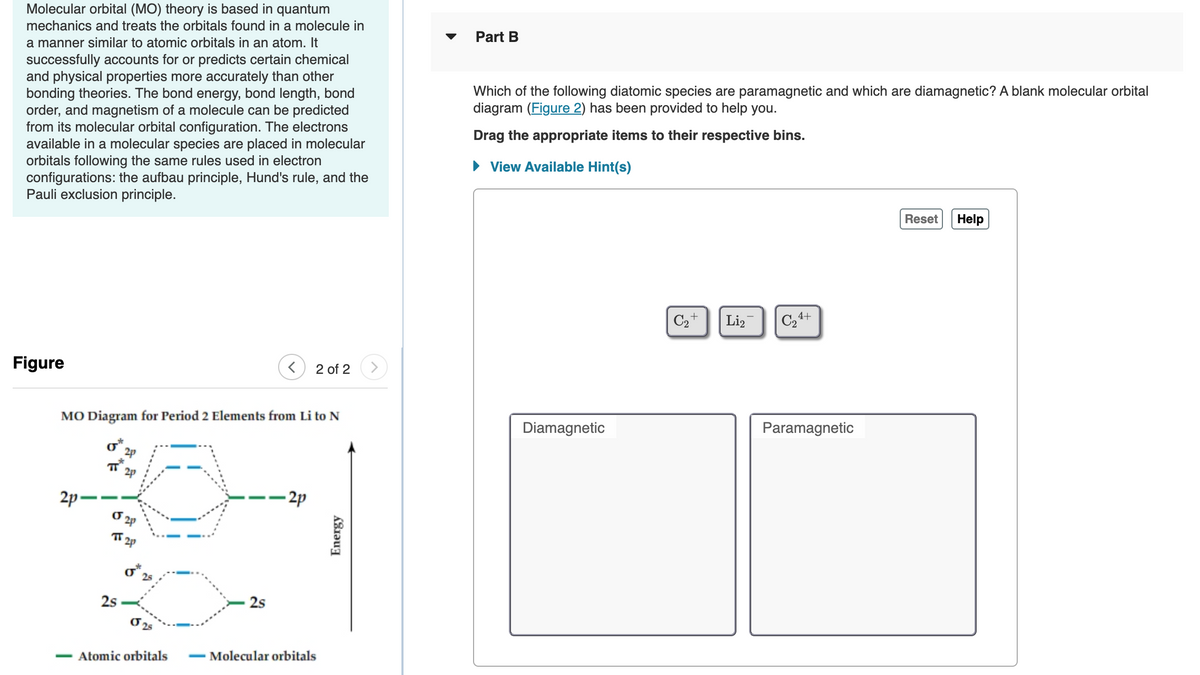
Which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? A blank molecular orbital
diagram (Figure 2) has been provided to help you.
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
C2+
Li,
C24+
Figure
2 of 2
MO Diagram for Period 2 Elements from Li to N
Diamagnetic
Paramagnetic
o*,
2p
2p -
- 2p
TT 2p
o 25
2s
2s
Atomic orbitals
- Molecular orbitals
Transcribed Image Text:Molecular orbital (MO) theory is based in quantum
mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in
a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom. It
Part A
successfully accounts for or predicts certain chemical
and physical properties more accurately than other
bonding theories. The bond energy, bond length, bond
order, and magnetism of a molecule can be predicted
from its molecular orbital configuration. The electrons
available in a molecular species are placed in molecular
orbitals following the same rules used in electron
configurations: the aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the
Pauli exclusion principle.
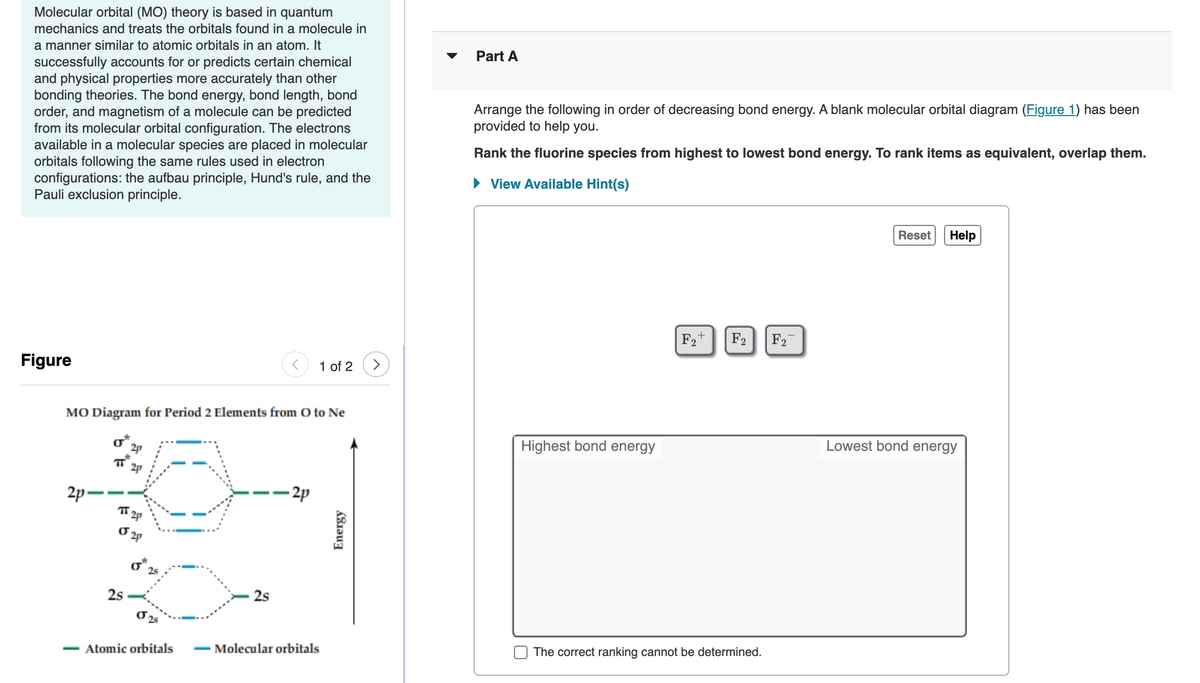
Arrange the following in order of decreasing bond energy. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been
provided to help you.
Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
F2+
F2
F2
Figure
1 of 2
MO Diagram for Period 2 Elements from O to Ne
Highest bond energy
Lowest bond energy
T 2p
2p-
- 2p
2p
25
2s
2s
Atomic orbitals
- Molecular orbitals
The correct ranking cannot be determined.
Energy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning