Medical researchers are interested in determining the relative effectiveness of two drug treatments on patients with a chronic mental illness. Treatment 1 has been around for many years, while treatment 2 has recently been developed based on the latest research. The researchers chose two independent test groups. The first group had 11 patients, all of whom received treatment 1 and had a mean time until remission of 170 days, with a standard deviation of 8 days. The second group had 8 patients, all of whom received treatment 2 and had a mean time until remission of 160 days, with a standard deviation of 9 days. Assume that the populations of times until remission for each of the two treatments are normally distributed with equal variance. Can we conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that μ₁, the mean number of days until remission after treatment 1, is greater than μ₂, the mean number of days until remission after treatment 2? Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis Ho and the alternative hypothesis H₁. μ O р X S HO H₁ :0 P (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. (Choose one) ▼ ロ=ロ 020 (c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) 0#0 OO 0 S ? (d) Find the p-value. (Round to three or more decimal places.) (e) Can we conclude that the mean number of days before remission after treatment 1 is greater than the mean number of days before remission after treatment 2? O Yes O No X OSO
Medical researchers are interested in determining the relative effectiveness of two drug treatments on patients with a chronic mental illness. Treatment 1 has been around for many years, while treatment 2 has recently been developed based on the latest research. The researchers chose two independent test groups. The first group had 11 patients, all of whom received treatment 1 and had a mean time until remission of 170 days, with a standard deviation of 8 days. The second group had 8 patients, all of whom received treatment 2 and had a mean time until remission of 160 days, with a standard deviation of 9 days. Assume that the populations of times until remission for each of the two treatments are normally distributed with equal variance. Can we conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that μ₁, the mean number of days until remission after treatment 1, is greater than μ₂, the mean number of days until remission after treatment 2? Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis Ho and the alternative hypothesis H₁. μ O р X S HO H₁ :0 P (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. (Choose one) ▼ ロ=ロ 020 (c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) 0#0 OO 0 S ? (d) Find the p-value. (Round to three or more decimal places.) (e) Can we conclude that the mean number of days before remission after treatment 1 is greater than the mean number of days before remission after treatment 2? O Yes O No X OSO
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
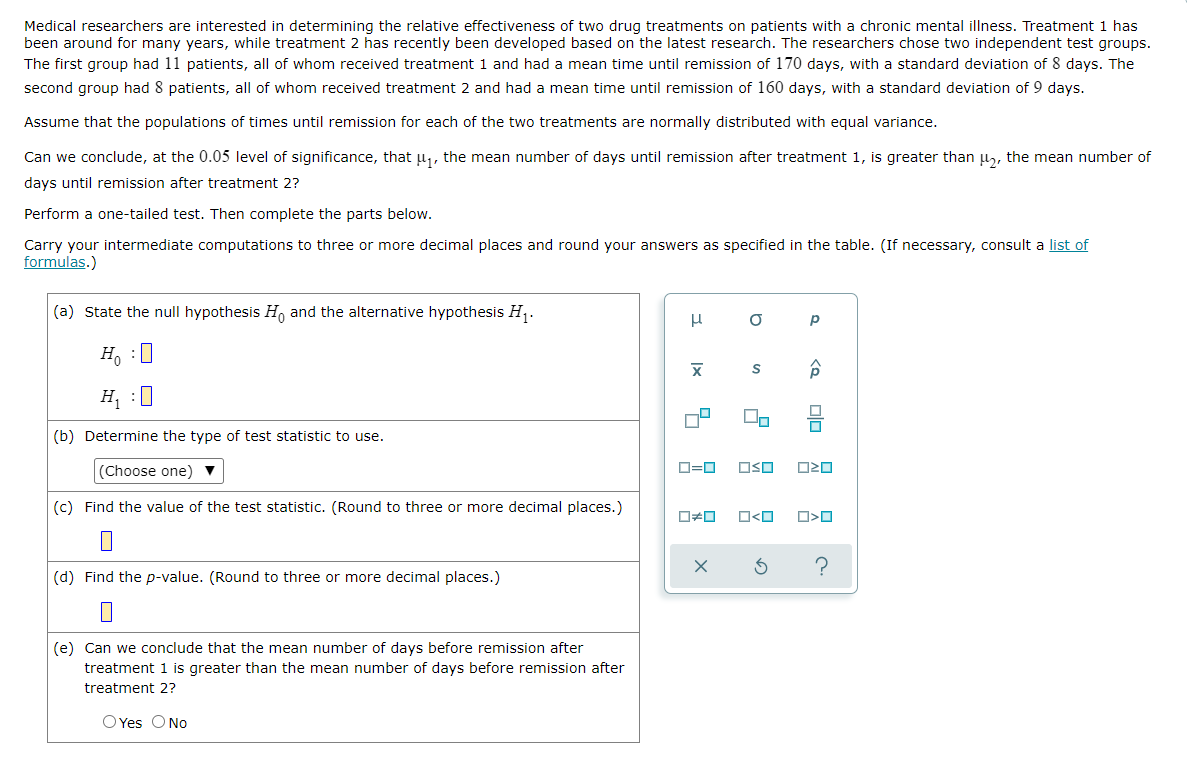
Transcribed Image Text:Medical researchers are interested in determining the relative effectiveness of two drug treatments on patients with a chronic mental illness. Treatment 1 has
been around for many years, while treatment 2 has recently been developed based on the latest research. The researchers chose two independent test groups.
The first group had 11 patients, all of whom received treatment 1 and had a mean time until remission of 170 days, with a standard deviation of 8 days. The
second group had 8 patients, all of whom received treatment 2 and had a mean time until remission of 160 days, with a standard deviation of 9 days.
Assume that the populations of times until remission for each of the two treatments are normally distributed with equal variance.
Can we conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that µ₁, the mean number of days until remission after treatment 1, is greater than μ₂, the mean number of
days until remission after treatment 2?
Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below.
Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of
formulas.)
(a) State the null hypothesis Ho and the alternative hypothesis H₁.
μ
Р
X
Â
Ho :
H₁ :0
(b) Determine the type of test statistic to use.
(Choose one) ▼
0=0 OSO
(c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
0#0
(d) Find the p-value. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
(e) Can we conclude that the mean number of days before remission after
treatment 1 is greater than the mean number of days before remission after
treatment 2?
O Yes O No
X
a
□<ロ
3
030
O>O
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman