Metals often form several cations with different charges. Cerium, for example, forms Ce³+ and Ce4+ ions, and thallium forms Tl† and TI³+ ions. Cerium and thallium ions react as follows: 2Ce++ (aq) + TI* (aq)→2Ce³+(aq) +TI³+ (aq) This reaction is very slow and is thought to occur in a single elementary step. The reaction is catalyzed by the addition of Mn²2+(aq) according to the following mechanism: Ce4+ (aq) + Mn²+(aq) → Ce³+(aq) + Mn³+(aq) Ce4+ (aq) + Mn³+(aq) → Ce³+(aq)+ Mn4+(aq) Mn4+(aq) + Tl+(aq) + Mn2+ (aq)+T³+ (aq)
Metals often form several cations with different charges. Cerium, for example, forms Ce³+ and Ce4+ ions, and thallium forms Tl† and TI³+ ions. Cerium and thallium ions react as follows: 2Ce++ (aq) + TI* (aq)→2Ce³+(aq) +TI³+ (aq) This reaction is very slow and is thought to occur in a single elementary step. The reaction is catalyzed by the addition of Mn²2+(aq) according to the following mechanism: Ce4+ (aq) + Mn²+(aq) → Ce³+(aq) + Mn³+(aq) Ce4+ (aq) + Mn³+(aq) → Ce³+(aq)+ Mn4+(aq) Mn4+(aq) + Tl+(aq) + Mn2+ (aq)+T³+ (aq)
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter11: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 75E: One mechanism for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is a. Which species is a...
Related questions
Question
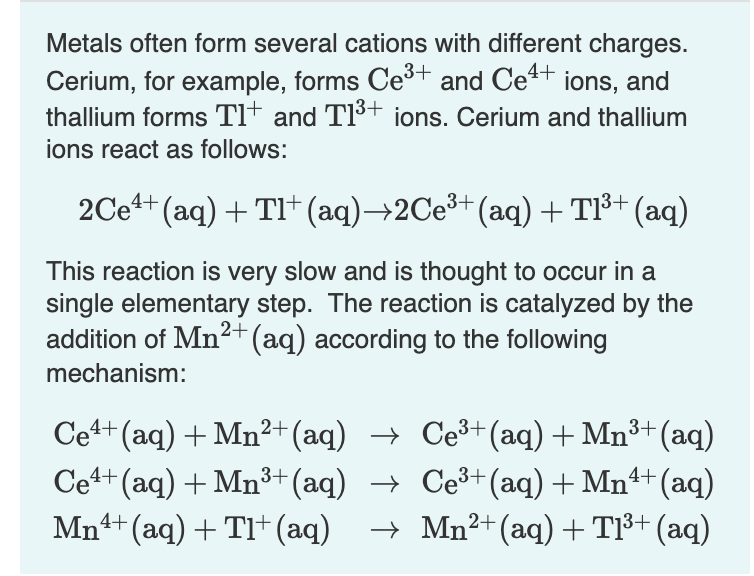
Transcribed Image Text:Metals often form several cations with different charges.
Cerium, for example, forms Ce³+ and Ce4+ ions, and
thallium forms Tl* and TI³+ ions. Cerium and thallium
ions react as follows:
2Ce4+ (aq) + TI+ (aq)→2CE³+ (aq)+ T1³+ (aq)
This reaction is very slow and is thought to occur in a
single elementary step. The reaction is catalyzed by the
addition of Mn2+(aq) according to the following
mechanism:
Ce+ (aq) + Mn²+ (aq) → Ce³+(aq) + Mn3+ (aq)
Cet+ (aq) + Mn³+(aq) → Ce³+(aq) + Mn+ (aq)
Mn4+ (aq) + TI+(aq)
→ Mn²+(aq) + T1³+ (aq)
![What is the rate law for the uncatalyzed reaction?
• View Available Hint(s)
rate = k[Ce+]
O rate = k[Ce*+][TI+j?
O rate = k[Ce+]² [TI+]²
rate = k[TI*]
O rate = k[Ce*+][TI*]
O rate = k[Ce+j°[TI*]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fb158f56a-86d6-40b2-b57e-d311cb867ac4%2F75a0443b-8910-4899-be9c-f1164b710d79%2Fd6a4l4k_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:What is the rate law for the uncatalyzed reaction?
• View Available Hint(s)
rate = k[Ce+]
O rate = k[Ce*+][TI+j?
O rate = k[Ce+]² [TI+]²
rate = k[TI*]
O rate = k[Ce*+][TI*]
O rate = k[Ce+j°[TI*]
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning