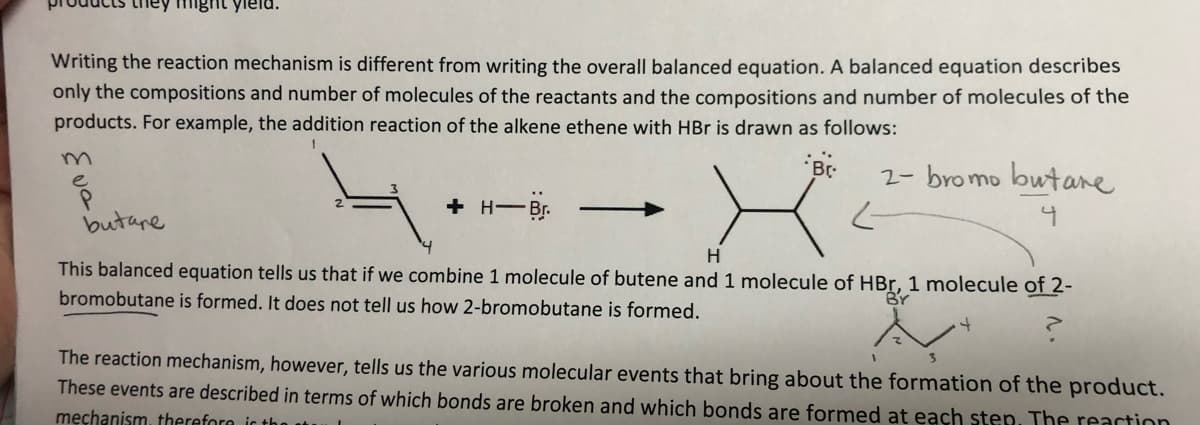
might yield. Writing the reaction mechanism is different from writing the overall balanced equation. A balanced equation describes only the compositions and number of molecules of the reactants and the compositions and number of molecules of the products. For example, the addition reaction of the alkene ethene with HBr is drawn as follows: 4. Br 2- bromo butane + H-Br. butare This balanced equation tells us that if we combine 1 molecule of butene and 1 molecule of HBr, 1 molecule of 2- bromobutane is formed. It does not tell us how 2-bromobutane is formed. BY The reaction mechanism, however, tells us the various molecular events that bring about the formation of the product. These events are described in terms of which bonds are broken and which bonds are formed at each sten. The reartion męchanism, therefore ic tho
Catalysis and Enzymatic Reactions
Catalysis is the kind of chemical reaction in which the rate (speed) of a reaction is enhanced by the catalyst which is not consumed during the process of reaction and afterward it is removed when the catalyst is not used to make up the impurity in the product. The enzymatic reaction is the reaction that is catalyzed via enzymes.
Lock And Key Model
The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity, based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the particular active site of the enzyme. This is significant in understanding the intermolecular interaction between proteins and plays a vital role in drug interaction.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









