Most Company has an opportunity to invest in one of two new projects. Project Y requires a $305,000 investment for new machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. Project Z requires a $305,000 investment for new machinery with a three-year life and no salvage value. The two projects yield the following predicted annual results. The company uses straight-line depreciation, and cash flows occur evenly throughout each year. (PV of $1, EV of $1, PVA of $1, and FVA of $1 )(Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Project Y Project 2 $385,000 $308,000 Sales Expenses Direct materials Direct labor Overhead including depreciation Selling and administrative expenses Total expenses Pretax income Income taxes (268) 53,900 000 ,רר 138,600 28,000 297,500 87,500 22,750 $ 64,750 38,500 46,200 138,600 27,000 250,300 57,700 15,002 Net income $ 42,698 4. Determine each project's net present value using 10% as the discount rate. Assume that cash flows occur at each year-end. (Round your intermediate calculations.)
Most Company has an opportunity to invest in one of two new projects. Project Y requires a $305,000 investment for new machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. Project Z requires a $305,000 investment for new machinery with a three-year life and no salvage value. The two projects yield the following predicted annual results. The company uses straight-line depreciation, and cash flows occur evenly throughout each year. (PV of $1, EV of $1, PVA of $1, and FVA of $1 )(Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Project Y Project 2 $385,000 $308,000 Sales Expenses Direct materials Direct labor Overhead including depreciation Selling and administrative expenses Total expenses Pretax income Income taxes (268) 53,900 000 ,רר 138,600 28,000 297,500 87,500 22,750 $ 64,750 38,500 46,200 138,600 27,000 250,300 57,700 15,002 Net income $ 42,698 4. Determine each project's net present value using 10% as the discount rate. Assume that cash flows occur at each year-end. (Round your intermediate calculations.)
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Chapter19: Capital Investment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10E: Roberts Company is considering an investment in equipment that is capable of producing more...
Related questions
Question
Can you please check my work
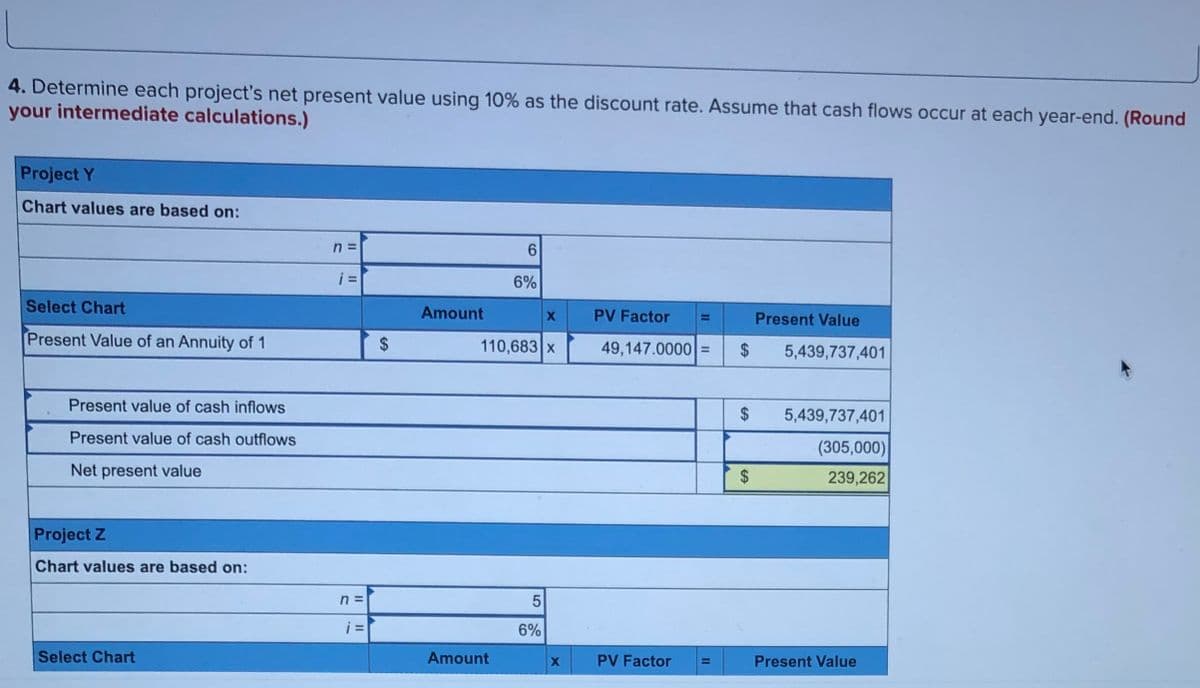
Transcribed Image Text:4. Determine each project's net present value using 10% as the discount rate. Assume that cash flows occur at each year-end. (Round
your intermediate calculations.)
Project Y
Chart values are based on:
6.
i =
6%
Select Chart
Amount
PV Factor
Present Value
Present Value of an Annuity of 1
$
110,683 x
49,147.0000
2$
5,439,737,401
%3D
Present value of cash inflows
5,439,737,401
Present value of cash outflows
(305,000)
Net present value
239,262
Project Z
Chart values are based on:
n =
6%
Select Chart
Amount
PV Factor
Present Value
%D
%24
%24
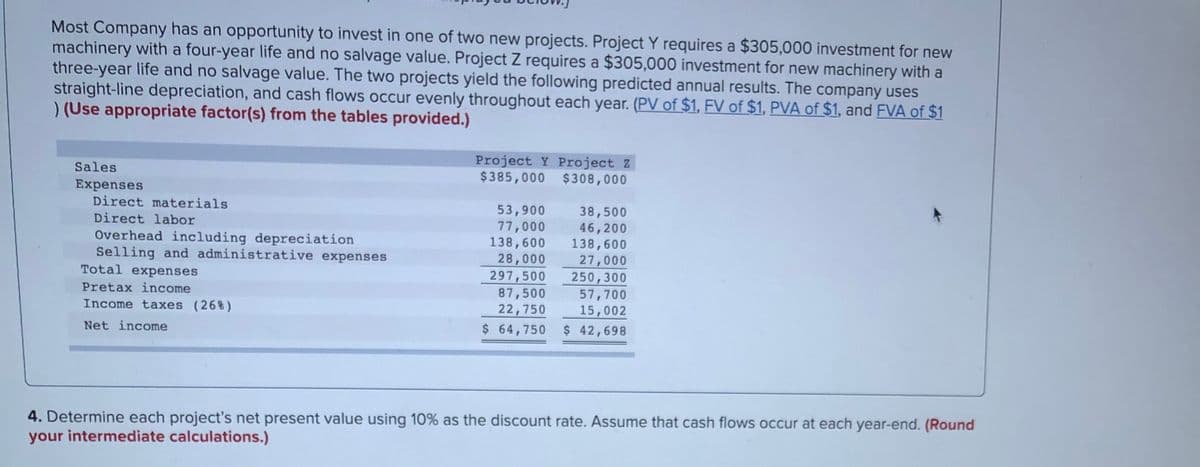
Transcribed Image Text:Most Company has an opportunity to invest in one of two new projects. Project Y requires a $305,000 investment for new
machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. Project Z requires a $305,000 investment for new machinery with a
three-year life and no salvage value. The two projects yield the following predicted annual results. The company uses
straight-line depreciation, and cash flows occur evenly throughout each year. (PV of $1, FV of $1, PVA of $1, and FVA of $1
)(Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.)
Project Y Project Z
$385,000 $308,000
Sales
Expenses
Direct materials
53,900
77,000
138,600
28,000
297,500
87,500
22,750
$ 64,750
38,500
46,200
138,600
27,000
250,300
57,700
15,002
$ 42,698
Direct labor
Overhead including depreciation
Selling and administrative expenses
Total expenses
Pretax income
Income taxes (26%)
Net income
4. Determine each project's net present value using 10% as the discount rate. Assume that cash flows occur at each year-end. (Round
your intermediate calculations.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
