mpare the average cost and the output in the long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm and a perfectly competitive firm mpleting the following table. Average Cost Output Under... (Dollars per jacket) (Thousands of jackets per month) lonopolistic Competition Perfect Competition cause this market is a monopolistically competitive market, the firm's average cost in long-run equilibrium is the long-run erage cost it would achieve as a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. e output of a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium is the output of a perfectly competitive firm. This erence in output is known as the of a monopolistically competitive firm.
mpare the average cost and the output in the long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm and a perfectly competitive firm mpleting the following table. Average Cost Output Under... (Dollars per jacket) (Thousands of jackets per month) lonopolistic Competition Perfect Competition cause this market is a monopolistically competitive market, the firm's average cost in long-run equilibrium is the long-run erage cost it would achieve as a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. e output of a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium is the output of a perfectly competitive firm. This erence in output is known as the of a monopolistically competitive firm.
Chapter10: Monopolistic Competition And Oligoply
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3SQP
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Compare the average cost and the output in the long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm and a perfectly competitive firm by
completing the following table.
Average Cost
Output
Under...
(Dollars per jacket)
(Thousands of jackets per month)
Monopolistic Competition
Perfect Competition
Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, the firm's average cost in long-run equilibrium is
the long-run
average cost it would achieve as a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
The output of a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium is
the output of a perfectly competitive firm. This
difference in output is known as the
of a monopolistically competitive firm.
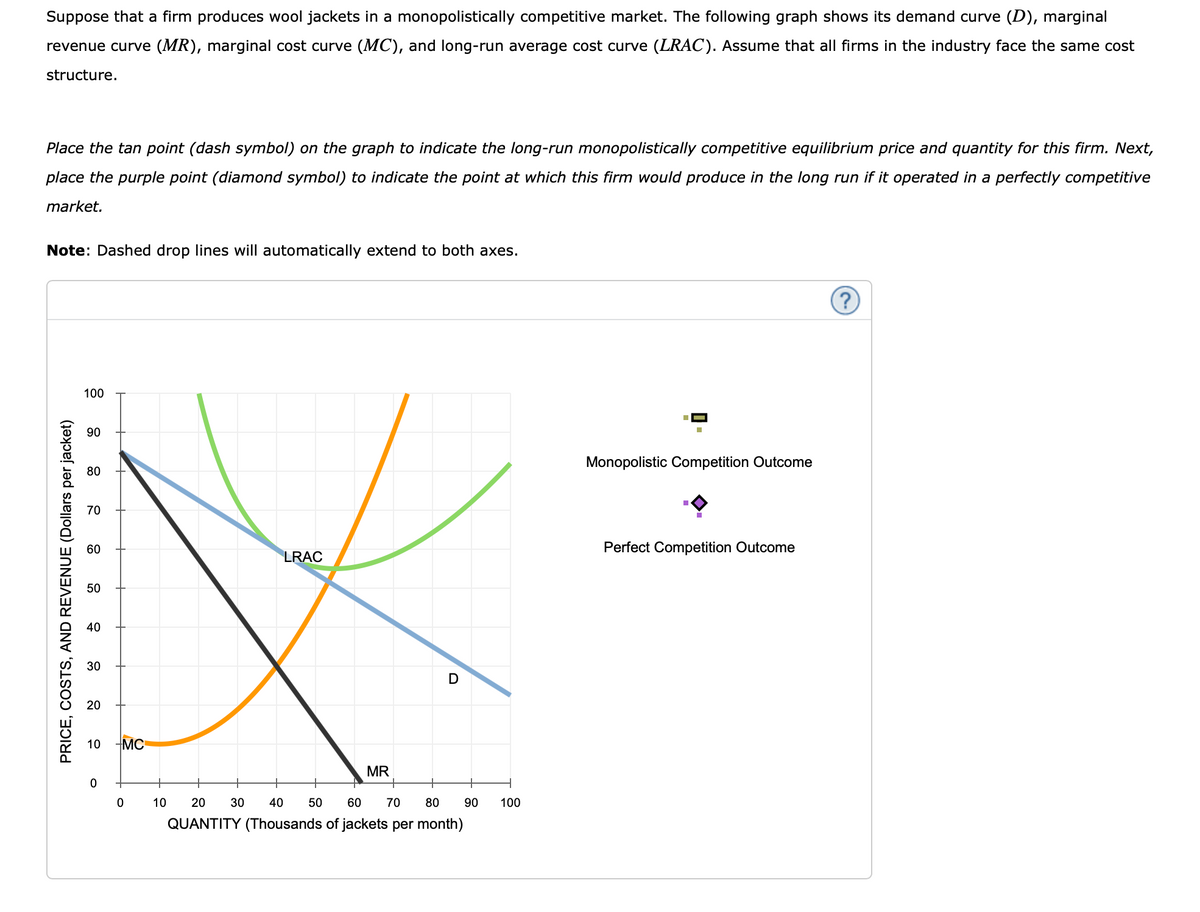
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that a firm produces wool jackets in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve (D), marginal
revenue curve (MR), marginal cost curve (MC), and long-run average cost curve (LRAC). Assume that all firms in the industry face the same cost
structure.
Place the tan point (dash symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next,
place the purple point (diamond symbol) to indicate the point at which this firm would produce in the long run if it operated in a perfectly competitive
market.
Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.
(?)
100
90
Monopolistic Competition Outcome
80
70
60
Perfect Competition Outcome
LRAC
50
40
30
20
10
MC
MR
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
QUANTITY (Thousands of jackets per month)
PRICE, COSTS, AND REVENUE (Dollars per jacket)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you







Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning