Not including crossing over (which significantly increases gamete variability), why are there already substantial differences between the genes in two daughter cells following Meiosis 1? because the cells normally experience aneuploidy O because of mutations during meiosis I because the maternal and paternal genes are segregated into different daughter cells because of independent assortment of the chromosomes
Not including crossing over (which significantly increases gamete variability), why are there already substantial differences between the genes in two daughter cells following Meiosis 1? because the cells normally experience aneuploidy O because of mutations during meiosis I because the maternal and paternal genes are segregated into different daughter cells because of independent assortment of the chromosomes
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Not including crossing over (which significantly increases gamete variability), why are there already
substantial differences between the genes in two daughter cells following Meiosis I?
because the cells normally experience aneuploidy
O because of mutations during meiosis I
because the maternal and paternal genes are segregated into different daughter cells
because of independent assortment of the chromosomes
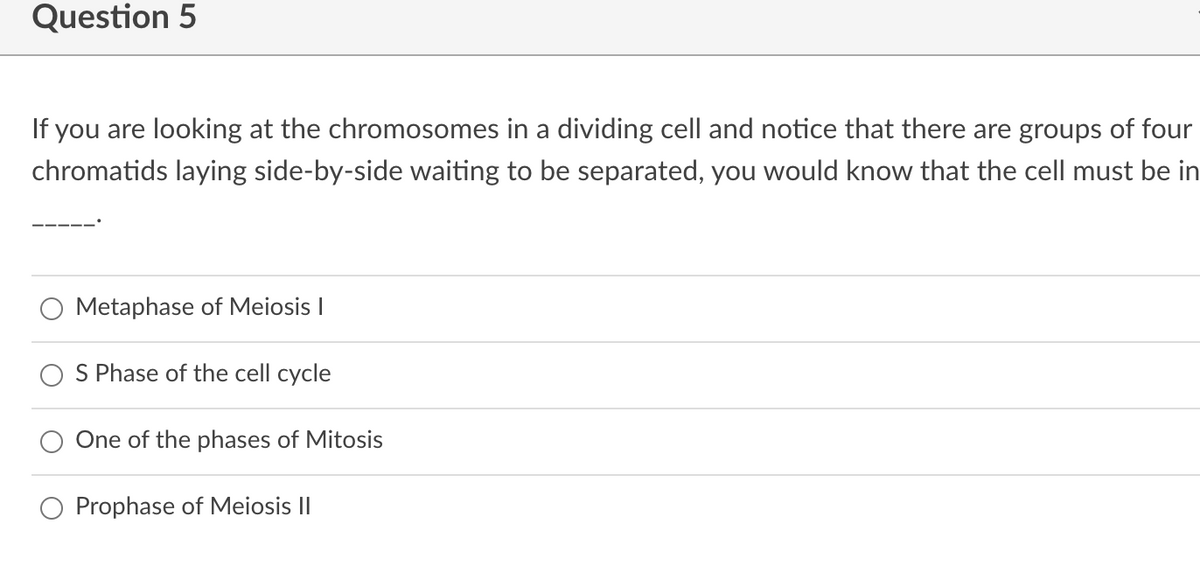
Transcribed Image Text:Question 5
If you are looking at the chromosomes in a dividing cell and notice that there are groups of four
chromatids laying side-by-side waiting to be separated, you would know that the cell must be in
Metaphase of Meiosis I
S Phase of the cell cycle
One of the phases of Mitosis
Prophase of Meiosis II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education