Now consider an excited state of He atom with electron configuration 1s' 2s'. In general, the wavefunction is a state: (r, 0, 6, o2) = ¥(r,0, ¢)Vo, where V(r, 0, 6) and Vo, represent the spatial and the spin part. The spatial part is constructed from the wavefunctions of the 1s' and 2s' orbitals denoted as o (r, 0, 6) and o (r, 0, ), where subscript k denotes which electron it belongs to (i.e., k is either 1 or 2 since we have two electrons). • The spatial part of the wavefunction can be written o(r, 0, ¢)* (r, 0, ¢) + ¢}"(r, 0, ¢)&*° (r, 0, 4) V2(r, 0, ø) = *(r, 0, 6)3"(r, 0, 4) – 63 (r, 0, ø)oF*(r, 0, ¢) Vī2(r, 0, ¢) = Explain (and demonstrate) which spatial wavefunction (2(r,0, ) or V2(r, 0, 6)) is symmetric with respect to exchange of two electrons? Which one corresponds to the singlet and triplet state (defined by the spin multiplicity)? • Based on you response to the previous question, write down the wavefunction for the (i) ground state of He and the (ii) singlet excited state of He. Use spatial orbitals (r, 0, 6), (r, 0, ¢) and spin components of V,, denoted as (†, ) or (t, t).
Now consider an excited state of He atom with electron configuration 1s' 2s'. In general, the wavefunction is a state: (r, 0, 6, o2) = ¥(r,0, ¢)Vo, where V(r, 0, 6) and Vo, represent the spatial and the spin part. The spatial part is constructed from the wavefunctions of the 1s' and 2s' orbitals denoted as o (r, 0, 6) and o (r, 0, ), where subscript k denotes which electron it belongs to (i.e., k is either 1 or 2 since we have two electrons). • The spatial part of the wavefunction can be written o(r, 0, ¢)* (r, 0, ¢) + ¢}"(r, 0, ¢)&*° (r, 0, 4) V2(r, 0, ø) = *(r, 0, 6)3"(r, 0, 4) – 63 (r, 0, ø)oF*(r, 0, ¢) Vī2(r, 0, ¢) = Explain (and demonstrate) which spatial wavefunction (2(r,0, ) or V2(r, 0, 6)) is symmetric with respect to exchange of two electrons? Which one corresponds to the singlet and triplet state (defined by the spin multiplicity)? • Based on you response to the previous question, write down the wavefunction for the (i) ground state of He and the (ii) singlet excited state of He. Use spatial orbitals (r, 0, 6), (r, 0, ¢) and spin components of V,, denoted as (†, ) or (t, t).
Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter11: Quantum Mechanics: Model Systems And The Hydrogen Atom
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.14E
Related questions
Question
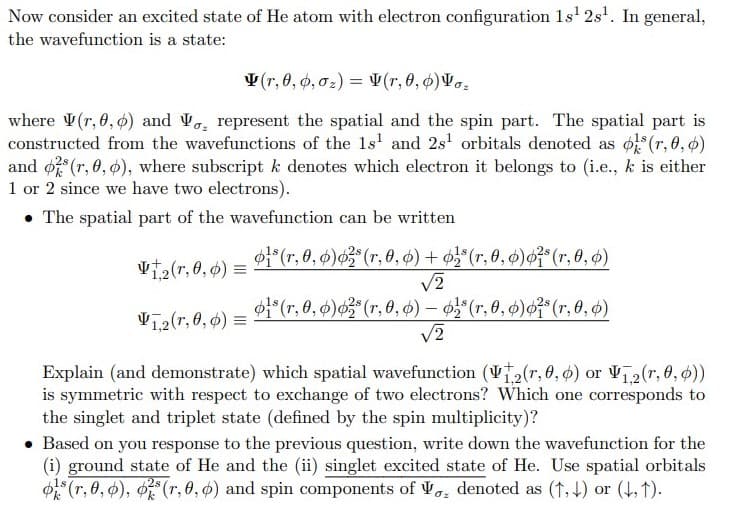
Transcribed Image Text:Now consider an excited state of He atom with electron configuration 1s' 2s'. In general,
the wavefunction is a state:
V (r, 0, 6, 02) = V(r, 0, ø)Vo.
where V(r, 0, ø) and V, represent the spatial and the spin part. The spatial part is
constructed from the wavefunctions of the 1s' and 2s' orbitals denoted as o (r, 0, 6)
and ø (r, 0, 6), where subscript k denotes which electron it belongs to (i.e., k is either
1 or 2 since we have two electrons).
• The spatial part of the wavefunction can be written
1*(r, 0, 4)o3* (r, 0, 4) + o(r, 0, ¢)o²*(r, 0, 4)
V2
F (r, 0, 4)«3"(r, 0, ø) – 05" (r, 0, 4)o²°(r, 0, ø)
V2
V2(r, 0, 6) =
Vī2(r, 0, 6) =
Explain (and demonstrate) which spatial wavefunction (V2(r, 0, 0) or V2(r, 0, 0))
is symmetric with respect to exchange of two electrons? Which one corresponds to
the singlet and triplet state (defined by the spin multiplicity)?
• Based on you response to the previous question, write down the wavefunction for the
(i) ground state of He and the (ii) singlet excited state of He. Use spatial orbitals
(r, 0, 6), (r, 0, 6) and spin components of V, denoted as (†, 4) or (4, 1).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning