NSULIN causes fat, liver, and muscle cells to take in glucose. In this situation the effector protein for the signaling pathway is ---. a metabolic enzyme a transport protein a tyrosine kinase receptor a transcription regulator a leukotreine an actin-binding protein
NSULIN causes fat, liver, and muscle cells to take in glucose. In this situation the effector protein for the signaling pathway is ---. a metabolic enzyme a transport protein a tyrosine kinase receptor a transcription regulator a leukotreine an actin-binding protein
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Chapter9: Cell Communication
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1VCQ: Figure 9.8 HER2 is a receptor tyrosine kinase. In 30 percent of human breast cancers, HER2 is...
Related questions
Question
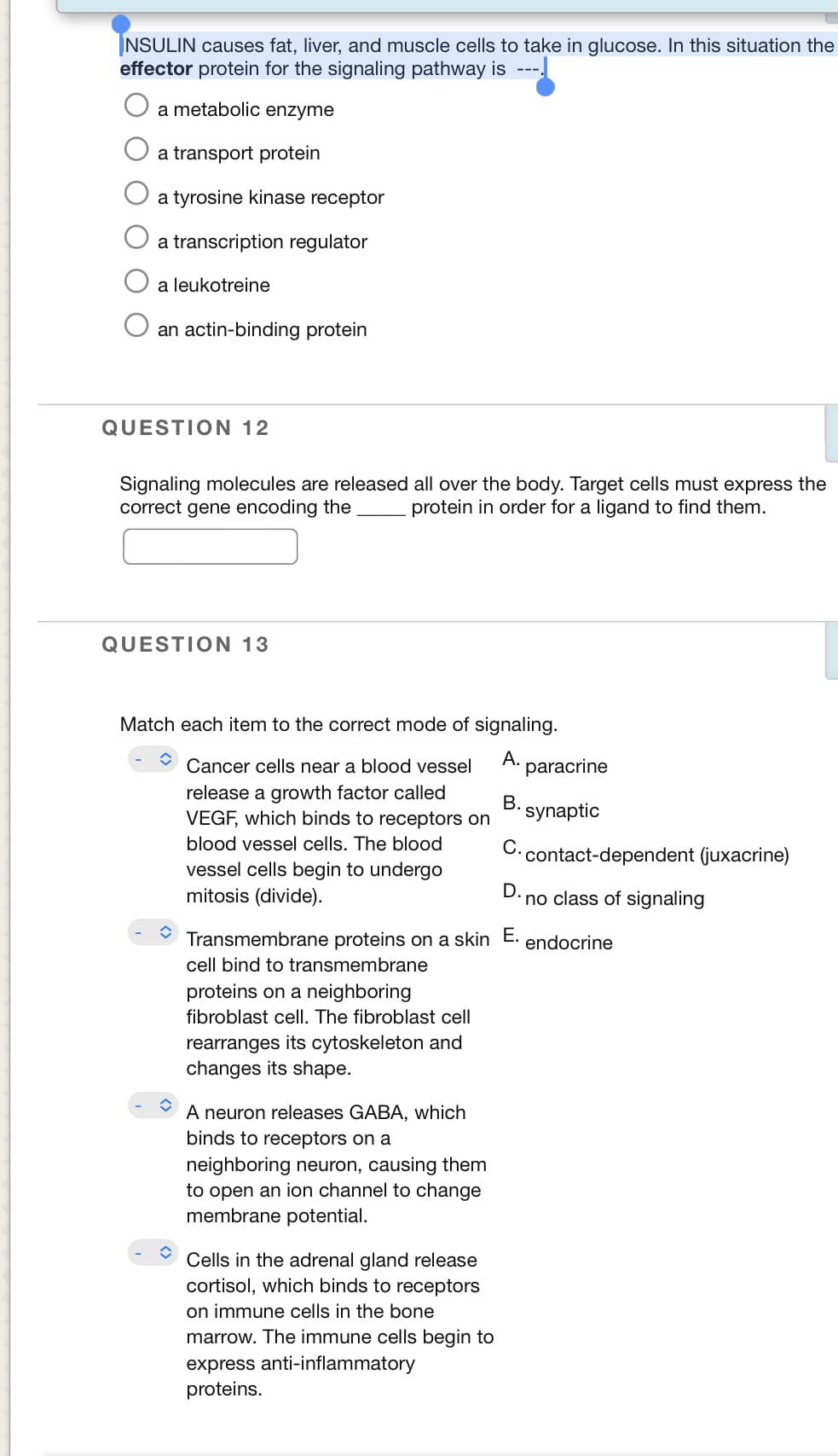
Transcribed Image Text:NSULIN causes fat, liver, and muscle cells to take in glucose. In this situation the
effector protein for the signaling pathway is ---,
a metabolic enzyme
a transport protein
a tyrosine kinase receptor
a transcription regulator
a leukotreine
an actin-binding protein
QUESTION 12
Signaling molecules are released all over the body. Target cells must express the
correct gene encoding the
protein in order for a ligand to find them.
QUESTION 13
Match each item to the correct mode of signaling.
Cancer cells near a blood vessel
А.
paracrine
release a growth factor called
VEGF, which binds to receptors on
B. synaptic
blood vessel cells. The blood
С.
contact-dependent (juxacrine)
vessel cells begin to undergo
mitosis (divide).
D.
no class of signaling
Transmembrane proteins on a skin E.
endocrine
cell bind to transmembrane
proteins on a neighboring
fibroblast cell. The fibroblast cell
rearranges its cytoskeleton and
changes its shape.
A neuron releases GABA, which
binds to receptors on a
neighboring neuron, causing them
to open an ion channel to change
membrane potential.
Cells in the adrenal gland release
cortisol, which binds to receptors
on immune cells in the bone
marrow. The immune cells begin to
express anti-inflammatory
proteins.
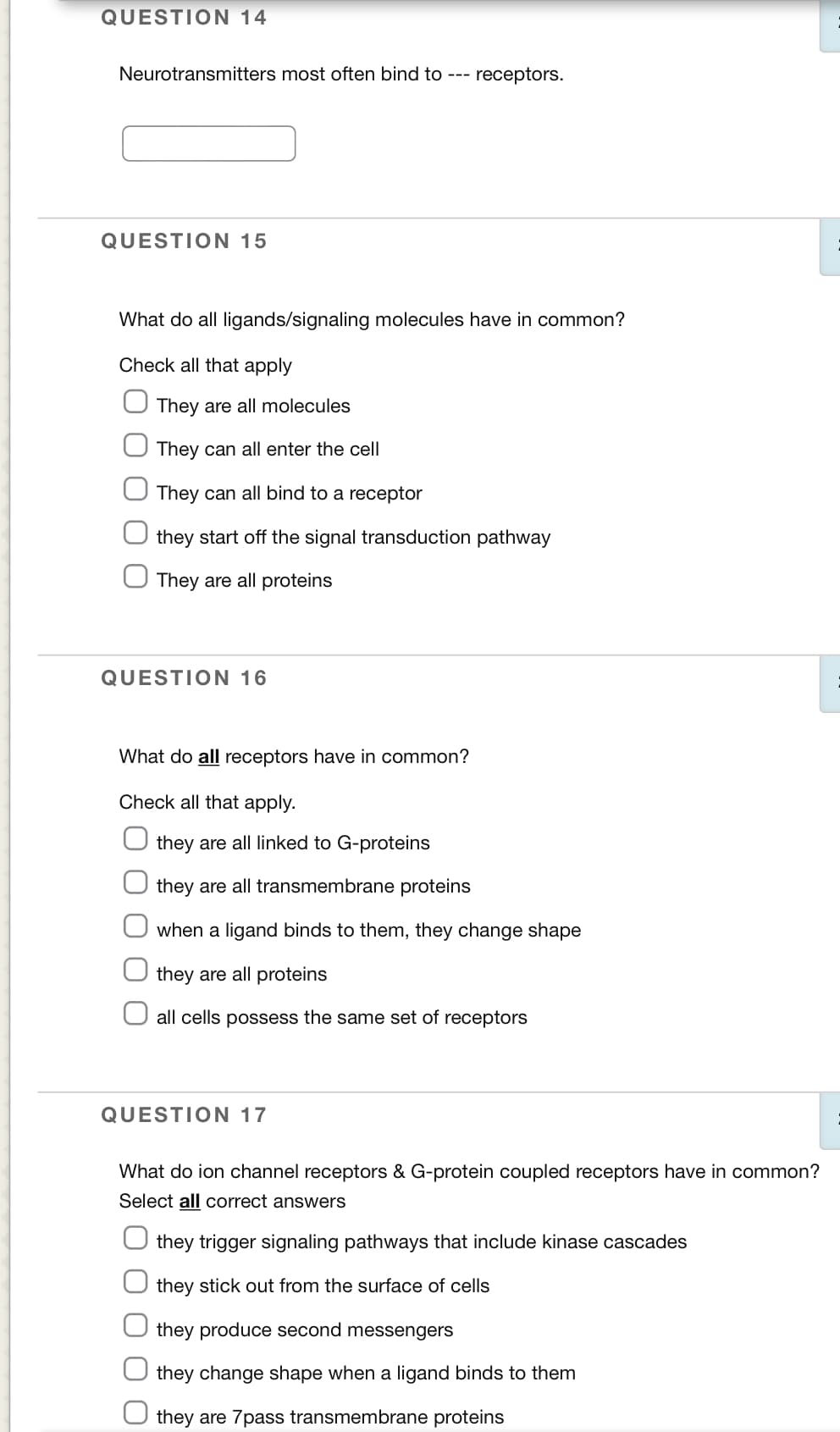
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 14
Neurotransmitters most often bind to ---
receptors.
QUESTION 15
What do all ligands/signaling molecules have in common?
Check all that apply
They are all molecules
They can all enter the cell
They can all bind to a receptor
they start off the signal transduction pathway
They are all proteins
QUESTION 16
What do all receptors have in common?
Check all that apply.
they are all linked to G-proteins
they are all transmembrane proteins
when a ligand binds to them, they change shape
they are all proteins
all cells possess the same set of receptors
QUESTION 17
What do ion channel receptors & G-protein coupled receptors have in common?
Select all correct answers
they trigger signaling pathways that include kinase cascades
they stick out from the surface of cells
they produce second messengers
they change shape when a ligand binds to them
they are 7pass transmembrane proteins
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax