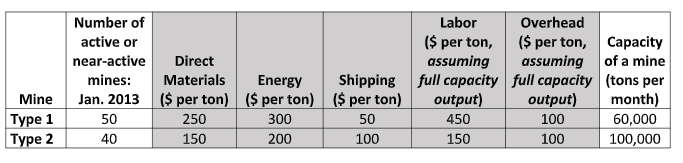
Number of active or near-active mines: Direct Labor ($ per ton, assuming Overhead ($ per ton, assuming Capacity of a mine full capacity full capacity (tons per Materials Energy Shipping Mine Type 1 Jan. 2013 ($ per ton) ($ per ton) ($ per ton) output) output) month) 50 250 300 50 450 100 60,000 Type 2 40 150 200 100 150 100 100,000
In the world market for copper, there are two types of copper mines: Type 1 (primarily located
in North America) and Type 2 (primarily located in Asia and South America). Each type of mine
incurs five “buckets” of costs: (1) direct materials; (2) energy inputs (such as electricity and
natural gas); (3) shipping; (4) production labor; and (5) production and administrative overhead.
Direct materials, energy inputs, and shipping services are purchased in competitive spot
markets, and the total monthly costs that a firm incurs on these items vary in direct linear
proportion to the quantity of copper produced in the mine during that month. If a mine
produces no copper in a particular month, it incurs no direct materials, energy, or shipping
costs.
By contrast, the total monthly costs for production labor and overhead are volume- insensitive:
the levels of these costs do not vary with the volume of production in the mine. Even if the
mine temporarily suspended operations for a month (i.e., produced zero output in that month),
the mine would still incur the same total monthly cost for labor and overhead that it would
have incurred had the mine produced a positive volume of copper. Labor and overhead costs
would “go away” only if the mine was permanently shut down and withdrawn from the
industry.
Each type of mine has a capacity that dictates the maximum amount of copper that can be
produced in a given month. The firm can produce any volume of output in the mine, provided
that it does not exceed this capacity.
The table below shows the cost profiles of the two different types of mines, as well as their
capacities (expressed as tons of copper per month). It also shows the number of mines that are
on active or near-active status in the world market as of January 2013. All costs are expressed
on an average cost basis (i.e., per ton of copper produced). The average costs of labor and
overhead indicate what the per-ton costs would be if a mine produced at full capacity.
Task 1: On the axes below (or using your own diagram) draw the marginal cost curve (MC) and
the
but they do not have to be absolutely, perfectly precise. You should, however, clearly label each
curve.
Task 2: On the axes below (or using your own diagram) draw the short-run industry supply
curve for the world copper market in January 2013. Please indicate how much copper would be
supplied in a given month if the
$500 per ton; and (d) $200 per ton.
Task 3: Suppose that the world demand curve for copper in January 2013 is expected to be
given by the formula D(P) = 6,700,000 – 1,000P, where D(P) denotes the quantity of copper
demanded (measured in tons per month) when the market price is P (measured in dollars per
ton). Given the supply curve you constructed, what would we expect to be the market
equilibrium price for copper in January 2013? How much copper will be bought and sold at this
equilibrium price? How much copper will be produced by all of the Type 1 mines together? How
much copper will be produced by all of the Type 2 mines together? (Drawing a careful picture of
the demand and supply curves can be helpful; you may want to use the axes below for this.)
Task 4: (Think of this part as “independent” from Task 3): Suppose that the market price of
copper is expected to be $1,000 per ton over the long run. Given this price expectation, would
the owners of Type 1 mines want to permanently shut down their mines and withdraw them
from the market? Would owners of Type 2 mines want to permanently shut down their mines
and withdraw them from the market? Briefly explain your answer. For the purpose of this
question, you may assume that a mine (other either type) has no scrap value and has no
alternative use to which it could be redeployed if it is withdrawn from the copper market.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images









