O Cr O H,O O Mg Figure I Figure 2 Two samples of Mg(s) of equal mass were placed in equal amounts of HCI(aq) contained in two separate reaction vessels. Particle representations of the mixing of Mg(s) and HCI(aq) in the two reaction vessels are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 above. Water molecules are not included in the particle representations. Which of the reactions will initially proceed faster, and why? The reaction in Figure 1, because the atoms of Mg are more concentrated than those in Figure 2 The reaction in Figure 1, because the Mg(s) in Figure 1 has a larger mass than the Mg(s) in Figure 2 The reaction in Figure 2, because more Mg atoms are exposed to HCI(aq) in Figure 2 than in Figure 1 The reaction in Figure 2, because the Mg(s) in Figure 2 has less surface area than the Mg(s) in
O Cr O H,O O Mg Figure I Figure 2 Two samples of Mg(s) of equal mass were placed in equal amounts of HCI(aq) contained in two separate reaction vessels. Particle representations of the mixing of Mg(s) and HCI(aq) in the two reaction vessels are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 above. Water molecules are not included in the particle representations. Which of the reactions will initially proceed faster, and why? The reaction in Figure 1, because the atoms of Mg are more concentrated than those in Figure 2 The reaction in Figure 1, because the Mg(s) in Figure 1 has a larger mass than the Mg(s) in Figure 2 The reaction in Figure 2, because more Mg atoms are exposed to HCI(aq) in Figure 2 than in Figure 1 The reaction in Figure 2, because the Mg(s) in Figure 2 has less surface area than the Mg(s) in
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:H. Stephen Stoker
Chapter9: Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.21EP: Classify each of the following reactions as (1) a redox reaction (2) a nonredox reaction or (3) cant...
Related questions
Question
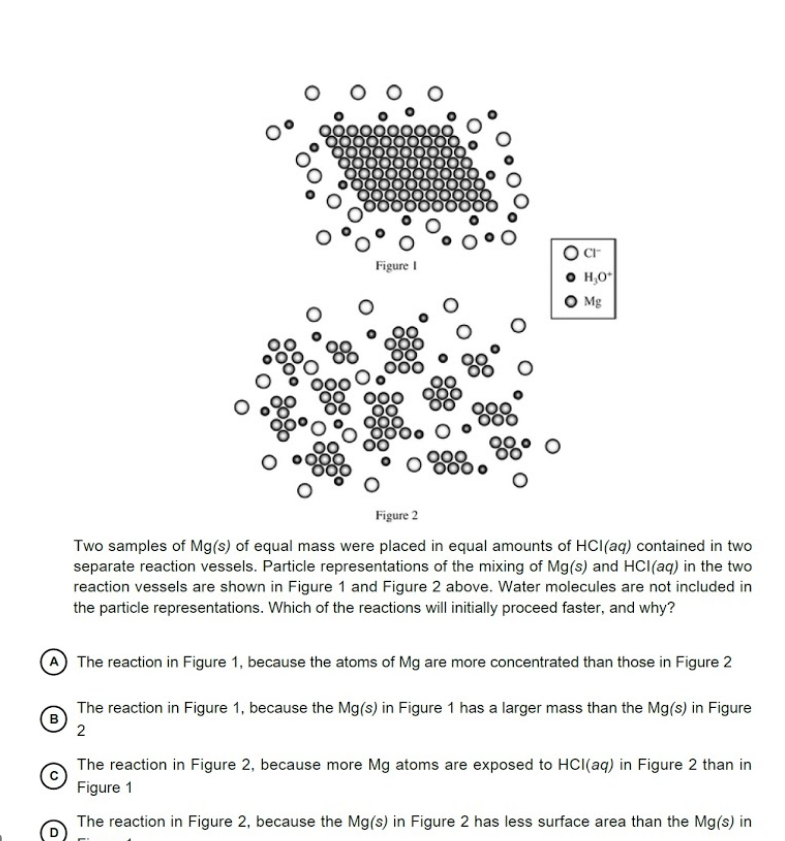
Transcribed Image Text:O Cr
O H,O
O Mg
Figure I
Figure 2
Two samples of Mg(s) of equal mass were placed in equal amounts of HCI(aq) contained in two
separate reaction vessels. Particle representations of the mixing of Mg(s) and HCI(aq) in the two
reaction vessels are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 above. Water molecules are not included in
the particle representations. Which of the reactions will initially proceed faster, and why?
The reaction in Figure 1, because the atoms of Mg are more concentrated than those in Figure 2
The reaction in Figure 1, because the Mg(s) in Figure 1 has a larger mass than the Mg(s) in Figure
(B
2
The reaction in Figure 2, because more Mg atoms are exposed to HCI(aq) in Figure 2 than in
Figure 1
The reaction in Figure 2, because the Mg(s) in Figure 2 has less surface area than the Mg(s) in
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning