One isomer of retinal is converted to a second isomer by the absorption of a photon: CH3 H CH3 H H;C CH; H CH3 H H;C CH; H C=0 H,C H,C' H H;C´ _H H2C_ CH2 H H H2C "CH2 H `CH3 `CH3 H This process is a key step in the chemistry of vision. Although free retinal (in the form shown to the left of the arrow) has an absorption maximum at 376 nm, in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum this absorption shifts into the visible range when the retinal is bound in a pro- tein, as it is in the eye. (a) How many of the C=C bonds are cis and how many are trans in each of the preceding structures? (When assigning labels, consider the relative positions of the two largest groups attached at each double bond.) Describe the motion that takes place upon absorption of a photon. (b) If the ring and the -CHO group in retinal were replaced by -CH; groups, would the absorption maximum in the molecule shift to longer or shorter wavelengths?
One isomer of retinal is converted to a second isomer by the absorption of a photon: CH3 H CH3 H H;C CH; H CH3 H H;C CH; H C=0 H,C H,C' H H;C´ _H H2C_ CH2 H H H2C "CH2 H `CH3 `CH3 H This process is a key step in the chemistry of vision. Although free retinal (in the form shown to the left of the arrow) has an absorption maximum at 376 nm, in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum this absorption shifts into the visible range when the retinal is bound in a pro- tein, as it is in the eye. (a) How many of the C=C bonds are cis and how many are trans in each of the preceding structures? (When assigning labels, consider the relative positions of the two largest groups attached at each double bond.) Describe the motion that takes place upon absorption of a photon. (b) If the ring and the -CHO group in retinal were replaced by -CH; groups, would the absorption maximum in the molecule shift to longer or shorter wavelengths?
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
ChapterL3: Carbon (13c) Nmr Spectroscopy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CTQ
Related questions
Question
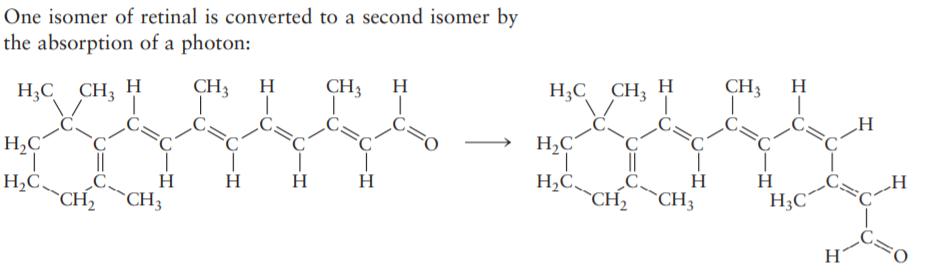
Transcribed Image Text:One isomer of retinal is converted to a second isomer by
the absorption of a photon:
CH3
H
CH3
H
H;C CH; H
CH3
H
H;C CH; H
C=0
H,C
H,C'
H
H;C´
_H
H2C_
CH2
H
H
H2C
"CH2
H
`CH3
`CH3
H
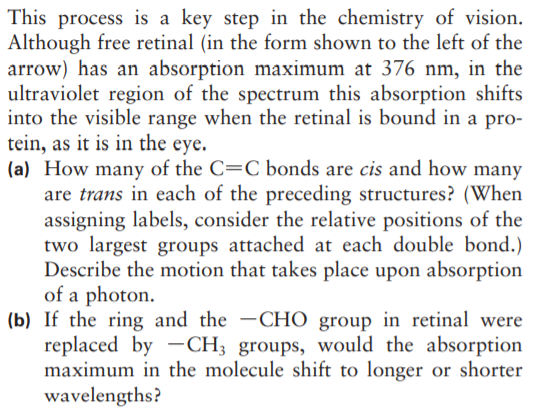
Transcribed Image Text:This process is a key step in the chemistry of vision.
Although free retinal (in the form shown to the left of the
arrow) has an absorption maximum at 376 nm, in the
ultraviolet region of the spectrum this absorption shifts
into the visible range when the retinal is bound in a pro-
tein, as it is in the eye.
(a) How many of the C=C bonds are cis and how many
are trans in each of the preceding structures? (When
assigning labels, consider the relative positions of the
two largest groups attached at each double bond.)
Describe the motion that takes place upon absorption
of a photon.
(b) If the ring and the -CHO group in retinal were
replaced by -CH; groups, would the absorption
maximum in the molecule shift to longer or shorter
wavelengths?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning