The New Age firm produces clean coal. New Age's production function is given by q = L3S3, where L denotes la and S denotes its cutting-edge machinery. The price of labor is given by the wage, w, and price of machiner denoted pc. Suppose that in the short run number of machines is fixed at 5 = 1 while L is variable. a. Write down the expression for the short-run production function. In no more than two sentenc describe the fundamental difference between the short-run and long-run time horizons in production b. Invert the short-run production and derive variable costs, VC(q) = wL(q), where labor is a function of level of output L(q). Next derive fixed costs and the short run cost function, C(q). Compute the marginal productivity of labor (MPL) and show that MPL is diminishing, i.e. d. Compute marginal cost (MC(q) = C) and show that it is increasing, i.e., . > 0. C. амс Sa aMPL SL <0.
The New Age firm produces clean coal. New Age's production function is given by q = L3S3, where L denotes la and S denotes its cutting-edge machinery. The price of labor is given by the wage, w, and price of machiner denoted pc. Suppose that in the short run number of machines is fixed at 5 = 1 while L is variable. a. Write down the expression for the short-run production function. In no more than two sentenc describe the fundamental difference between the short-run and long-run time horizons in production b. Invert the short-run production and derive variable costs, VC(q) = wL(q), where labor is a function of level of output L(q). Next derive fixed costs and the short run cost function, C(q). Compute the marginal productivity of labor (MPL) and show that MPL is diminishing, i.e. d. Compute marginal cost (MC(q) = C) and show that it is increasing, i.e., . > 0. C. амс Sa aMPL SL <0.
Chapter11: The Firm: Production And Costs
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15P
Related questions
Question
can you solve for D E F please thanking you
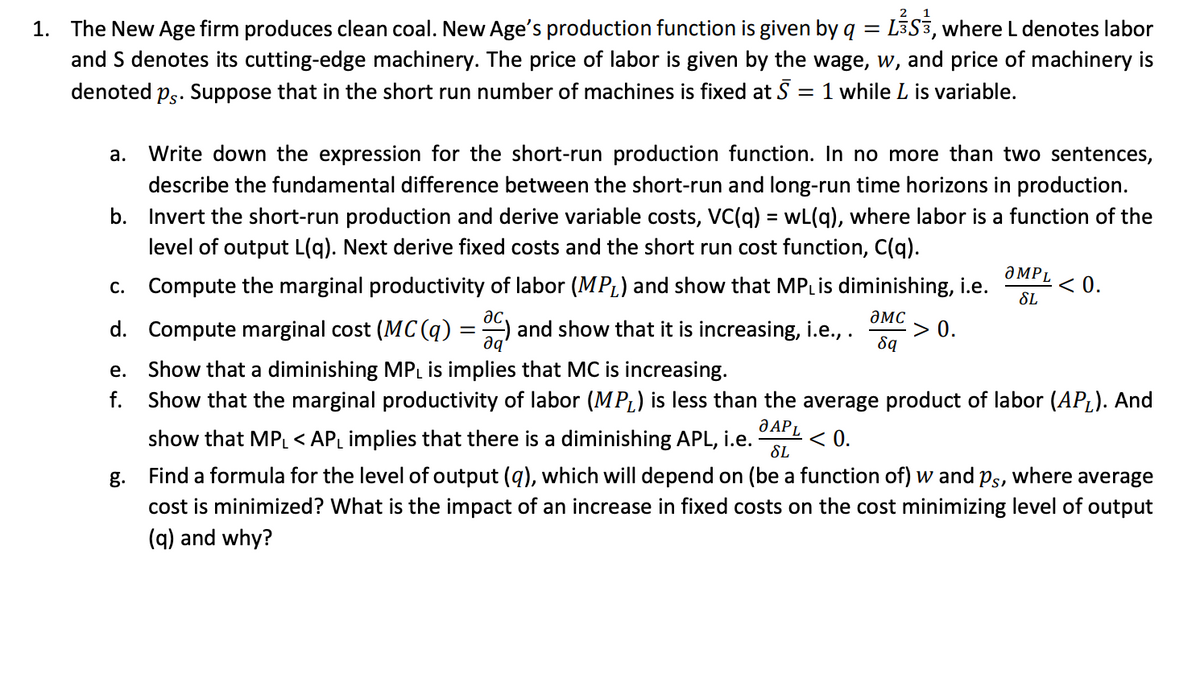
Transcribed Image Text:1. The New Age firm produces clean coal. New Age's production function is given by q = LS3, where L denotes labor
and S denotes its cutting-edge machinery. The price of labor is given by the wage, w, and price of machinery is
denoted ps. Suppose that in the short run number of machines is fixed at 5 1 while L is variable.
=
a. Write down the expression for the short-run production function. In no more than two sentences,
describe the fundamental difference between the short-run and long-run time horizons in production.
b. Invert the short-run production and derive variable costs, VC(q) = wL(q), where labor is a function of the
level of output L(q). Next derive fixed costs and the short run cost function, C(q).
C. Compute the marginal productivity of labor (MPL) and show that MPL is diminishing, i.e.
ac,
дис
d. Compute marginal cost (MC(q) = C) and show that it is increasing, i.e., . > 0.
да
8q
e.
f.
g.
ƏMPL
SL
< 0.
Show that a diminishing MPL is implies that MC is increasing.
Show that the marginal productivity of labor (MP) is less than the average product of labor (AP₁). And
O APL
show that MPL < AP₁ implies that there is a diminishing APL, i.e. < 0.
SL
Find a formula for the level of output (q), which will depend on (be a function of) w and ps, where average
cost is minimized? What is the impact of an increase in fixed costs on the cost minimizing level of output
(q) and why?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
for part f, how does APL equal L^(2/3)//(1/L^(1/3))? Where is the 1/3 coming from for labor?
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc



Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

