What is the Cost of a Short-Run and a Long-Run?
Cost of short-run and the long-run is an economic term that describes the cost involved in the production of goods in a firm in the short as well as long period.
Short Run
The short-run is a certain future period of production where the firm’s one input of production is fixed while others are variable. The short-run does not specify the extent of time but rather is unique to the firm, industry, or economic variable. During the short-run period, the firm faces both fixed and variable costs. It differs in the long run.
For example, leases, contracts, wage agreements limit the firm decisions to adjust production or wages to maintain a profit rate. So, when we relate this to economics, the short-run states the idea that an economy’s behavior will vary based on how much time is there to react.
In the example of a shopping mall where the demand in a year is lower than expected, but the housekeeping staff, administration staff, are being hired at a contract of one year, then the shopping mall authorities have no choice but to swallow the cut in profit as the salaries and wages are fixed during the contract agreement.
Long Run
The long-run is a hypothetical perception where all markets are in equilibrium and quantity and price are fully adjusted. During the long-run period, all the factors of production and costs involved in the production are variable. During this period, a firm can adjust its costs. During the long run, a firm becomes in the position to research more technologies for production which can further help in the production of the desired level of output at a lowered cost. The firm can minimize the cost of every unit as the firm gets time to recover the losses, if any, and search for more efficient ways of production.
A manufacturer becomes flexible in its production decision which results in the expansion or decline in the production capacity and enters into a new industry based on the profit or loss earned.
The long-run is the period of macroeconomic when the factors of production like long-run general price level, wage adjust fully to the state of the economy.
For example, a company may change the scale of production on the basis of the profit or loss earned during the long run. If the firm is doing good and earning a profit, the firm may decide upon more investment in a new plant or add a production line. However, if a firm incurs losses, it may do some research on how to minimize the additional cost and make wise decisions to revert the loss into profit.
Cost of Short-Run and Long-Run Functions
In the long-run cost, the firm can diverge all its inputs whereas, in the short run, some of these inputs are fixed. The cost of producing any output in the short run is greater than the long-run cost as the firm is constrained in the short run and not in the long run.
The graph shows the Short-run total cost curve and long-run total cost curve.
At point L, Short-run total cost STC is tangent to Long-run total cost LTC. The firms vary their output in the short run as some of the costs, in the long run, are fixed in nature. The short-run cost is the same till Q0 output. The short-run cost is not efficient as the cost may be higher. But when it entered in the long-run cost, the total costs become variable.
This is because, in the long run, firms try to expand their output, so it has to bring efficiency in the production process and ensure that a cost-efficient plan is prepared to earn more profit. The cost per unit, in the long run, is less because the firm is in the situation of preparing more flexible plans.
Relationship between Long-Run and Short-Run Costs
The short-run cost and long-run cost where SRAC stands for short-run average costs. Short-run average cost refers to average variable costs of output.
LRAC stands for long-run average costs. Long-run average costs are the average cost of output achievable when all the factors of production are variable.
The firm’s long-run average cost that is LRAC, is affected by the short-run average cost that is SRAC curves. The short-run average cost of SRAC is decreasing over time.
The long-run costs are the sub-groups of the multiple short-run costs. This is because the short-run costs are accumulated in real-time during the production process. While fixed costs don’t have an effect on short-run costs but the variable costs and revenues may affect the short-run cost, and they may be changed during the production process.
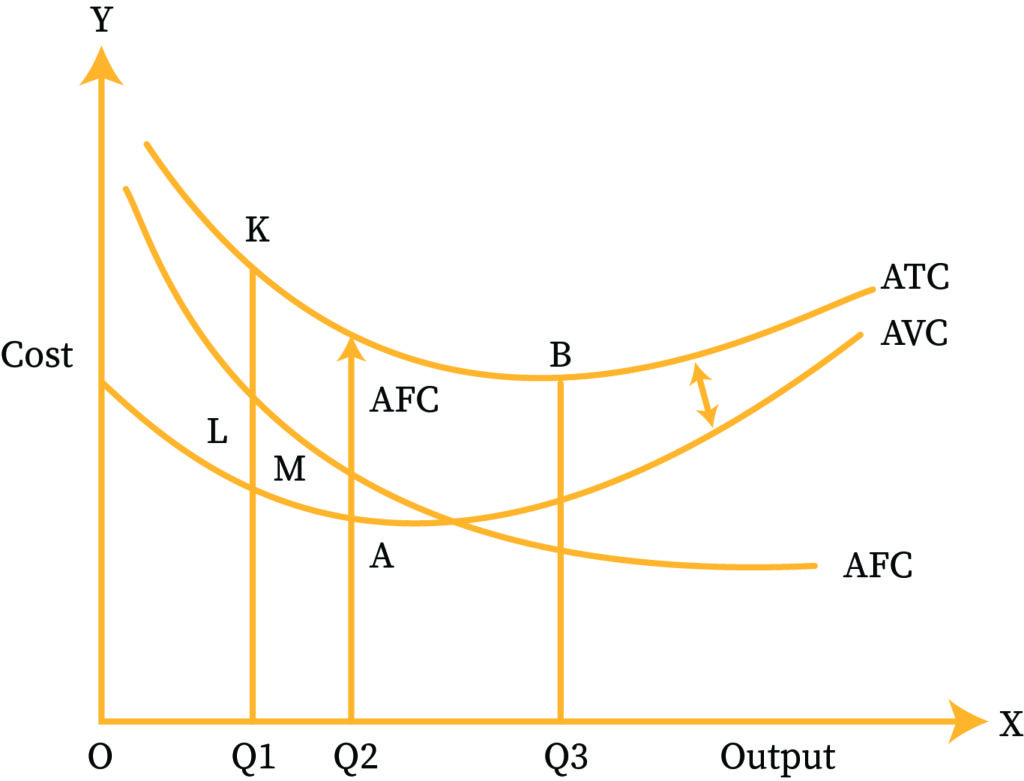
Cost Curves
Total cost (TC) is the sum of total fixed cost (TFC) and total variable cost (TVC). TVC is the cost that changes with the production of the firm. TFC is the cost that firms have to incur, no matter what the production is.

The marginal cost (MC) of production is the difference between the overall cost of production and the cost of creating or producing one more unit. Divide the change in production costs by the change in quantity to calculate the marginal cost. The goal of MC analysis is to figure out when an organization may reach economies of scale to improve production and total operations. The manufacturer can make a profit if the MC of producing one additional unit is less than the per-unit pricing.

Economies of Scale
In simple words, economies of scale refer to the efficiency of production. This is possible when a firm increases production and lowers the cost of production. It can be both internal and external. During the economies of scale, the firm improves the efficiency of production and becomes a cost advantage. It gives the firm advantages like competitive advantage and becomes profit earning.
Economies of Scale in the long run cost: when the average cost in the long run decreases and the output increases, the firm achieves its economies of scale. When the long-run average cost increases, the firm experiences the diseconomies of scale.
Achieving economies of scale in the short run cost is difficult as the cost efficiency that is producing more output in the less cost is difficult in the short run cost.
Content and Applications
This topic is significant in the professional exams for both undergraduate and graduate courses, especially for
- B.A Economics
- M.A Economics
Want more help with your economics homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Short-Run Costs and Long-Run Costs Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Short-Run Costs and Long-Run Costs homework questions.