or the following questions, you will need the following formula: let Xo be the initial value, X, be the value after t periods and g the growth rate by period, then X₁ = Xo(1+g)¹. ou may also need the log properties: log(a) = blog(a) and log(ab) = log(a) +log(b). The properties imply: log(X₂) = log(X₁) + tlog(1+g). a. Suppose the initial real per capita GDP for countries A and B is 14 thousand dollars. If the annual growth rates of countries A and B are respectively 2.8% and 4.8 %, what is the the ratio X/X₁ after 51 years? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal. Number b. Suppose the annual growth rates of countries A and B are respectively 2.8% and 4.8%. How many years it will take for each country to double their respective real per capita GDP? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal. Country A: Number Country B: Number c. Suppose the initial real per capita GDP of countries A, B and C are respectively 10, 10 and 50 thousand dollars. If their annual growth rates are respectively 2.8%, 4.8% and 1.0%, how many years it will take for countries A and B to converge to country C? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal. Country A: Number Country B: Number
or the following questions, you will need the following formula: let Xo be the initial value, X, be the value after t periods and g the growth rate by period, then X₁ = Xo(1+g)¹. ou may also need the log properties: log(a) = blog(a) and log(ab) = log(a) +log(b). The properties imply: log(X₂) = log(X₁) + tlog(1+g). a. Suppose the initial real per capita GDP for countries A and B is 14 thousand dollars. If the annual growth rates of countries A and B are respectively 2.8% and 4.8 %, what is the the ratio X/X₁ after 51 years? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal. Number b. Suppose the annual growth rates of countries A and B are respectively 2.8% and 4.8%. How many years it will take for each country to double their respective real per capita GDP? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal. Country A: Number Country B: Number c. Suppose the initial real per capita GDP of countries A, B and C are respectively 10, 10 and 50 thousand dollars. If their annual growth rates are respectively 2.8%, 4.8% and 1.0%, how many years it will take for countries A and B to converge to country C? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal. Country A: Number Country B: Number
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter5: Business And Economic Forecasting
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
Someone, please help accurately
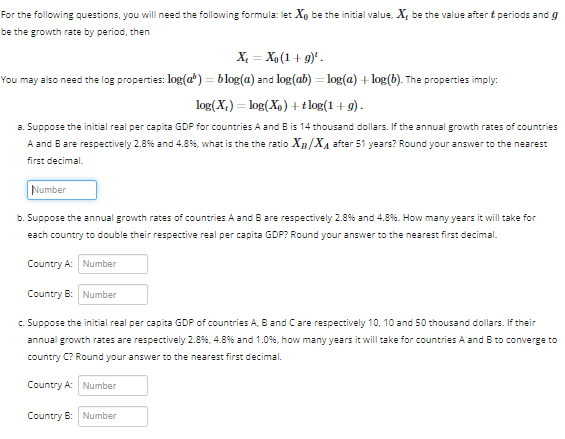
Transcribed Image Text:For the following questions, you will need the following formula: let Xo be the initial value, X, be the value after & periods and g
be the growth rate by period, then
X = Xo (1+g)¹.
You may also need the log properties: log(a) = blog(a) and log(ab) = log(a) + log(b). The properties imply:
log(X₂) = log(X) + tlog(1+g).
a. Suppose the initial real per capita GDP for countries A and B is 14 thousand dollars. If the annual growth rates of countries
A and B are respectively 2.8% and 4.8%, what is the the ratio X/X₁ after 51 years? Round your answer to the nearest
first decimal.
Number
b. Suppose the annual growth rates of countries A and B are respectively 2.8% and 4.8%. How many years it will take for
each country to double their respective real per capita GDP? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal.
Country A: Number
Country B: Number
c. Suppose the initial real per capita GDP of countries A, B and C are respectively 10, 10 and 50 thousand dollars. If their
annual growth rates are respectively 2.8%, 4.8% and 1.0%, how many years it will take for countries A and B to converge to
country C? Round your answer to the nearest first decimal.
Country A: Number
Country B: Number
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning