Oxygen can be converted into ozone by the action of lightning or electric sparks: 302(g) +203(g) For this reaction, AH = +68 kcal/mol (+285 kJ/mol) and K = 2.68 x 10-29 at 25 °C. ▼ ▼ Y Part A Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? O exothermic O endothermic Submit Part B Are the reactants or the products favored at equilibrium? O reactants O products Request Answer Submit Request Answer Part C Explain the effect on the equilibrium of (1) increasing pressure by decreasing volume. (2) increasing the concentration of O₂ (g). (3) increasing the concentration of O3(g) (4) adding a catalyst (5) increasing the temperature. Review | Constants | Periodic Table Submit Essay answers are limited to about 500 words (3800 characters maximum, including spaces). Provide Feedback Request Answer 3800 Character(s) remaining Next >
Oxygen can be converted into ozone by the action of lightning or electric sparks: 302(g) +203(g) For this reaction, AH = +68 kcal/mol (+285 kJ/mol) and K = 2.68 x 10-29 at 25 °C. ▼ ▼ Y Part A Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? O exothermic O endothermic Submit Part B Are the reactants or the products favored at equilibrium? O reactants O products Request Answer Submit Request Answer Part C Explain the effect on the equilibrium of (1) increasing pressure by decreasing volume. (2) increasing the concentration of O₂ (g). (3) increasing the concentration of O3(g) (4) adding a catalyst (5) increasing the temperature. Review | Constants | Periodic Table Submit Essay answers are limited to about 500 words (3800 characters maximum, including spaces). Provide Feedback Request Answer 3800 Character(s) remaining Next >
Chapter7: Statistical Data Treatment And Evaluation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.9QAP
Related questions
Question
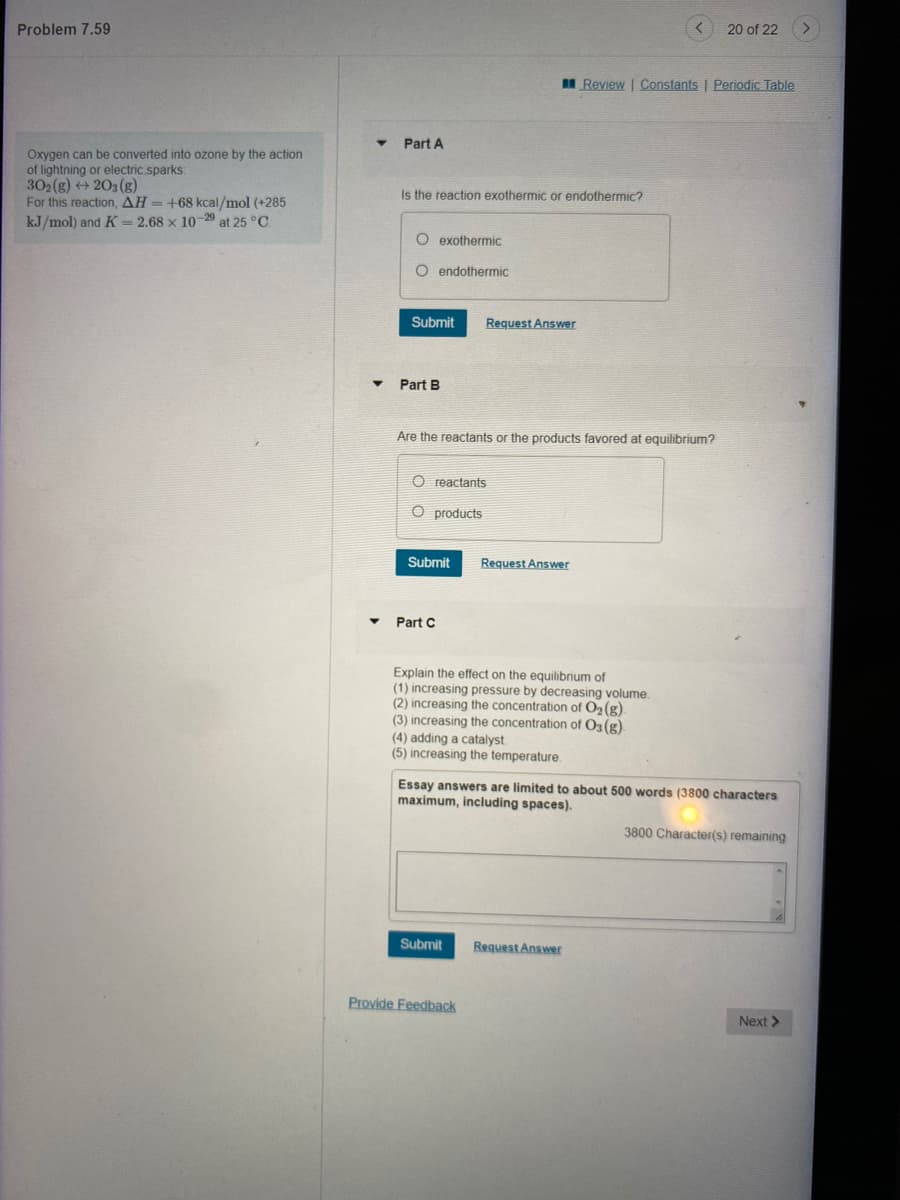
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 7.59
Oxygen can be converted into ozone by the action
of lightning or electric sparks:
302(g) → 203(g)
For this reaction, AH = +68 kcal/mol (+285
kJ/mol) and K = 2.68 x 10-29 at 25 °C.
▼
▼
Part A
Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
O exothermic
O endothermic
Submit Request Answer
Part B
Are the reactants or the products favored at equilibrium?
O reactants
O products
Submit
Part C
Request Answer
Explain the effect on the equilibrium of
(1) increasing pressure by decreasing volume.
(2) increasing the concentration of O₂(g)
(3) increasing the concentration of O3(g).
(4) adding a catalyst.
(5) increasing the temperature.
Submit
Review | Constants | Periodic Table
Provide Feedback
Essay answers are limited to about 500 words (3800 characters
maximum, including spaces).
20 of 22
Request Answer
3800 Character(s) remaining
Next >
>
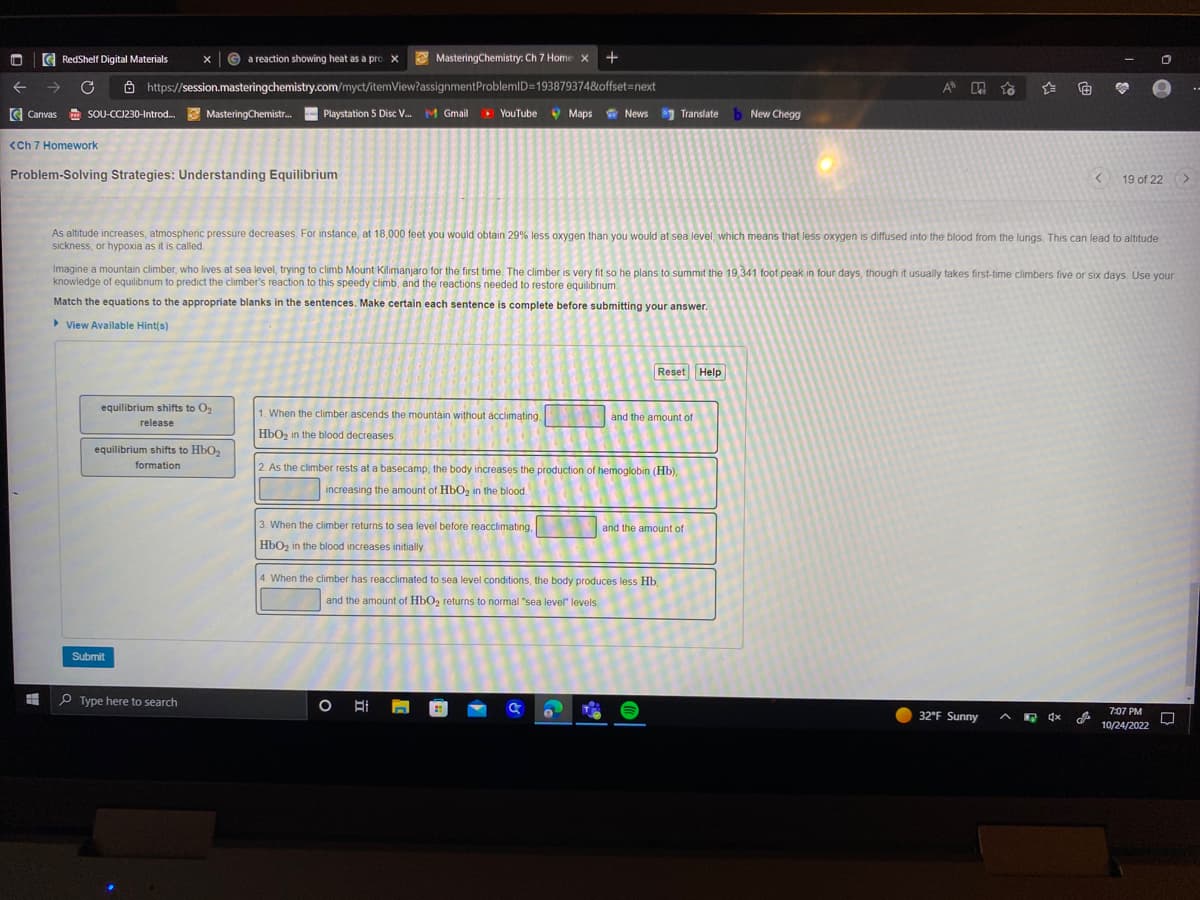
Transcribed Image Text:RedShelf Digital Materials
X Ga reaction showing heat as a pro X
https://session.masteringchemistry.com/myct/itemView?assignmentProblemID=193879374&offset=next
Canvas SOU-CC1230-Introd.... MasteringChemistr... Playstation 5 Disc V... M Gmail YouTube Maps News Translate b New Chegg
<Ch 7 Homework
Problem-Solving Strategies: Understanding Equilibrium
equilibrium shifts to O₂
release
equilibrium shifts to HbO₂
formation
MasteringChemistry: Ch 7 Home X +
Submit
As altitude increases, atmospheric pressure decreases. For instance, at 18,000 feet you would obtain 29% less oxygen than you would at sea level, which means that less oxygen is diffused into the blood from the lungs. This can lead to altitude
sickness, or hypoxia as it is called.
Type here to search
Imagine a mountain climber, who lives at sea level, trying to climb Mount Kilimanjaro for the first time. The climber is very fit so he plans to summit the 19,341 foot peak in four days, though it usually takes first-time climbers five or six days. Use your
knowledge of equilibrium to predict the climber's reaction to this speedy climb, and the reactions needed to restore equilibrium
Match the equations to the appropriate blanks in the sentences. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer.
▸View Available Hint(s)
1. When the climber ascends the mountain without acclimating.
HbO₂ in the blood decreases
3. When the climber returns to sea level before reacclimating,
HbO₂ in the blood increases initially.
2. As the climber rests at a basecamp, the body increases the production of hemoglobin (Hb),
increasing the amount of HbO₂ in the blood
O
Reset Help
and the amount of
a
4. When the climber has reacclimated to sea level conditions, the body produces less Hb,
and the amount of HbO₂ returns to normal "sea level" levels
A m
and the amount of
€
32°F Sunny
<
A M 4x
19 of 22 >
0
7:07 PM
10/24/2022
..
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

