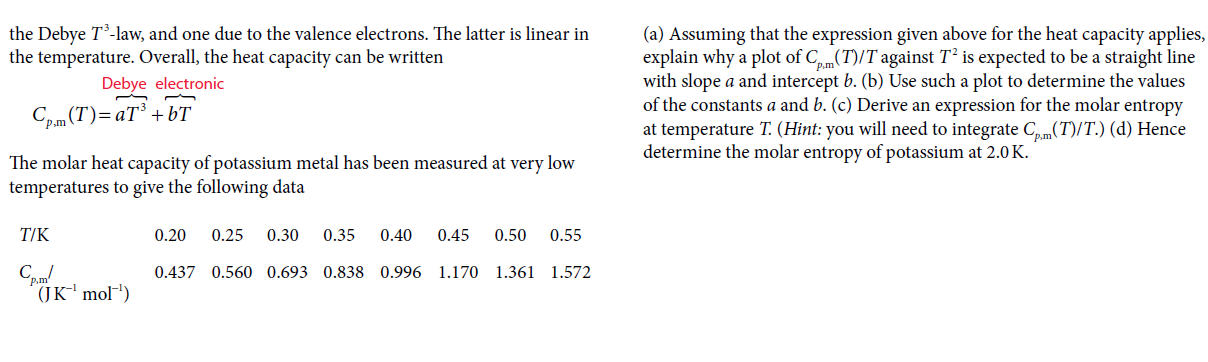
P3C.9 At low temperatures there are two contributions to the heat capacity of a metal, one associated with lattice vibrations, which is well-approximated by the Debye T-law, and one due to the valence electrons. The latter is linear in the temperature. Overall, the heat capacity can be written (a) Assuming that the expression given above for the heat capacity applies, explain why a plot of C,m(T)/T against T² is expected to be a straight line with slope a and intercept b. (b) Use such a plot to determine the values of the constants a and b. (c) Derive an expression for the molar entropy at temperature T. (Hint: you will need to integrate Cm(T)/T.) (d) Hence determine the molar entropy of potassium at 2.0 K. Debye electronic Cp.m (T)= aT³ + bT The molar heat capacity of potassium metal has been measured at very low temperatures to give the following data T/K 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.437 0.560 0.693 0.838 0.996 1.170 1.361 1.572 (JK' mol')
P3C.9 At low temperatures there are two contributions to the heat capacity of a metal, one associated with lattice vibrations, which is well-approximated by the Debye T-law, and one due to the valence electrons. The latter is linear in the temperature. Overall, the heat capacity can be written (a) Assuming that the expression given above for the heat capacity applies, explain why a plot of C,m(T)/T against T² is expected to be a straight line with slope a and intercept b. (b) Use such a plot to determine the values of the constants a and b. (c) Derive an expression for the molar entropy at temperature T. (Hint: you will need to integrate Cm(T)/T.) (d) Hence determine the molar entropy of potassium at 2.0 K. Debye electronic Cp.m (T)= aT³ + bT The molar heat capacity of potassium metal has been measured at very low temperatures to give the following data T/K 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.437 0.560 0.693 0.838 0.996 1.170 1.361 1.572 (JK' mol')
Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter2: The First Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.56E: What are the numerical values of the heat capacities c-v and c-p of a monatomic ideal gas,in units...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:P3C.9 At low temperatures there are two contributions to the heat capacity of
a metal, one associated with lattice vibrations, which is well-approximated by
Transcribed Image Text:the Debye T-law, and one due to the valence electrons. The latter is linear in
the temperature. Overall, the heat capacity can be written
(a) Assuming that the expression given above for the heat capacity applies,
explain why a plot of C,m(T)/T against T² is expected to be a straight line
with slope a and intercept b. (b) Use such a plot to determine the values
of the constants a and b. (c) Derive an expression for the molar entropy
at temperature T. (Hint: you will need to integrate Cm(T)/T.) (d) Hence
determine the molar entropy of potassium at 2.0 K.
Debye electronic
Cp.m (T)= aT³ + bT
The molar heat capacity of potassium metal has been measured at very low
temperatures to give the following data
T/K
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
0.55
0.437 0.560 0.693 0.838 0.996 1.170 1.361 1.572
(JK' mol')
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 12 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,