Part B - Calculate the shear force The block is subjected to a force V that produces a deflection of A = 0.14 cm. What is the applied force Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures. > View Available Hint(s) HA V =Value Units Submit - Part C- Calculate the deflection The block is subjected to a force V = 56.25 kN . What is the resulting deflection A? %3D Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
Part B - Calculate the shear force The block is subjected to a force V that produces a deflection of A = 0.14 cm. What is the applied force Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures. > View Available Hint(s) HA V =Value Units Submit - Part C- Calculate the deflection The block is subjected to a force V = 56.25 kN . What is the resulting deflection A? %3D Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter11: Columns
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.3.5P: Solve Problem 11.3-3 for a W 10 × 45 steel column having a length L = 28 ft.
Related questions
Question
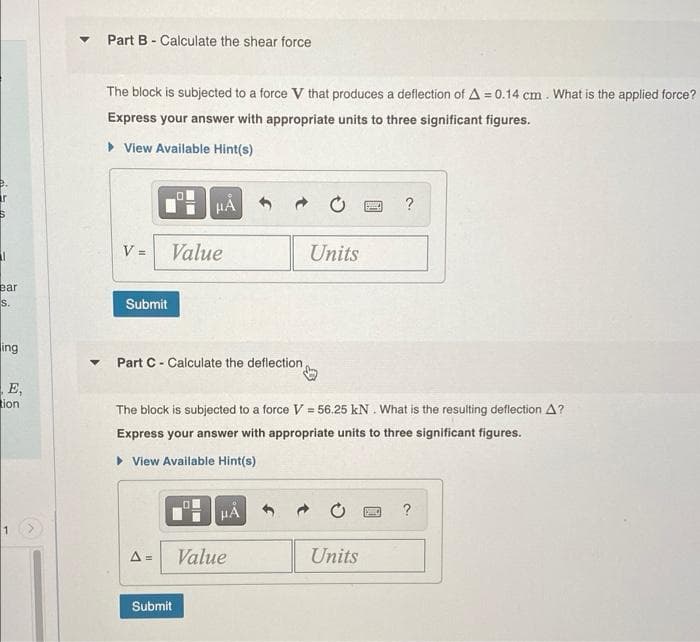
Transcribed Image Text:Part B - Calculate the shear force
The block is subjected to a force V that produces a deflection of A = 0.14 cm. What is the applied force?
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
> View Available Hint(s)
HA
V =
Value
Units
ear
S.
Submit
ing
Part C- Calculate the deflection
E,
tion
The block is subjected to a force V = 56.25 kN . What is the resulting deflection A?
Express your answer with appropriate units to three significant figures.
> View Available Hint(s)
HA
1
Value
Units
Submit
Transcribed Image Text:Ree
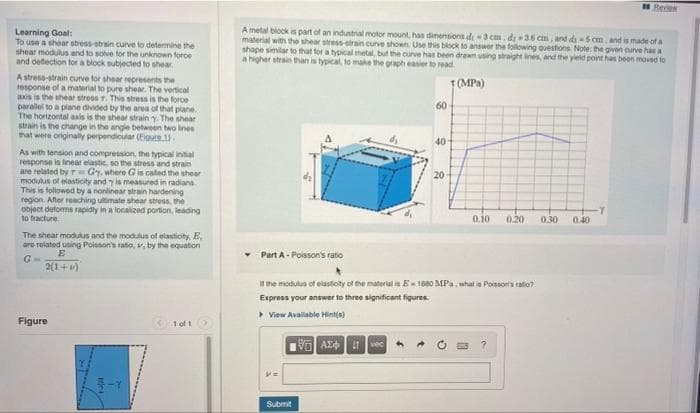
Learning Goal:
To use a shear stress strain curve to determine the
shear modulus and to solve for the unknown force
and deftection for a block subjected to shear
A metal biock is part of an industral motor mount, has dinensions di 3 cm, di 36 cni, and da 5 cm, and is made of a
material with the shear stress-etrain curve shown. Use this block to answer the following ouestions Note: the given ourve has a
shape similar to that tor a typical metal, but the curve has been drawn using straight ines, and the yield point has beon moved to
a higher strain than is typical, to make the graph easier to read.
A stress-strain curve for shear represents the
response of a material to pure shear. The vertical
axis is the shear stress T. This stress is the force
paralel to a plane divided by the area of that plane.
The horizontal axis is the shear strain y. The shear
strain is the change in the angle between two ines
that were originally perpendicular (Eoure 1.
F(MPa)
60
40
As with tension and compression, the typical intial
response is linear elastic, so the stress and strain
are related by r Gy, where G is caled the shear
modulus of elasticity and y is measured in radiana
This is followed by a nonlinear strain hardening
region. After reaching ultimate shear stress, the
object deforms rapidly in a localized portion, leading
to fracture.
20
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
The shear moduus and the modulus of elasticity, E,
oro related using Poisson's ratio, v, by the equation
Part A- Poisson's ratio
G
2(1+)
the modulus of elastioity of the material is E 1880 MPa, what is Poissonta ratio?
Express your answer to three significant figures.
> View Available Hint(s)
Figure
1 of 1
V AX ivec
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning