Part B For the following systems at equilibrium C: CaCO3(s) D: PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) = CaO(s)+CO2(g) AH=+178 kJ/mol = PC5(g) ΔΗ-88 kJ/mol classify these changes by their effect. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
Part B For the following systems at equilibrium C: CaCO3(s) D: PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) = CaO(s)+CO2(g) AH=+178 kJ/mol = PC5(g) ΔΗ-88 kJ/mol classify these changes by their effect. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter13: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 123CP: A sample of gaseous nitrosyl bromide (NOBr) was placed in a container tiued with a frictionless,...
Related questions
Question
Please answer question 11 Part A and B

Transcribed Image Text:Part B
For the following systems at equilibrium
C: CaCO3(s)
D: PC|3(g)+ Cl2 (g) = PCI5 (g)
= CaO(s)+ CO2(g) AH= +178 kJ/mol
AH = -88 kJ/mol
classify these changes by their effect.
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
System C
Increase temperature
System C
Decrease temperature
System D
Increase temperature
System D
Decrease temperature
Leftward shift
No shift
Rightward shift
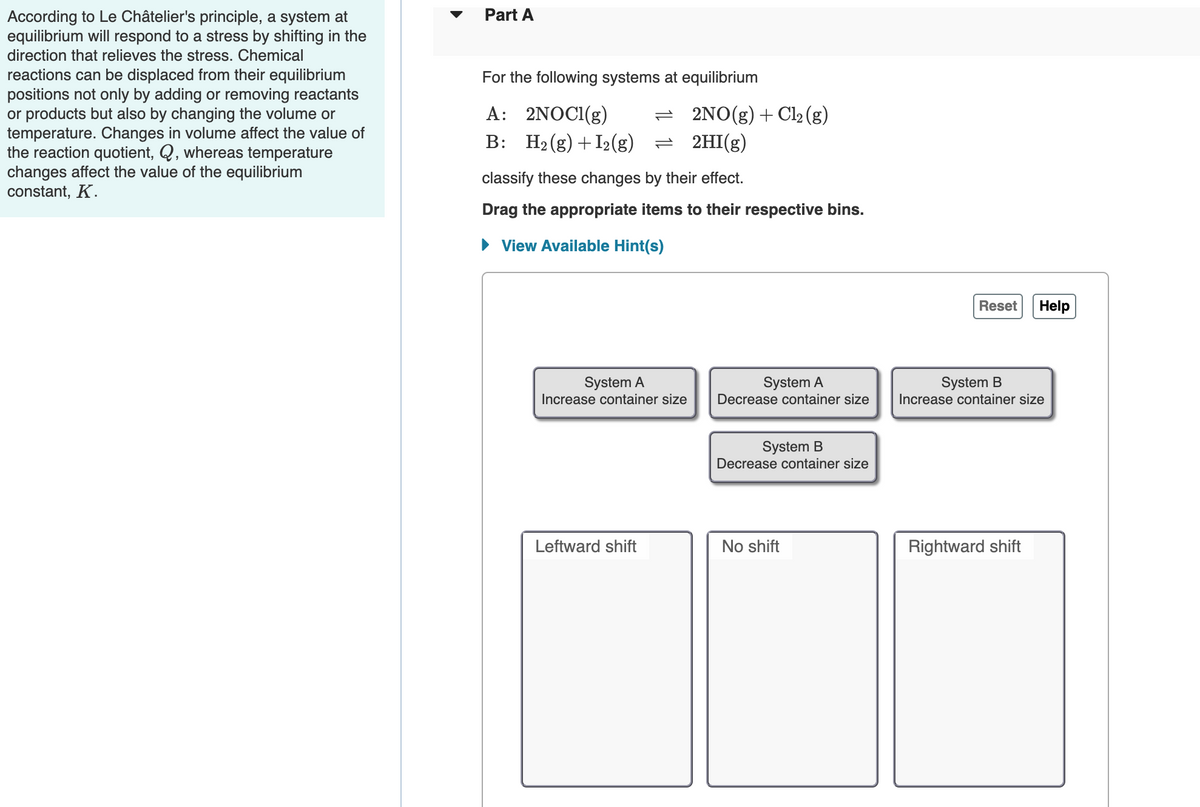
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
According to Le Châtelier's principle, a system at
equilibrium will respond to a stress by shifting in the
direction that relieves the stress. Chemical
reactions can be displaced from their equilibrium
positions not only by adding or removing reactants
or products but also by changing the volume or
temperature. Changes in volume affect the value of
the reaction quotient, Q, whereas temperature
changes affect the value of the equilibrium
constant, K.
For the following systems at equilibrium
A: 2NOCI(g)
= 2NO(g)+Cl2 (g)
B: H2 (g) + I2(g) = 2HI(g)
classify these changes by their effect.
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
System A
Increase container size
System A
Decrease container size
System B
Increase container size
System B
Decrease container size
Leftward shift
No shift
Rightward shift
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning