Per-unit cost (P) P = 12 10 8 80 90 100 Marginal Cost long run, Average Cost Average Variable Cost Output The figure above shows the Marginal Cost, Average Cost, and Average Variable Cost for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market, along with the prevailing market price of 12. At the current equilibrium, the firm is producing + units of output, resulting in achieving the long-run market price equal to Suppose the market price decreases to $7 per unit. In the short run, the firm will ◆ ◆ profit. In the long run, and earn profit. In the
Per-unit cost (P) P = 12 10 8 80 90 100 Marginal Cost long run, Average Cost Average Variable Cost Output The figure above shows the Marginal Cost, Average Cost, and Average Variable Cost for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market, along with the prevailing market price of 12. At the current equilibrium, the firm is producing + units of output, resulting in achieving the long-run market price equal to Suppose the market price decreases to $7 per unit. In the short run, the firm will ◆ ◆ profit. In the long run, and earn profit. In the
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Course List)
16th Edition
ISBN:9781305506725
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Chapter24: Price-searcher Markets With High Entry Barriers
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13CQ
Related questions
Question
blank one options: 0 , OR 80, OR 90, OR 100
blank two options: zero, OR negative, OR positive
Blank three options: firms will enter the market, OR firms will exit the market, OR the firms in the market will be unchanged
Blank four options: 0, OR 8, OR 10, OR 12
blank five options: stay open, OR shut down
blank six options: zero, OR negative, OR positive
Blank seven options: more firms will enter the market, OR more firms will exit the market, OR the firms in the market will be unchanged
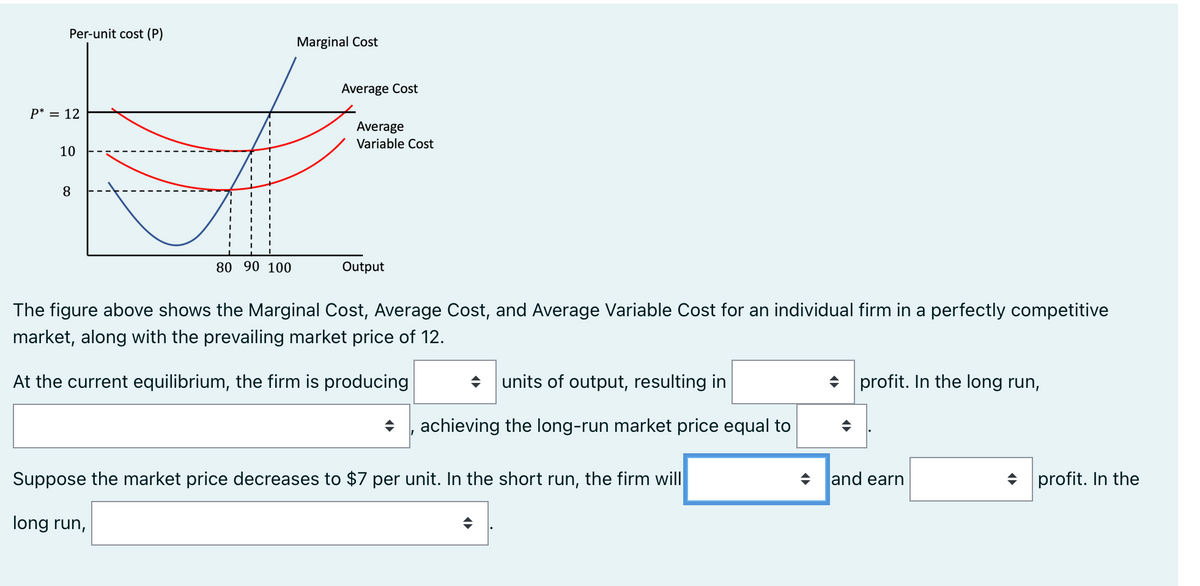
Transcribed Image Text:Per-unit cost (P)
P* = 12
10
8
I
I
I
long run,
80 90 100
Marginal Cost
Average Cost
Average
Variable Cost
Output
The figure above shows the Marginal Cost, Average Cost, and Average Variable Cost for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive
market, along with the prevailing market price of 12.
At the current equilibrium, the firm is producing
◆ units of output, resulting in
achieving the long-run market price equal to
Suppose the market price decreases to $7 per unit. In the short run, the firm will
profit. In the long run,
and earn
profit. In the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax