Problem 24-3E. A pipeline containing natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains 80% methane gas (CH4, species A) and 20% ethane (C₂H6, species B) gas at 3.0 atm and 17 °C. We are concerned that if the pipeline leaks, then the gas mixture can transfer through the porous layer above the pipeline and ultimately escape to the atmosphere, as shown in Figure 24-3E. As part of this analysis, it will be necessary to estimate the effective diffusion coefficient of methane and ethane through the porous material. Please answer the following questions related to this process: (a) What is the molar concentration of ethane (B) gas inside the pipeline? (b) What is the molecular diffusion coefficient of methane gas (CH4, species A) in ethane gas (C₂H6, species B) inside the pipe at (P = 3.0 atm) by the Fuller-Schettler-Giddings approach? (c) What is the effective diffusion coefficient of methane in the methane/ethane gas mixture through the porous layer (D'Ae), assuming the gas space inside the porous layer is at 1.0 atm (P = 1.0 atm)? You may assume that the gas space in the porous layer contains only methane and ethane. Addition information: porous layer, & = 0.3, dpore = 0.0010 cm, MA = 16 g/gmole, MB = 30 g/gmole gas leak to atmosphere porous layer 17 °C, 1.0 atm ε = 0.3, dpore = 0.001 cm 80% CH4 gas, 20% C₂H₁ gas 3.0 atm, 17 °C pipeline
Problem 24-3E. A pipeline containing natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains 80% methane gas (CH4, species A) and 20% ethane (C₂H6, species B) gas at 3.0 atm and 17 °C. We are concerned that if the pipeline leaks, then the gas mixture can transfer through the porous layer above the pipeline and ultimately escape to the atmosphere, as shown in Figure 24-3E. As part of this analysis, it will be necessary to estimate the effective diffusion coefficient of methane and ethane through the porous material. Please answer the following questions related to this process: (a) What is the molar concentration of ethane (B) gas inside the pipeline? (b) What is the molecular diffusion coefficient of methane gas (CH4, species A) in ethane gas (C₂H6, species B) inside the pipe at (P = 3.0 atm) by the Fuller-Schettler-Giddings approach? (c) What is the effective diffusion coefficient of methane in the methane/ethane gas mixture through the porous layer (D'Ae), assuming the gas space inside the porous layer is at 1.0 atm (P = 1.0 atm)? You may assume that the gas space in the porous layer contains only methane and ethane. Addition information: porous layer, & = 0.3, dpore = 0.0010 cm, MA = 16 g/gmole, MB = 30 g/gmole gas leak to atmosphere porous layer 17 °C, 1.0 atm ε = 0.3, dpore = 0.001 cm 80% CH4 gas, 20% C₂H₁ gas 3.0 atm, 17 °C pipeline
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Please note when values are sourced from an appendix/table. Include any assumptions.
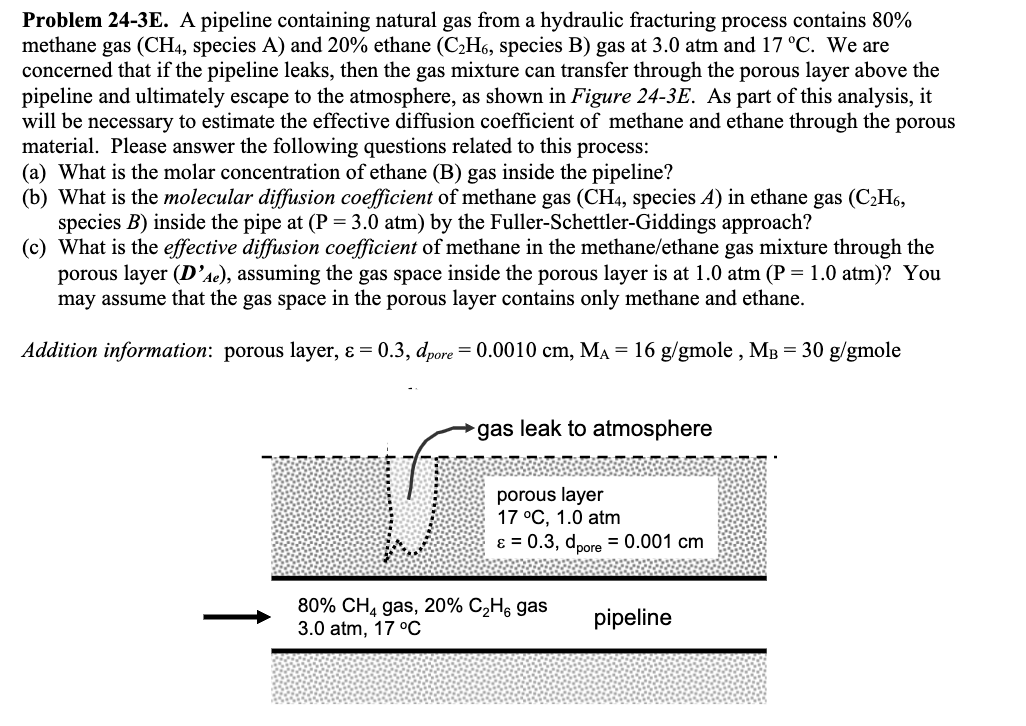
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 24-3E. A pipeline containing natural gas from a hydraulic fracturing process contains 80%
methane gas (CH4, species A) and 20% ethane (C₂H6, species B) gas at 3.0 atm and 17 °C. We are
concerned that if the pipeline leaks, then the gas mixture can transfer through the porous layer above the
pipeline and ultimately escape to the atmosphere, as shown in Figure 24-3E. As part of this analysis, it
will be necessary to estimate the effective diffusion coefficient of methane and ethane through the porous
material. Please answer the following questions related to this process:
(a) What is the molar concentration of ethane (B) gas inside the pipeline?
(b) What is the molecular diffusion coefficient of methane gas (CH4, species A) in ethane gas (C₂H6,
species B) inside the pipe at (P = 3.0 atm) by the Fuller-Schettler-Giddings approach?
(c) What is the effective diffusion coefficient of methane in the methane/ethane gas mixture through the
porous layer (D'Ae), assuming the gas space inside the porous layer is at 1.0 atm (P = 1.0 atm)? You
may assume that the gas space in the porous layer contains only methane and ethane.
Addition information: porous layer, & = 0.3, dpore = 0.0010 cm, M₁ = 16 g/gmole, MB = 30 g/gmole
gas leak to atmosphere
√
porous layer
17 °C, 1.0 atm
ε = 0.3, dpore = 0.001 cm
80% CH4 gas, 20% C₂H, gas
3.0 atm, 17 °C
pipeline
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The