Q1) (A) Two solid circular cross-section bar as shown in the Figure. If the stress in left portion is limited to 150 MN/m2, determine the diameter of the left portion(D). Find also the length of the right portion(a) if the total elongation of the bar is to be 0.2mm. Young's modulus is E =210 GN/m2. (B) If, in order to reduce weight whilst keeping the external diameter constant, the left portion is bored axially to produce a cylinder of uniform thickness, whatis the maximum diameter of bore possible given that the maximum allowable stress of the left portion is 180 MN/m2? The load can be assumed to remain constant at 160 kN. 0.03 m 160 kN D 160 kN diameter a
Q1) (A) Two solid circular cross-section bar as shown in the Figure. If the stress in left portion is limited to 150 MN/m2, determine the diameter of the left portion(D). Find also the length of the right portion(a) if the total elongation of the bar is to be 0.2mm. Young's modulus is E =210 GN/m2. (B) If, in order to reduce weight whilst keeping the external diameter constant, the left portion is bored axially to produce a cylinder of uniform thickness, whatis the maximum diameter of bore possible given that the maximum allowable stress of the left portion is 180 MN/m2? The load can be assumed to remain constant at 160 kN. 0.03 m 160 kN D 160 kN diameter a
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter5: Stresses In Beams (basic Topics)
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.12.14P: A circular post, a rectangular post, and a post of cruciform cross section are each compressed by...
Related questions
Question
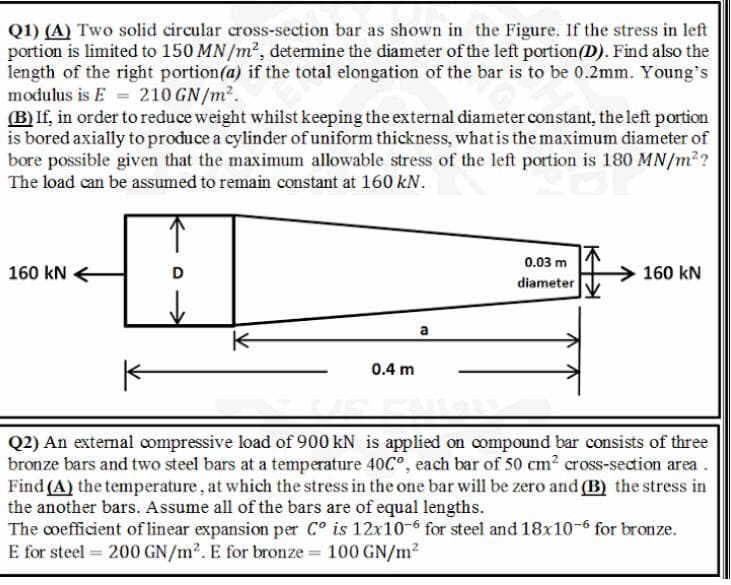
Transcribed Image Text:Q1) (A) Two solid circular cross-section bar as shown in the Figure. If the stress in left
portion is limited to 150 MN /m2, determine the diameter of the left portion(D). Find also the
length of the right portion(a) if the total elongation of the bar is to be 0.2mm. Young's
modulus is E = 210 GN/m2.
(B) If, in order to reduce weight whilst keeping the external diameter constant, the left portion
is bored axially to produce a cylinder ofuniform thickness, whatis the maximum diameter of
bore possible given that the maximum allowable stress of the left portion is 180 MN/m2?
The load can be assumed to remain constant at 160 kN.
0.03 m
160 kN
160 kN
diameter
a
0.4 m
Q2) An extemal compressive load of 900 kN is applied on compound bar consists of three
bronze bars and two steel bars at a temperature 40C°, each bar of 50 cm? cross-sedion area.
Find (A) the temperature, at which the stress in the one bar will be zero and (B) the stress in
the another bars. Assume all of the bars are of equal lengths.
The coefficient of linear expansion per C° is 12x10-6 for steel and 18x10-6 for bronze.
E for steel = 200 GN/m2. E for bronze = 100 GN/m?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning