Quality Guard, which used a standard cost accounting system, manufactured 200,000 boat fenders during the year, using 1,250,000 feet of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.20 per foot. Production required 4,000 direct labor hours that cost $12.50 per hour. The materials standard was 6 feet of vinyl per fender at a standard cost of $1.35 per foot. The labor standard was 0.026 direct labor hour per fender at a standard cost of $12.00 per hour. Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Compute the price and quantity variances for direct materials. Compute the rate and efficiency variances for direct labor. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter currency amounts to the nearest cent and your answers to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variances as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Abbreviations used: DM = Direct materials, DL= Direct labor.) Begin with the variances for direct materials. First, determine the formula for the direct materials price variance, then compute the price variance for direct materials. (Assume that the quantity of materials purchased is equal to the quantity of materials used.)
Quality Guard, which used a standard cost accounting system, manufactured 200,000 boat fenders during the year, using 1,250,000 feet of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.20 per foot. Production required 4,000 direct labor hours that cost $12.50 per hour. The materials standard was 6 feet of vinyl per fender at a standard cost of $1.35 per foot. The labor standard was 0.026 direct labor hour per fender at a standard cost of $12.00 per hour. Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Compute the price and quantity variances for direct materials. Compute the rate and efficiency variances for direct labor. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter currency amounts to the nearest cent and your answers to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variances as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Abbreviations used: DM = Direct materials, DL= Direct labor.) Begin with the variances for direct materials. First, determine the formula for the direct materials price variance, then compute the price variance for direct materials. (Assume that the quantity of materials purchased is equal to the quantity of materials used.)
Chapter8: Standard Costs And Variances
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4PA: April Industries employs a standard costing system in the manufacturing of its sole product, a park...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Requirements
1. Compute the price and quantity variances for direct materials. Compute the
rate and efficiency variances for direct labor.
2.
Does the pattern of variances suggest that the company's managers have
been making trade-offs? Explain.
Print
Done
-
X
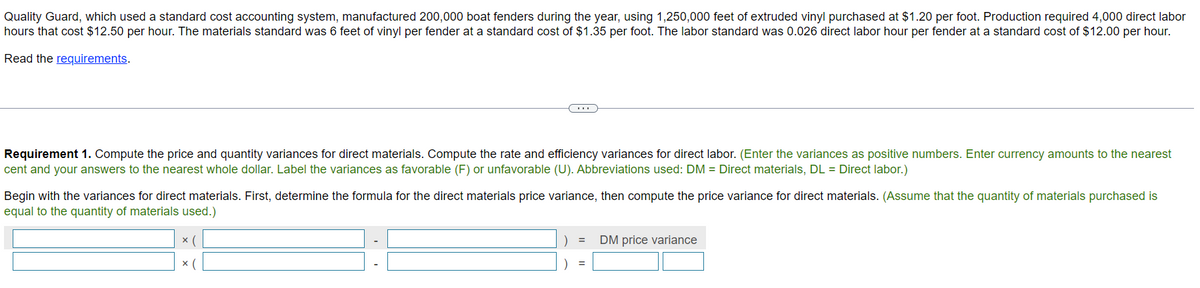
Transcribed Image Text:Quality Guard, which used a standard cost accounting system, manufactured 200,000 boat fenders during the year, using 1,250,000 feet of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.20 per foot. Production required 4,000 direct labor
hours that cost $12.50 per hour. The materials standard was 6 feet of vinyl per fender at a standard cost of $1.35 per foot. The labor standard was 0.026 direct labor hour per fender at a standard cost of $12.00 per hour.
Read the requirements.
Requirement 1. Compute the price and quantity variances for direct materials. Compute the rate and efficiency variances for direct labor. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter currency amounts to the nearest
cent and your answers to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variances as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Abbreviations used: DM = Direct materials, DL = Direct labor.)
Begin with the variances for direct materials. First, determine the formula for the direct materials price variance, then compute the price variance for direct materials. (Assume that the quantity of materials purchased is
equal to the quantity of materials used.)
x (
x (
=
DM price variance
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning