Question 12W A 5.00 g-sample of KOH(s) at 25.0 C was added to 100.0 g of H2O(1) temperature of the solution had increased. Based on the information given, which of the following best justifies the claim that the dissolution of KOH(s) is a thermodynamically favorable process? room temperature inside an insulated cup calorimeter, and the contents were stirred. After all the KOH(s) dissolved, the The forces between the ions and the water molecules are strọnger than the forces between water molecules, thus AH < 0. Also, the ions become less dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus A AS >0. Therefore, AG < 0. The energy required to break the bonds between the ions in the solid is less than that released as the ion-dipole attractions form during solvation, thus AH < 0. Also, the ions become more B widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS > 0. Therefore, AG < 0. The average kinetic energy of the particles increases, resulting in AH >0. Also, the ions become more widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS > 0. Therefore, AG > 0. The average kinetic energy of the particles increases, resulting in AH >0. Also, the ions become more widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS < 0. Therefore, AG > 0. D
Question 12W A 5.00 g-sample of KOH(s) at 25.0 C was added to 100.0 g of H2O(1) temperature of the solution had increased. Based on the information given, which of the following best justifies the claim that the dissolution of KOH(s) is a thermodynamically favorable process? room temperature inside an insulated cup calorimeter, and the contents were stirred. After all the KOH(s) dissolved, the The forces between the ions and the water molecules are strọnger than the forces between water molecules, thus AH < 0. Also, the ions become less dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus A AS >0. Therefore, AG < 0. The energy required to break the bonds between the ions in the solid is less than that released as the ion-dipole attractions form during solvation, thus AH < 0. Also, the ions become more B widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS > 0. Therefore, AG < 0. The average kinetic energy of the particles increases, resulting in AH >0. Also, the ions become more widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS > 0. Therefore, AG > 0. The average kinetic energy of the particles increases, resulting in AH >0. Also, the ions become more widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS < 0. Therefore, AG > 0. D
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter6: Thermochemisty
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.109QP: A 21.3-mL sample of 0.977 M NaOH is mixed with 29.5 mL of 0.918 M HCl in a coffee-cup calorimeter...
Related questions
Question
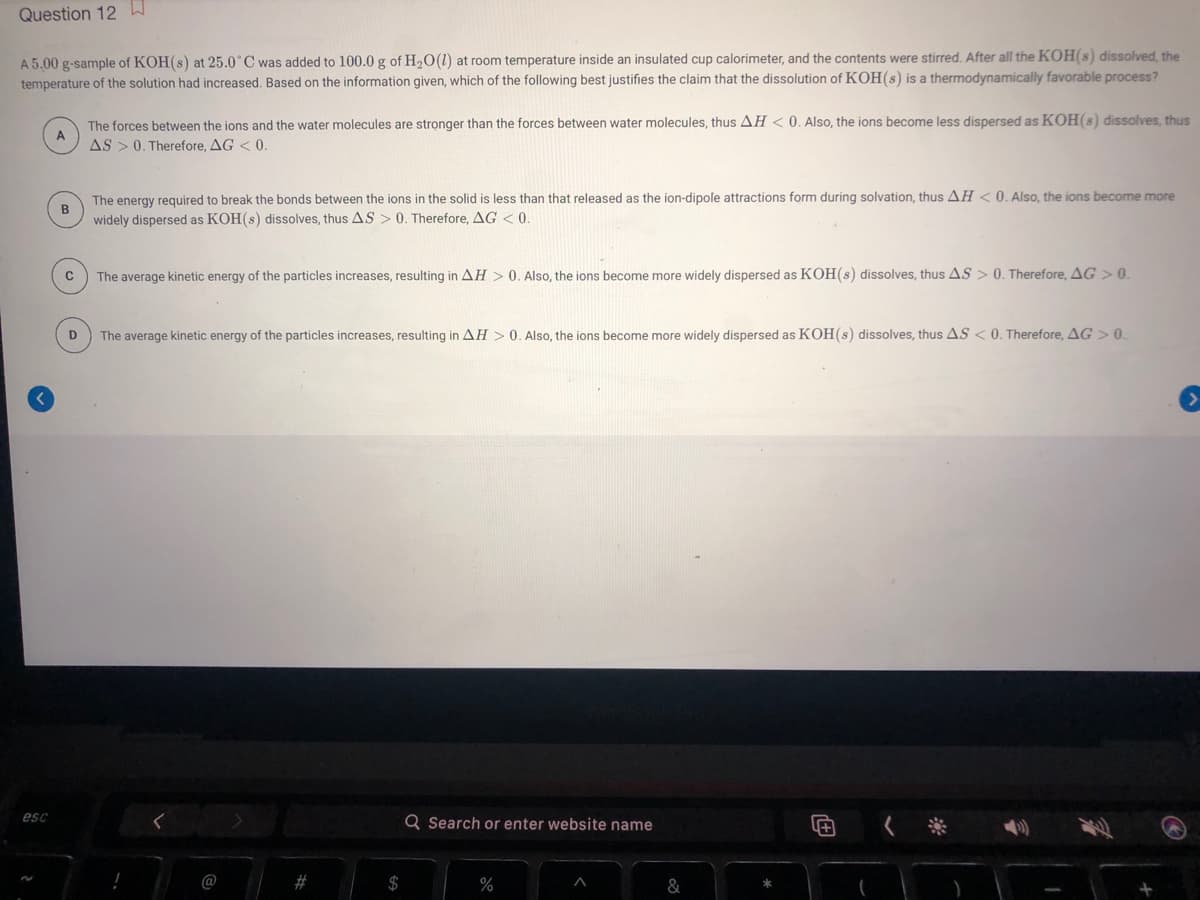
Transcribed Image Text:Question 12 W
A 5.00 g-sample of KOH(s) at 25.0°C was added to 100.0 g of H2O(1) at room temperature inside an insulated cup calorimeter, and the contents were stirred. After all the KOH(s) dissolved, the
temperature of the solution had increased. Based on the information given, which of the following best justifies the claim that the dissolution of KOH(s) is a thermodynamically favorable process?
The forces between the ions and the water molecules are strọnger than the forces between water molecules, thus AH < 0. Also, the ions become less dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus
AS >0. Therefore, AG < 0.
less than that released as the ion-dipole attractions form during solvation, thus AH < 0. Also, the ions become more
The energy required to break the bonds between the ions in the solid
widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS > 0. Therefore, AG < 0.
The average kinetic energy of the particles increases, resulting in AH > 0. Also, the ions become more widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS > 0. Therefore. AG > 0.
D
The average kinetic energy of the particles increases, resulting in AH > 0. Also, the ions become more widely dispersed as KOH(s) dissolves, thus AS < 0. Therefore. AG > 0.
esc
Q Search or enter website name
@
#
$
%
&
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
