QUESTION 7 Review the following figure. Suppose the price of gasoline is $1.60 per gallon. . What would happen to the quantity demanded? . What would happen to the quantity supplied? . At $1.60, is the market in equilibrium, a shortage, or a surplus? P ($ per gallon) $2.20 $1.80 $1.40 $1.20 $1.00 50.60 Excess supply or surplus S An above-equilibrium price Equilibrium price A below equilibrium price Excess demand or shortage D 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Quantity of Gasoline (millions of gallons) rise fall surplus shortage no change a shift in demand a shift in supply
QUESTION 7 Review the following figure. Suppose the price of gasoline is $1.60 per gallon. . What would happen to the quantity demanded? . What would happen to the quantity supplied? . At $1.60, is the market in equilibrium, a shortage, or a surplus? P ($ per gallon) $2.20 $1.80 $1.40 $1.20 $1.00 50.60 Excess supply or surplus S An above-equilibrium price Equilibrium price A below equilibrium price Excess demand or shortage D 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Quantity of Gasoline (millions of gallons) rise fall surplus shortage no change a shift in demand a shift in supply
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter3: Demand And Supply
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 53P: Table 3.8 shows information on the demand and supply for bicycles, where the quantities of bicycles...
Related questions
Question
Q7.
Select 1 answer for each question.
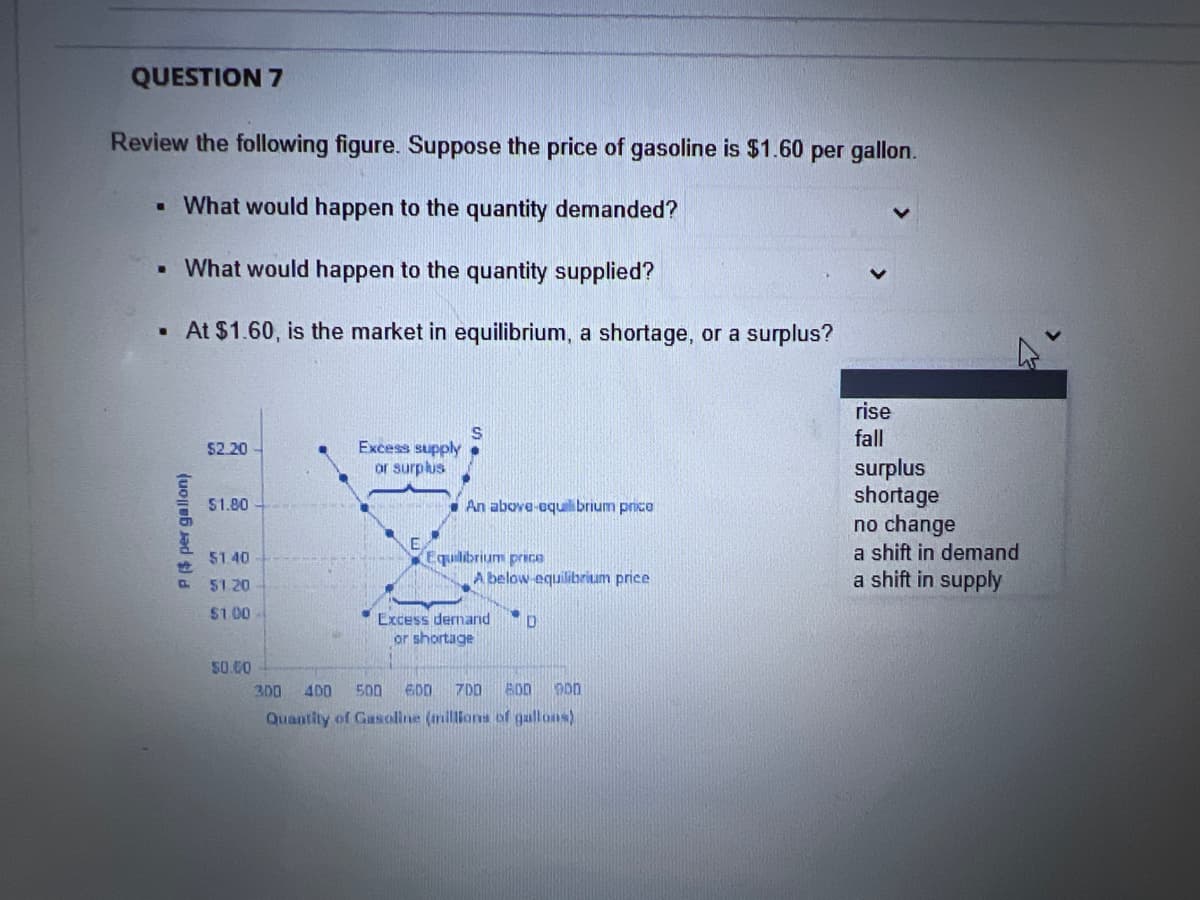
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 7
Review the following figure. Suppose the price of gasoline is $1.60 per gallon.
▪ What would happen to the quantity demanded?
. What would happen to the quantity supplied?
. At $1.60, is the market in equilibrium, a shortage, or a surplus?
P ($ per gallon)
$2.20
$1.80
$1.40
$1.20
$1.00
50.60
Excess supply
or surplus
An above-aquilibrium price
Equilibrium price
A below-equilibrium price
Excess demand D
or shortage
300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Quantity of Gasoline (millions of gallons)
rise
fall
surplus
shortage
no change
a shift in demand
a shift in supply
Expert Solution
Introduction
Market equilibrium: At the market equilibrium we have demand equals to supply. Or at market equilibrium point the maximum price which the consumers are willing to pay is exactly equals the minimum price at which the sellers are willing to sell.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc