Question b of 13 6. How might an industry's costs change in the long run? a. Costs may decrease due to constant returns to scale. economies of scale. diseconomies of scale. re-economies of scale. b. Costs may increase because an expanding industry bids up resource or input costs. profits can only be made in the long run. in the long run, price is always equal to average total cost.
Question b of 13 6. How might an industry's costs change in the long run? a. Costs may decrease due to constant returns to scale. economies of scale. diseconomies of scale. re-economies of scale. b. Costs may increase because an expanding industry bids up resource or input costs. profits can only be made in the long run. in the long run, price is always equal to average total cost.
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter13: The Cost Of Production
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10PA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Question 6 of 13
6. How might an industry's costs change in the long run?
a. Costs
may
decrease due to
constant returns to scale.
economies of scale.
diseconomies of scale.
O re-economies of scale.
b. Costs may increase because
an expanding industry bids up resource or input costs.
profits can only be made in the long run.
in the long run, price is always equal to average total cost.
a
39°F
A D
36
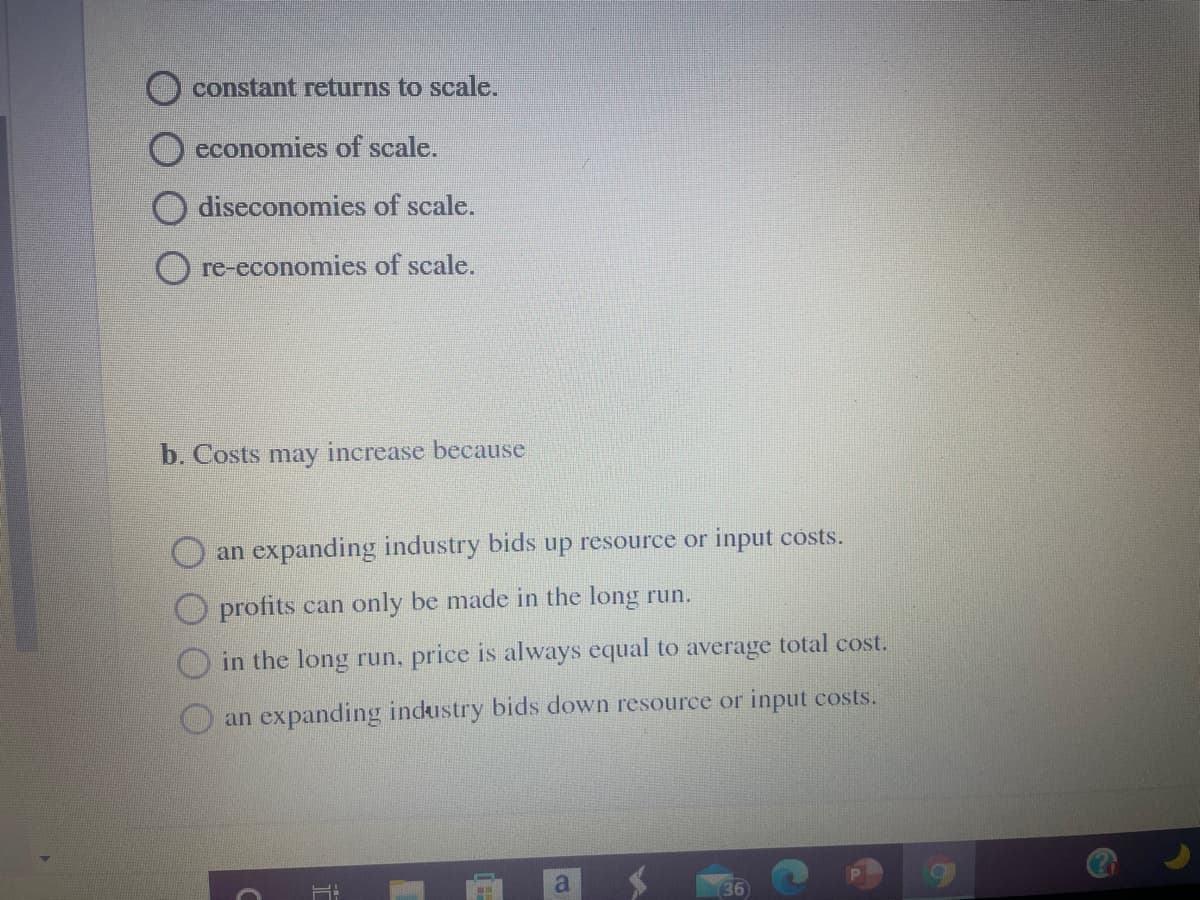
Transcribed Image Text:constant returns to scale.
economies of scale.
diseconomies of scale.
O re-economies of scale.
b. Costs may increase because
an expanding industry bids up resource or input costs.
O profits can only be made in the long run.
in the long run, price is always equal to average total cost.
an expanding industry bids down resource or input costs.
a
(36
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning