Reaction Rates, Activation Energy, and Catalysts Base your answers to practice questions 9 through 12 on the information below. An investigation was conducted to study the effect of the concentration of a reactant on the total time needed to complete a chemical reaction. Four trials of the same reaction were performed. In each trial the initial concentration of the reactant was different. The time needed for the chemical reaction to be completed was measured. The data for each of the four trials are shown in the data table below. Reaction Time Versus Initial Concentration Reactant Concentration and Reaction Time Initial Concentration Reaction Time Trial (M) (s) 0.020 11 0.015 14 0.010 23 0.005 58 0.000 0.005 0.010 0.015 0.020 0.025 Initial Concentration (M) 9. On the grid, mark an appropriate scale on the axis labeled "Reaction Time(s)." An appropriate scale is one that allows a trend to be seen. 10. On the same grid, plot the data from the table. Circle and connect the points. 11. State the effect of the concentration of the reactant on the rate of the chemical reaction. Reaction Time (s)
Reaction Rates, Activation Energy, and Catalysts Base your answers to practice questions 9 through 12 on the information below. An investigation was conducted to study the effect of the concentration of a reactant on the total time needed to complete a chemical reaction. Four trials of the same reaction were performed. In each trial the initial concentration of the reactant was different. The time needed for the chemical reaction to be completed was measured. The data for each of the four trials are shown in the data table below. Reaction Time Versus Initial Concentration Reactant Concentration and Reaction Time Initial Concentration Reaction Time Trial (M) (s) 0.020 11 0.015 14 0.010 23 0.005 58 0.000 0.005 0.010 0.015 0.020 0.025 Initial Concentration (M) 9. On the grid, mark an appropriate scale on the axis labeled "Reaction Time(s)." An appropriate scale is one that allows a trend to be seen. 10. On the same grid, plot the data from the table. Circle and connect the points. 11. State the effect of the concentration of the reactant on the rate of the chemical reaction. Reaction Time (s)
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Chapter18: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18.4TC: a What happens to a reaction rate as temperature drops? Give two explanations for the change. State...
Related questions
Question
FYI: 9-12 is like a),b),c) and d)
This is not a writing assignment or essay.
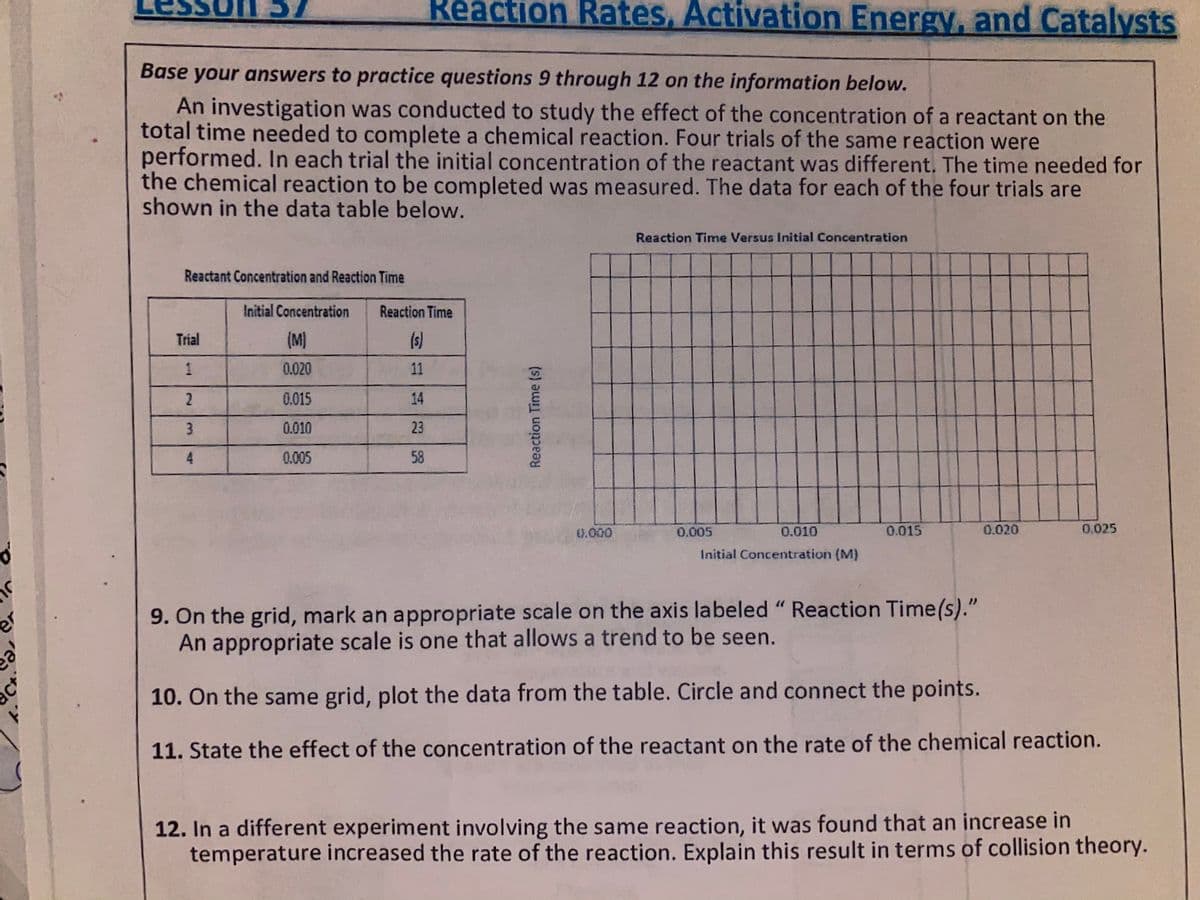
Transcribed Image Text:Reaction Rates, Activation Energy, and Catalysts
Base your answers to practice questions 9 through 12 on the information below.
An investigation was conducted to study the effect of the concentration of a reactant on the
total time needed to complete a chemical reaction. Four trials of the same reaction were
performed. In each trial the initial concentration of the reactant was different. The time needed for
the chemical reaction to be completed was measured. The data for each of the four trials are
shown in the data table below.
Reaction Time Versus Initial Concentration
Reactant Concentration and Reaction Time
Initial Concentration
Reaction Time
Trial
(M)
(s)
1
0.020
11
0.015
14
0.010
23
4.
0.005
58
0.000
0.005
0.010
0.015
0.020
0.025
Initial Concentration (M)
9. On the grid, mark an appropriate scale on the axis labeled "Reaction Time(s)."
An appropriate scale is one that allows a trend to be seen.
10. On the same grid, plot the data from the table. Circle and connect the points.
11. State the effect of the concentration of the reactant on the rate of the chemical reaction.
12. In a different experiment involving the same reaction, it was found that an increase in
temperature increased the rate of the reaction. Explain this result in terms of collision theory.
Reaction Time (s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
