Required information Use the following information for the Exercises below. [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Date Activities 1 Beginning inventory Units Acquired at Cost 165 unitse $9.00 - $1,485 Units sold at Retail Jan. Jan. 10 Sales 125 units @ $18.00 Jan. 20 Purchase 110 units@ $8.00 - 880 Jan. 25 Sales 125 units @ $18.00 Jan. 30 Purchase 230 units@ $7.50 = 1,725 Totals 505 units $4,090 250 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 255 units, where 230 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 20 are from beginning inventory.
Required information Use the following information for the Exercises below. [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Date Activities 1 Beginning inventory Units Acquired at Cost 165 unitse $9.00 - $1,485 Units sold at Retail Jan. Jan. 10 Sales 125 units @ $18.00 Jan. 20 Purchase 110 units@ $8.00 - 880 Jan. 25 Sales 125 units @ $18.00 Jan. 30 Purchase 230 units@ $7.50 = 1,725 Totals 505 units $4,090 250 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 255 units, where 230 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 20 are from beginning inventory.
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter7: Inventories: Cost Measurement And Flow Assumptions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8P: Comprehensive The following information for 2019 is available for Marino Company: 1. The beginning...
Related questions
Question
Practice Pack
![Required Information
Use the following information for the Exercises below.
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Date
Activities
Units Acquired at Cost
165 units@ $9.00 - $1,485
Units sold at Retail
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory
Jan. 10 Sales
125 units @
$18.00
Jan. 20 Purchase
Jan. 25 Sales
110 units@ $8.00 =
880
125 units @ $18.00
Jan. 30 Purchase
230 units@ $7.50 -
1,725
Totals
505 units
$4,090
250 units
The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 255 units, where
230 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 20 are from beginning inventory.
Exercise 5-3 Perpetual: Inventory costing methods LO P1
Required:
1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification.
2. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using weighted average.
3. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO.
4. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Prev
1
2
of 5
Next >](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F0d416ab4-4b03-4405-a6c3-34e7f4422377%2F990991bf-00ad-4e5e-b695-844fcec4282c%2F05l5oqh_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Required Information
Use the following information for the Exercises below.
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Date
Activities
Units Acquired at Cost
165 units@ $9.00 - $1,485
Units sold at Retail
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory
Jan. 10 Sales
125 units @
$18.00
Jan. 20 Purchase
Jan. 25 Sales
110 units@ $8.00 =
880
125 units @ $18.00
Jan. 30 Purchase
230 units@ $7.50 -
1,725
Totals
505 units
$4,090
250 units
The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 255 units, where
230 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 20 are from beginning inventory.
Exercise 5-3 Perpetual: Inventory costing methods LO P1
Required:
1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification.
2. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using weighted average.
3. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO.
4. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Prev
1
2
of 5
Next >
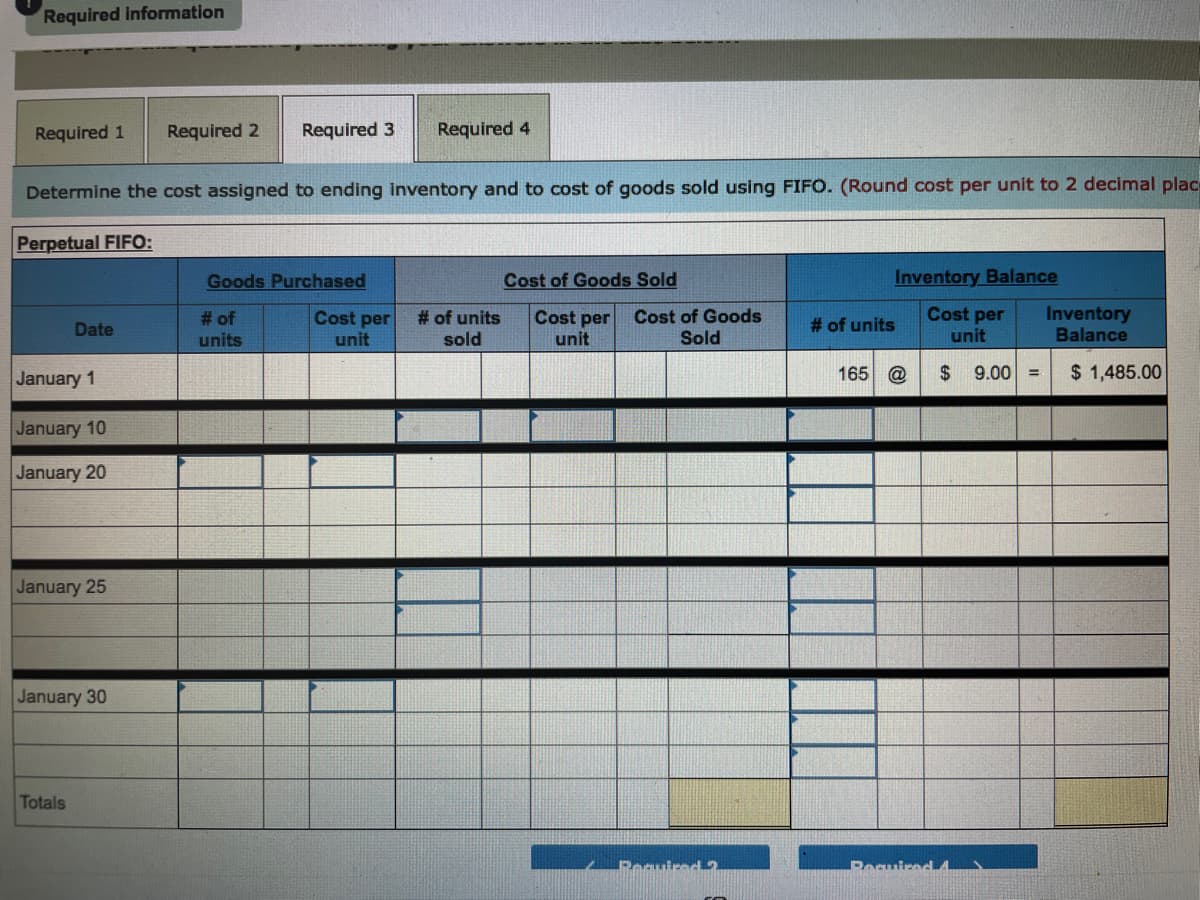
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
Required 1
Required 2
Required 3
Required 4
Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal plac
Perpetual FIFO:
Goods Purchased
Cost of Goods Sold
Inventory Balance
Cost per
# of
units
Cost per
unit
# of units
sold
Cost per
unit
Cost of Goods
Sold
Inventory
Balance
Date
# of units
unit
January 1
165
$ 9.00 =
$ 1,485.00
January 10
January 20
January 25
January 30
Totals
Reguired
ReguiredLA.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Includes step-by-step video
Learn your way
Includes step-by-step video
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn Journal
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337679503
Author:
Gilbertson
Publisher:
Cengage

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn Journal
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337679503
Author:
Gilbertson
Publisher:
Cengage

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning