reservoir (inflow) and where the water flo (outflow). Compare these values to your graph and estimate the concentration of each. ESTIMATED Concentration (M) Absorbance Inflow: 0.17 Outflow: 0.85 Now, on your graph, select the "Use Equation" option to "Label" your trendline. Write the equation you get below (in y=mx+b form) y = - X + Recall that Absorbance is your y-axis and Concentration is your x-axis. Plug each Absorbance value into your equation for "y" and solve for "x", the Concentration. Show calculations and record.
reservoir (inflow) and where the water flo (outflow). Compare these values to your graph and estimate the concentration of each. ESTIMATED Concentration (M) Absorbance Inflow: 0.17 Outflow: 0.85 Now, on your graph, select the "Use Equation" option to "Label" your trendline. Write the equation you get below (in y=mx+b form) y = - X + Recall that Absorbance is your y-axis and Concentration is your x-axis. Plug each Absorbance value into your equation for "y" and solve for "x", the Concentration. Show calculations and record.
Chapter29: Mass Spectrometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 29.5QAP
Related questions
Question
is one able to help? please
Transcribed Image Text:10
BISA
G
H
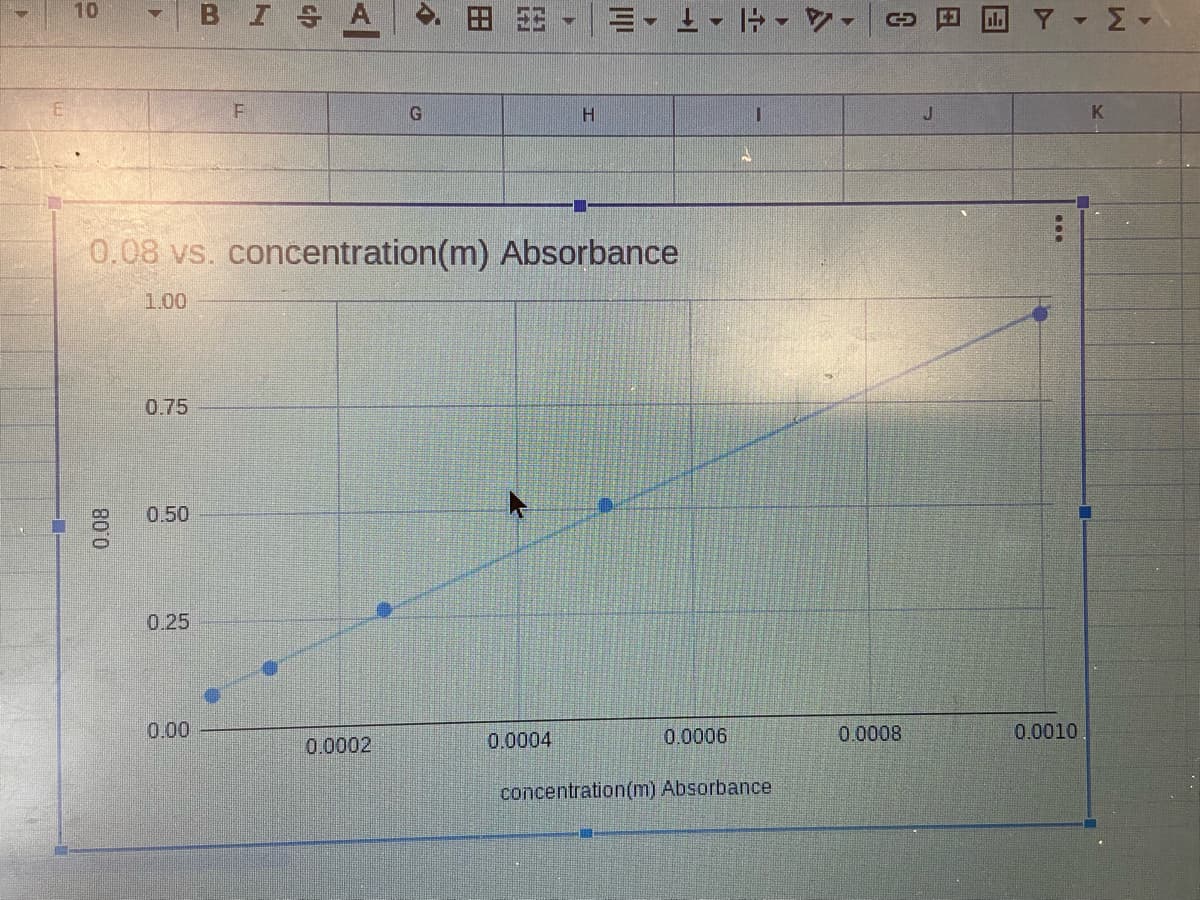
0.08 vs. concentration (m) Absorbance
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0.00
0.0004
0.0006
concentration(m) Absorbance
800
0.0002
LtJ
A
I
GO
0.0008
ΠΥ - Σ -
K
0.0010
Transcribed Image Text:then "Chart". From the drop
Under "Customize" click "Series" then "Trendline"
●
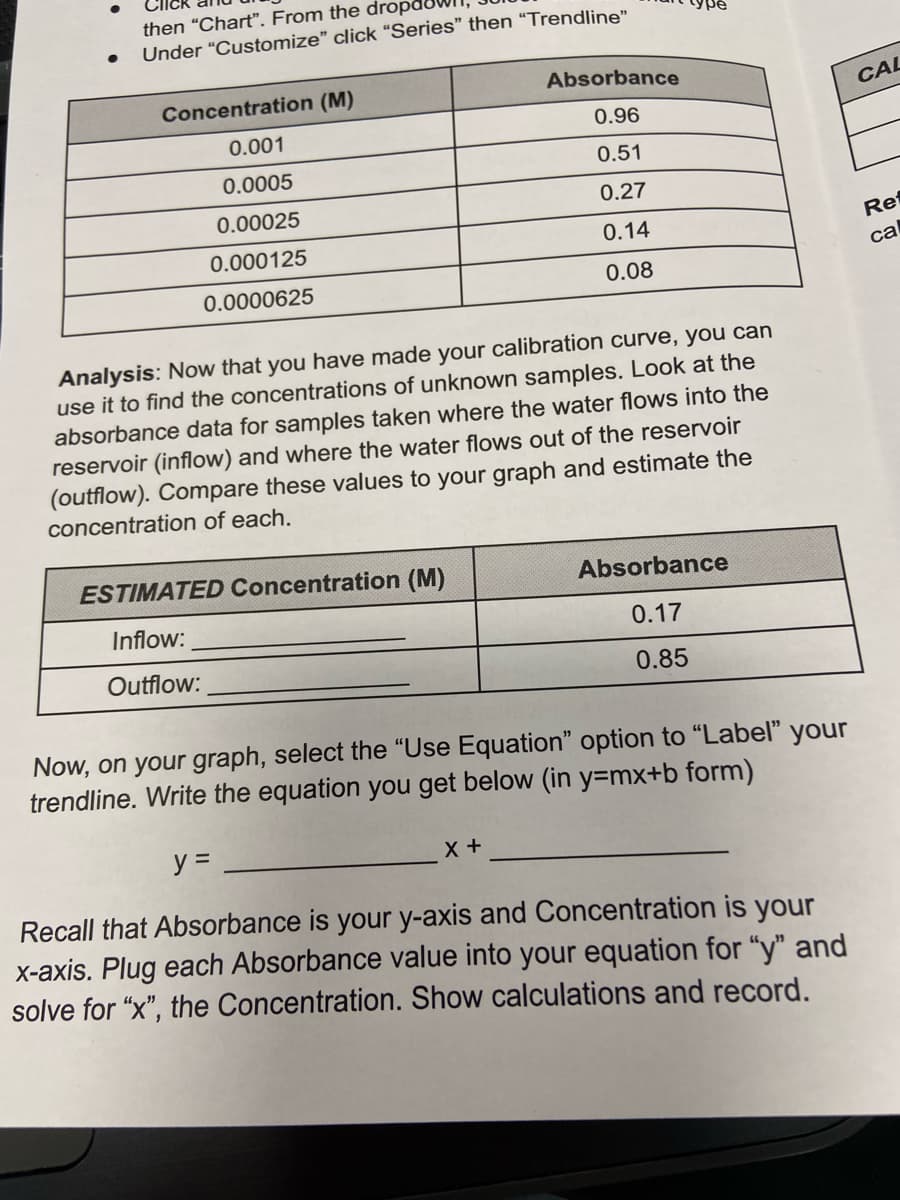
Absorbance
Concentration (M)
0.96
0.001
0.51
0.0005
0.27
0.00025
0.14
0.000125
0.08
0.0000625
Analysis: Now that you have made your calibration curve, you can
use it to find the concentrations of unknown samples. Look at the
absorbance data for samples taken where the water flows into the
reservoir (inflow) and where the water flows out of the reservoir
(outflow). Compare these values to your graph and estimate the
concentration of each.
ESTIMATED Concentration (M)
Absorbance
Inflow:
0.17
Outflow:
0.85
Now, on your graph, select the "Use Equation" option to "Label" your
trendline. Write the equation you get below (in y=mx+b form)
y =
X +
Recall that Absorbance is your y-axis and Concentration is your
x-axis. Plug each Absorbance value into your equation for "y" and
solve for "x", the Concentration. Show calculations and record.
CAL
Re
cal
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning