Rev MISSED THIS? Read Section 4.4 (Pages 149 - 155); Watch KCV 4.4, IWE 4.6. Correct answer is shown. Your answer 233.2 kg was either rounded differently significant figures than required for this part. Important: If you use this answer in later parts, use the full unrounded value in y The theoretical yield is the mass of product that could hypothetically be produce- determine the theoretical yield of urea (CH N20), convert the molar amount of reactant (NH3) as determined in Part A to kilograms (kg). Use the molar mass moles (mol) to grams (g). Then, convert grams to kilograms using the convers Urea (CH,N2O) is a common fertilizer that can be synthesized by the reaction of ammonia (NH) with carbon dioxide as follows: 2NH3(aq) + CO2(aq) CH N20(aq) + H20(1) In an industrial synthesis of urea, a chemist combines 132.1 kg of ammonia with 211.4 kg of carbon dioxide and obtains 163.8 kg of urea. 60.06 g CH,N,O 1 mol CH N,O 1 kg 3880.7 mol CH,N20 x 1000 g Part C Determine the percent yield for the reaction. Express your answer using three significant figures. » View Available Hint(s) Submit
Rev MISSED THIS? Read Section 4.4 (Pages 149 - 155); Watch KCV 4.4, IWE 4.6. Correct answer is shown. Your answer 233.2 kg was either rounded differently significant figures than required for this part. Important: If you use this answer in later parts, use the full unrounded value in y The theoretical yield is the mass of product that could hypothetically be produce- determine the theoretical yield of urea (CH N20), convert the molar amount of reactant (NH3) as determined in Part A to kilograms (kg). Use the molar mass moles (mol) to grams (g). Then, convert grams to kilograms using the convers Urea (CH,N2O) is a common fertilizer that can be synthesized by the reaction of ammonia (NH) with carbon dioxide as follows: 2NH3(aq) + CO2(aq) CH N20(aq) + H20(1) In an industrial synthesis of urea, a chemist combines 132.1 kg of ammonia with 211.4 kg of carbon dioxide and obtains 163.8 kg of urea. 60.06 g CH,N,O 1 mol CH N,O 1 kg 3880.7 mol CH,N20 x 1000 g Part C Determine the percent yield for the reaction. Express your answer using three significant figures. » View Available Hint(s) Submit
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter20: Environmental Chemistry-earth's Environment, Energy, And Sustainability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 41PS
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:MRev
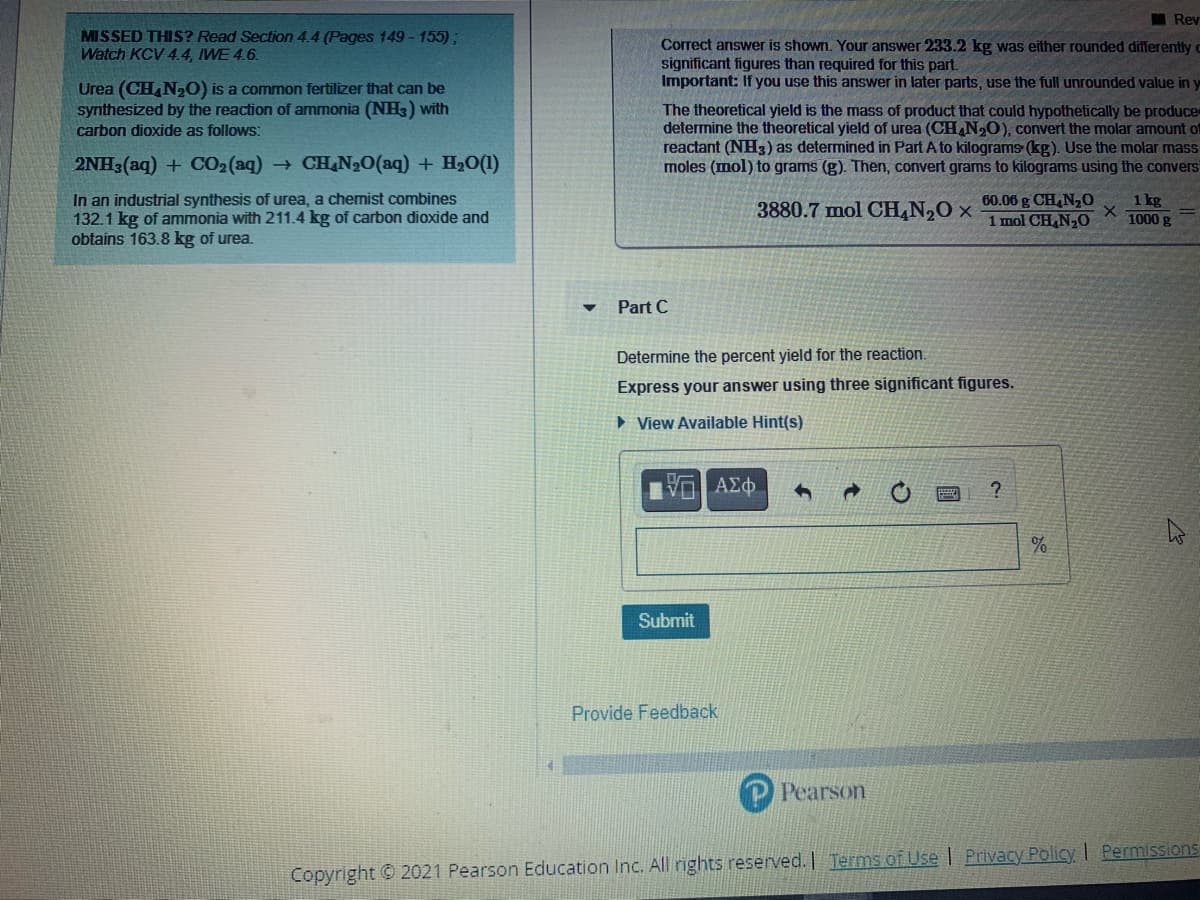
MISSED THIS? Read Section 4.4 (Pages 149 - 155);
Watch KCV 4.4, IWE 4.6.
Correct answer is shown. Your answer 233.2 kg was either rounded differently c
significant figures than required for this part.
Important: If you use this answer in later parts, use the full unrounded value in y
Urea (CH,N2O) is a common fertilizer that can be
synthesized by the reaction of ammonia (NH) with
The theoretical yield is the mass of product that could hypothetically be produce
determine the theoretical yield of urea (CH,N,0), convert the molar amount of
reactant (NH3) as determined in Part A to kilograms (kg). Use the molar mass
moles (mol) to grams (g). Then, convert grams to kilograms using the convers
carbon dioxide as follows:
2NH3(aq) + CO2(aq) CH N20(aq) + H20(1)
In an industrial synthesis of urea, a chemist combines
132.1 kg of ammonia with 211.4 kg of carbon dioxide and
obtains 163.8 kg of urea.
60.06 g CH,N,0
1 mol CH N,O
1 kg
1000 g
3880.7 mol CH,N20 ×
Part C
Determine the percent yield for the reaction.
Express your answer using three significant figures.
> View Available Hint(s)
ΑΣΦ
Submit
Provide Feedback
P Pearson
Copyright © 2021 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms o Use | Privacy Policy I Permissions
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning