Select correct and most relevant mechanism for each of the following reaction. Hint: Review Chapter 11.4. Br dilute HBr Mechanism A: H. CH2 nucleophilic attack HO HCH2 proton transfer H proton Br dilute H-Br: Br transfer Mechanism B: proton transfer dilute H-Br: tertiary carbocation hydrogen migration (rearrangement) HOCH3 H HCH3 = secondary carbocation Mechanism C: tertiary carbocation nucleophilic attack nucleophilic attack CH3 nucleophilic attack dilute H-Br: proton transfer primary carbanion Br: elimination H-Br: dilute H-Br: proton disassosiation Mechanism D: dilute H-Br: A B C proton transfer Br Br :Br-H secondary carbanion ..☺ CH2 proton transfer Н H CH3 H-Br: dilute H-Br: H-Br: proton transfer elimination proton disassosiation nucleophilic attack tertiary carbocation H HCH3 Br
Select correct and most relevant mechanism for each of the following reaction. Hint: Review Chapter 11.4. Br dilute HBr Mechanism A: H. CH2 nucleophilic attack HO HCH2 proton transfer H proton Br dilute H-Br: Br transfer Mechanism B: proton transfer dilute H-Br: tertiary carbocation hydrogen migration (rearrangement) HOCH3 H HCH3 = secondary carbocation Mechanism C: tertiary carbocation nucleophilic attack nucleophilic attack CH3 nucleophilic attack dilute H-Br: proton transfer primary carbanion Br: elimination H-Br: dilute H-Br: proton disassosiation Mechanism D: dilute H-Br: A B C proton transfer Br Br :Br-H secondary carbanion ..☺ CH2 proton transfer Н H CH3 H-Br: dilute H-Br: H-Br: proton transfer elimination proton disassosiation nucleophilic attack tertiary carbocation H HCH3 Br
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter21: Benzene And The Concept Of Aromaticity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21.58P
Related questions
Question
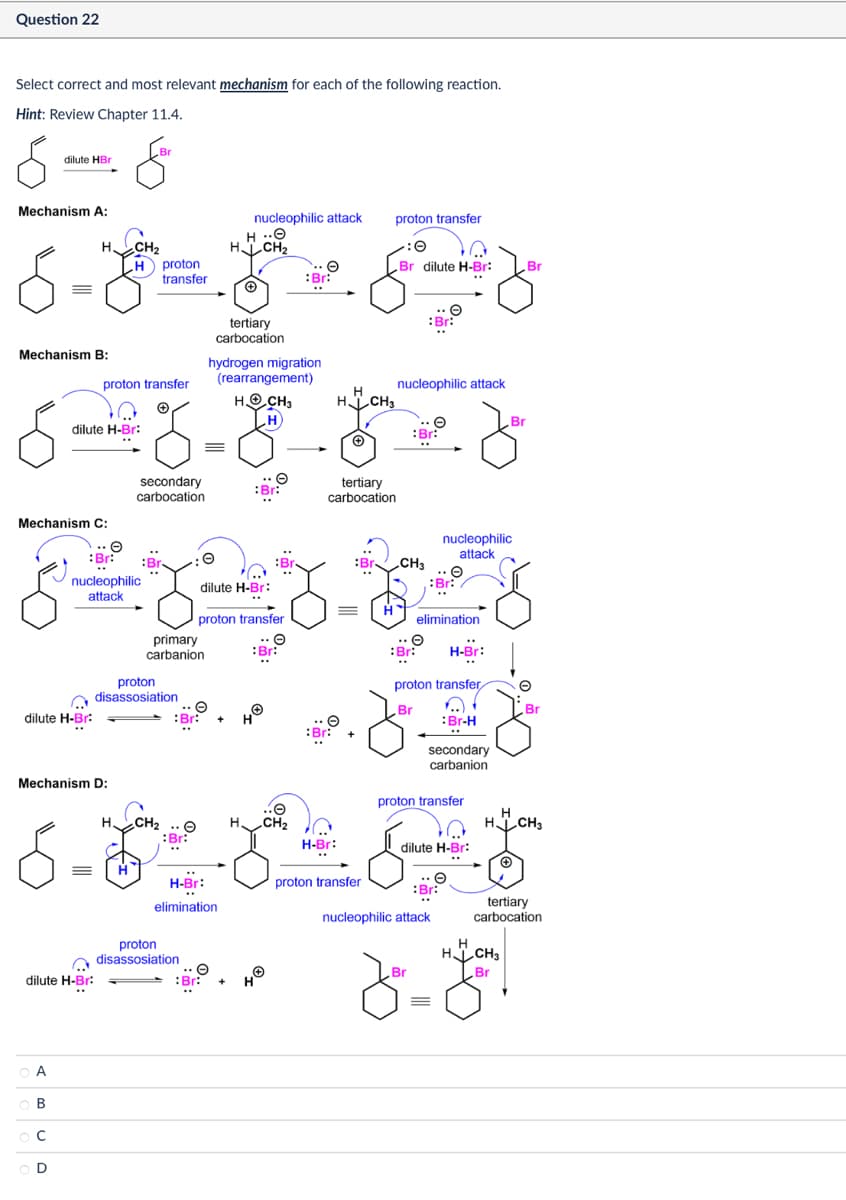
Transcribed Image Text:Question 22
Select correct and most relevant mechanism for each of the following reaction.
Hint: Review Chapter 11.4.
Br
dilute HBr
Mechanism A:
H.
CH2
Hproton
transfer
nucleophilic attack
H ..O
HCH2
proton transfer
Br dilute H-Br:
Br
Mechanism B:
proton transfer
tertiary
carbocation
hydrogen migration
(rearrangement)
HCH3
dilute H-Br:
Mechanism C:
secondary
carbocation
:Br:
nucleophilic attack
H
HCH3
Br
tertiary
carbocation
:Br:
nucleophilic
attack
nucleophilic
attack
CH3
dilute H-Br:
Η
proton transfer
elimination
primary
carbanion
O
:Br:
H-Br:
proton
disassosiation
proton transfer
Br
Br
dilute H-Br:
:Br:
:Br-H
Mechanism D:
dilute H-Br:
B
с
secondary
carbanion
proton transfer
H.
CH2
CH2
H
H CH3
H-Br:
dilute H-Br:
H-Br:
proton transfer
:Br:
elimination
proton
disassosiation
nucleophilic attack
tertiary
carbocation
H
H CH3
Br
:Br:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning