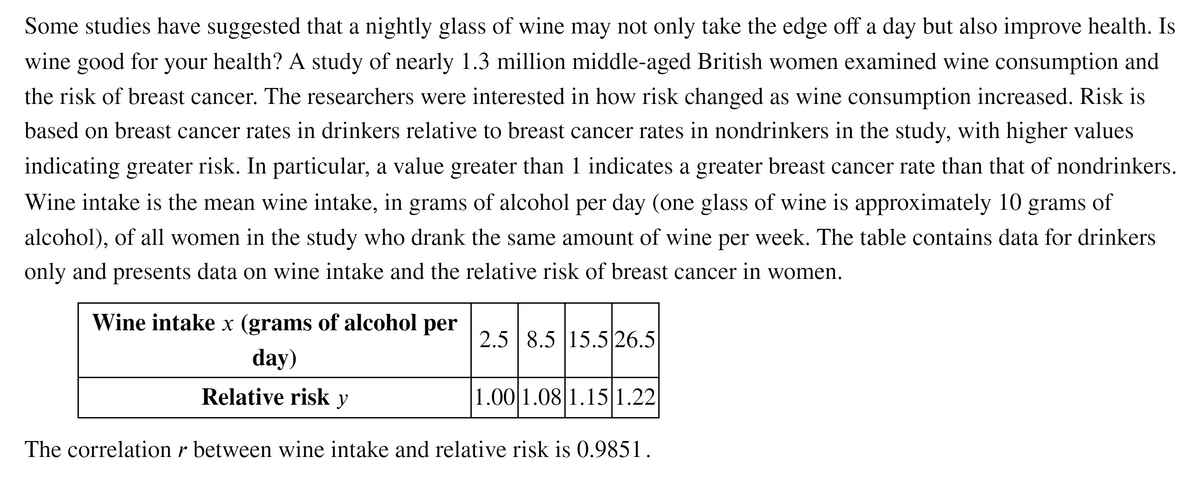
Some studies have suggested that a nightly glass of wine may not only take the edge off a day but also improve health. Is wine good for your health? A study of nearly 1.3 million middle-aged British women examined wine consumption and the risk of breast cancer. The researchers were interested in how risk changed as wine consumption increased. Risk is based on breast cancer rates in drinkers relative to breast cancer rates in nondrinkers in the study, with higher values indicating greater risk. In particular, a value greater than 1 indicates a greater breast cancer rate than that of nondrinkers. Wine intake is the mean wine intake, in grams of alcohol per day (one glass of wine is approximately 10 grams of alcohol), of all women in the study who drank the same amount of wine per week. The table contains data for drinkers only and presents data on wine intake and the relative risk of breast cancer in women. Wine intake x (grams of alcohol per 2.5 8.5 15.5 26.5 day) Relative risk y |1.00 1.08 1.15|1.22 The correlation r between wine intake and relative risk is 0.9851.
Correlation
Correlation defines a relationship between two independent variables. It tells the degree to which variables move in relation to each other. When two sets of data are related to each other, there is a correlation between them.
Linear Correlation
A correlation is used to determine the relationships between numerical and categorical variables. In other words, it is an indicator of how things are connected to one another. The correlation analysis is the study of how variables are related.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical method in which it estimates the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variable. In simple terms dependent variable is called as outcome variable and independent variable is called as predictors. Regression analysis is one of the methods to find the trends in data. The independent variable used in Regression analysis is named Predictor variable. It offers data of an associated dependent variable regarding a particular outcome.
Help!!
(c) If drinking an additional gram of alcohol each day raised the relative risk of breast cancer by exactly 0.01 , what would be the

Introduction:
It is given that the correlation coefficient, r between mean amount of alcohol intake per day, and the relative risk of developing breast cancer is 0.985.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps






