Suppose that a researcher, using data on class size (CS) and average test scores from 100 third-grade classes, estimates the OLS regression TestScore= 562.0320 + (-6.2856)x CS, R=0.11, ER = 12.4 (22.0320) (2.0111) Construct a 95% confidence interval for B,, the regression slope coefficient. The 95% confidence interval for B,, the regression slope coefficient, is ( D (Round your responses to two decimal places.) The t-statistic for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.) Note: Assume a normal distribution. The p-value for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.) Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% level? O A. Yes, because the t-statistic is less than 2.58. O B. Yes, because the p-value is less than 0.01. O C. Yes, because the t-statistic is greater than 2.58. O D. No, because the p-value is greater than 0.01.
Suppose that a researcher, using data on class size (CS) and average test scores from 100 third-grade classes, estimates the OLS regression TestScore= 562.0320 + (-6.2856)x CS, R=0.11, ER = 12.4 (22.0320) (2.0111) Construct a 95% confidence interval for B,, the regression slope coefficient. The 95% confidence interval for B,, the regression slope coefficient, is ( D (Round your responses to two decimal places.) The t-statistic for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.) Note: Assume a normal distribution. The p-value for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.) Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% level? O A. Yes, because the t-statistic is less than 2.58. O B. Yes, because the p-value is less than 0.01. O C. Yes, because the t-statistic is greater than 2.58. O D. No, because the p-value is greater than 0.01.
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter4A: Problems In Applying The Linear Regression Model
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
Please help
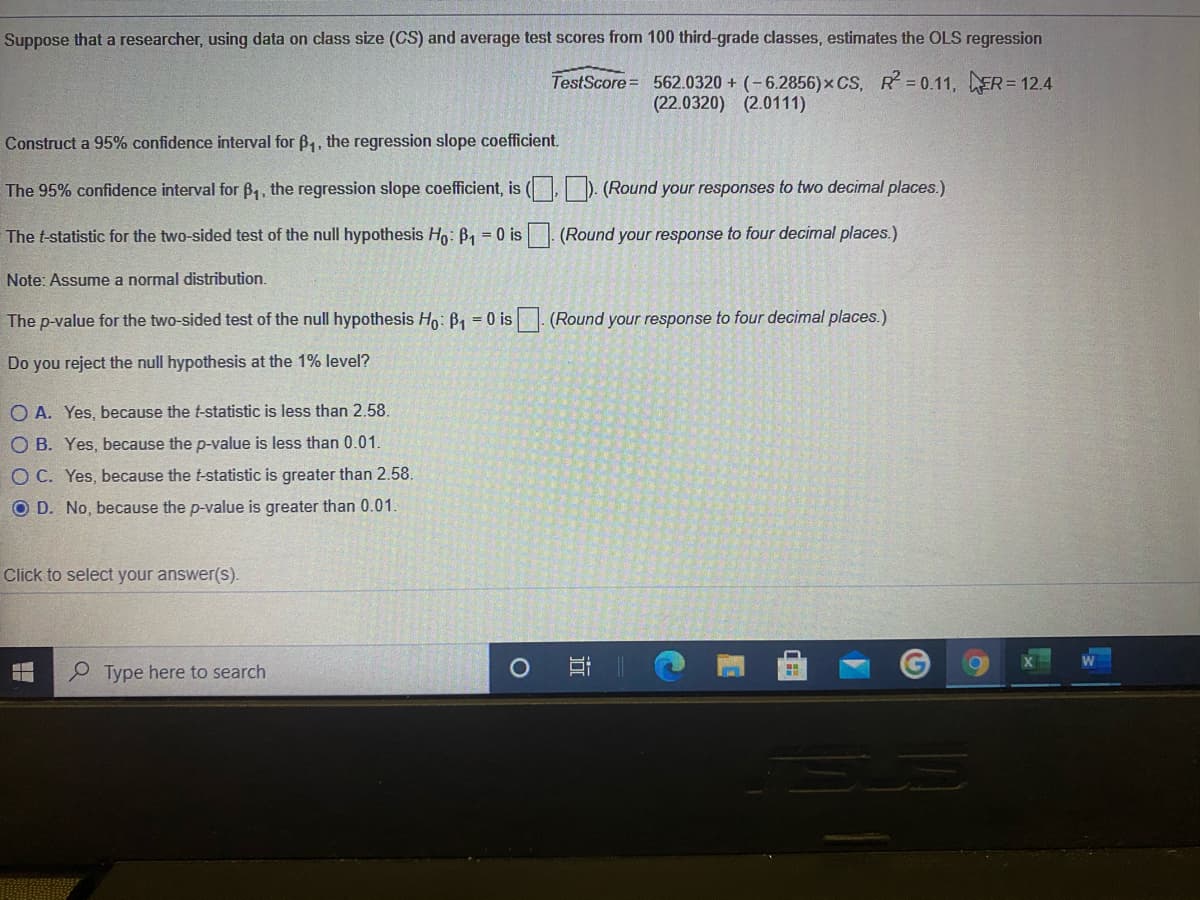
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that a researcher, using data on class size (CS) and average test scores from 100 third-grade classes, estimates the OLS regression
TestScore= 562.0320 + (-6.2856)x CS, R 0.11, ER= 12.4
(22.0320) (2.0111)
Construct a 95% confidence interval for B,, the regression slope coefficient.
The 95% confidence interval for B,, the regression slope coefficient, is ( ). (Round your responses to two decimal places.)
The t-statistic for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.)
Note: Assume a normal distribution.
The p-value for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.)
Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% level?
O A. Yes, because the t-statistic is less than 2.58.
O B. Yes, because the p-value is less than 0.01.
O C. Yes, because the t-statistic is greater than 2.58.
O D. No, because the p-value is greater than 0.01.
Click to select your answer(s).
P Type here to search
耳|

Transcribed Image Text:This Question: 2 pts
2 of 21 (20 complete)
LHe 33 70 LUmuence nervai iui P1, uEleyiessiOII Siope CueIICient, iS (| J:| V- RUUnu youi TespUnses iU tWu ueciiai pldues.)
The t-statistic for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B, = 0 is
(Round your response to four decimal places.)
Note: Assume a normal distribution.
The p-value for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B1 = 0 is . (Round your response to four decimal places.)
Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% level?
O A. Yes, because the t-statistic is less than 2.58.
O B. Yes, because the p-value is less than 0.01.
O C. Yes, because the t-statistic is greater than 2.58.
O D. No, because the p-value is greater than 0.01.
The p-value for the two-sided test of the null hypothesis Ho: B, = -6.0 is (Round your response to four decimal places.)
Without doing any additional calculations, determine whether - 6.0 is contained in the 95% confidence interval for B.
O A. No, -6.0 is not contained in the 95% confidence interval for B,
O B. Yes, -6.0 is contained in the 95% confidence interval for B1
Click to select your answer(s).
9 Type here to search
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning