Suppose that Maria is starting a food ordering and delivery company. Customers order meals online. Employees prepare the meals and deliver them to customers. Maintenance of the online platform for ordering meals costs the company $5 per day. The company also rents space where orders are prepared. Rent costs $50 per day. To make the deliveries, the business also rents two delivery cars that cost $10 each per day. The costs of ingredients for preparing different numbers of meals are provided in the table below. Maria also has to hire between 0 and 10 workers (depending on the number of meals she chooses to make) to buy ingredients, prepare meals, and deliver the orders. She will pay each employee $120 per day. The first two columns of the table below show how many meals different number of workers can prepare and deliver. Price per meal $50 Workers Meals (Labor L) (Output Q) o 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 30 42 52 60 67 73 79 85 90 95 MPL FC Cost of ingredients $10 $75 $100 $121 $138 $152 $165 $177 $189 $199 $210 VC TC AFC AVC b) Use Excel functions to find the marginal product of labor (MPL) and enter it into the third column of the table. Note: MPL = change in Q/ change in L. Graph MPL as a function of the number of workers Maria hires. ATC MC TR Profit Profit per meal
Suppose that Maria is starting a food ordering and delivery company. Customers order meals online. Employees prepare the meals and deliver them to customers. Maintenance of the online platform for ordering meals costs the company $5 per day. The company also rents space where orders are prepared. Rent costs $50 per day. To make the deliveries, the business also rents two delivery cars that cost $10 each per day. The costs of ingredients for preparing different numbers of meals are provided in the table below. Maria also has to hire between 0 and 10 workers (depending on the number of meals she chooses to make) to buy ingredients, prepare meals, and deliver the orders. She will pay each employee $120 per day. The first two columns of the table below show how many meals different number of workers can prepare and deliver. Price per meal $50 Workers Meals (Labor L) (Output Q) o 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 30 42 52 60 67 73 79 85 90 95 MPL FC Cost of ingredients $10 $75 $100 $121 $138 $152 $165 $177 $189 $199 $210 VC TC AFC AVC b) Use Excel functions to find the marginal product of labor (MPL) and enter it into the third column of the table. Note: MPL = change in Q/ change in L. Graph MPL as a function of the number of workers Maria hires. ATC MC TR Profit Profit per meal
Chapter22: Supply: The Costs Of Doing Business
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14E
Related questions
Question
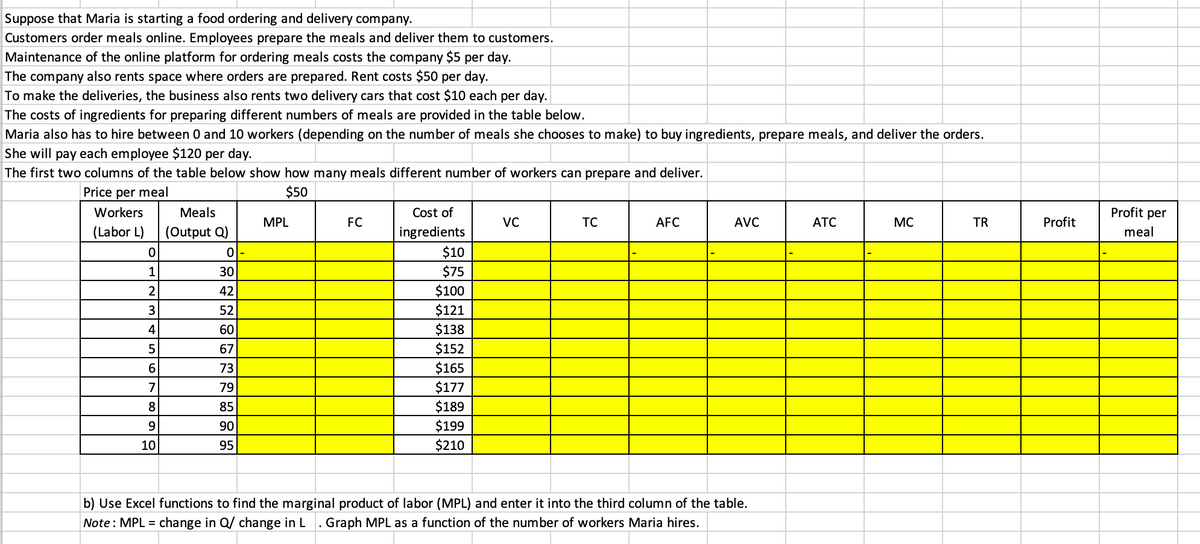
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that Maria is starting a food ordering and delivery company.
Customers order meals online. Employees prepare the meals and deliver them to customers.
Maintenance of the online platform for ordering meals costs the company $5 per day.
The company also rents space where orders are prepared. Rent costs $50 per day.
To make the deliveries, the business also rents two delivery cars that cost $10 each per day.
The costs of ingredients for preparing different numbers of meals are provided in the table below.
Maria also has to hire between 0 and 10 workers (depending on the number of meals she chooses to make) to buy ingredients, prepare meals, and deliver the orders.
She will pay each employee $120 per day.
The first two columns of the table below show how many meals different number of workers can prepare and deliver.
Price per meal
$50
Workers
(Labor L)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Meals
(Output Q)
ol-
30
42
52
60
67
73
79
85
90
95
MPL
FC
Cost of
ingredients
$10
$75
$100
$121
$138
$152
$165
$177
$189
$199
$210
VC
TC
AFC
AVC
b) Use Excel functions to find the marginal product of labor (MPL) and enter it into the third column of the table.
Note: MPL = change in Q/ change in L Graph MPL as a function of the number of workers Maria hires.
ATC
MC
TR
Profit
Profit per
meal
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning