Suppose the market supply is given by L=2.8w. Assume the product market is competitive and the product price is p=$12. Also suppose MPL=8.6-0.8L and that the firm has monopsony power. A.Graph . The vertical intercept of this curve is equal to the marginal revenue product of labour. The slope of this curve is equal to Write the formula for the inverse supply of labour and graph the supply curve. The slope of this supply curve is B. For this firm, the fully simplified formula for marginal cost is MC₁=__L (Enter the value which completes the formula. Do not enter the variable, it has been given) Illustrate this market graphically, including accurate numbers for slopes and intercepts. Write the condition which the monopsonist's optimal choice of labour must satisfy. This monopsonist will choose employment level . At this employment level, the firm will offer the wage $ , and the value marginal product of labour is $ The average cost of labour for this monopsonist is $ and the firm's profit from the marginal worker is $ C. The competitive outcome would occur at the intersection of which two curves? Indicate this point on your graph. Based on the equations given, the competitive level of employment would be and the competitive wage would be $ . Relative to the monopsony outcome, competitive employment is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower). (Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower) and competitive wages are Now suppose the union insists wages must not be below $4.79: D. Carefully draw the firm's new marginal cost of labour. For employment levels up to L= that, the marginal cost of labour , the firm's marginal cost of labour will be $4.79. For levels of employment greater than (Enter "1" for increases, "0" for stays the same, "-1" for decreases). Explain why. and workers will be paid $ E. Has the condition for the monopsonist's optimal choice of L changed? After the union influence, the level of employment will be When the union insists on at least $4.79 then, relative to the monopsony outcome, employment is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower) and worker pay is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower). When the union insists on at least $4.79 then, relative to the competitive outcome, employment is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower) and worker pay is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower). Do you think the union can insist on a wage higher than $4? Write down what you think determines the minimum wage insisted on by the union.
Suppose the market supply is given by L=2.8w. Assume the product market is competitive and the product price is p=$12. Also suppose MPL=8.6-0.8L and that the firm has monopsony power. A.Graph . The vertical intercept of this curve is equal to the marginal revenue product of labour. The slope of this curve is equal to Write the formula for the inverse supply of labour and graph the supply curve. The slope of this supply curve is B. For this firm, the fully simplified formula for marginal cost is MC₁=__L (Enter the value which completes the formula. Do not enter the variable, it has been given) Illustrate this market graphically, including accurate numbers for slopes and intercepts. Write the condition which the monopsonist's optimal choice of labour must satisfy. This monopsonist will choose employment level . At this employment level, the firm will offer the wage $ , and the value marginal product of labour is $ The average cost of labour for this monopsonist is $ and the firm's profit from the marginal worker is $ C. The competitive outcome would occur at the intersection of which two curves? Indicate this point on your graph. Based on the equations given, the competitive level of employment would be and the competitive wage would be $ . Relative to the monopsony outcome, competitive employment is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower). (Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower) and competitive wages are Now suppose the union insists wages must not be below $4.79: D. Carefully draw the firm's new marginal cost of labour. For employment levels up to L= that, the marginal cost of labour , the firm's marginal cost of labour will be $4.79. For levels of employment greater than (Enter "1" for increases, "0" for stays the same, "-1" for decreases). Explain why. and workers will be paid $ E. Has the condition for the monopsonist's optimal choice of L changed? After the union influence, the level of employment will be When the union insists on at least $4.79 then, relative to the monopsony outcome, employment is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower) and worker pay is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower). When the union insists on at least $4.79 then, relative to the competitive outcome, employment is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower) and worker pay is (Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower). Do you think the union can insist on a wage higher than $4? Write down what you think determines the minimum wage insisted on by the union.
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305971493
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter18: The Markets For The Factor Of Production
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3PA
Related questions
Question
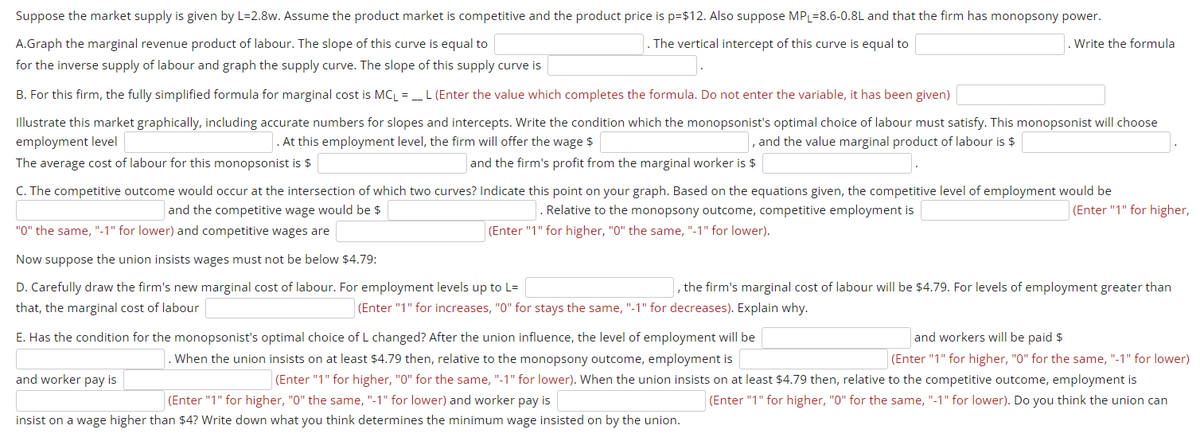
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the market supply is given by L=2.8w. Assume the product market is competitive and the product price is p=$12. Also suppose MPL=8.6-0.8L and that the firm has monopsony power.
A.Graph the marginal revenue product of labour. The slope of this curve is equal to
The vertical intercept of this curve is equal to
.Write the formula
for the inverse supply of labour and graph the supply curve. The slope of this supply curve is
B. For this firm, the fully simplified formula for marginal cost is MC₁ = __ L (Enter the value which completes the formula. Do not enter the variable, it has been given)
Illustrate this market graphically, including accurate numbers for slopes and intercepts. Write the condition which the monopsonist's optimal choice of labour must satisfy. This monopsonist will choose
employment level
. At this employment level, the firm will offer the wage $
, and the value marginal product of labour is $
The average cost of labour for this monopsonist is $
and the firm's profit from the marginal worker is $
C. The competitive outcome would occur at the intersection of which two curves? Indicate this point on your graph. Based on the equations given, the competitive level of employment would be
and the competitive wage would be $
. Relative to the monopsony outcome, competitive employment is
(Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower).
(Enter "1" for higher,
"0" the same, "-1" for lower) and competitive wages are
Now suppose the union insists wages must not be below $4.79:
D. Carefully draw the firm's new marginal cost of labour. For employment levels up to L=
that, the marginal cost of labour
, the firm's marginal cost of labour will be $4.79. For levels of employment greater than
(Enter "1" for increases, "0" for stays the same, "-1" for decreases). Explain why.
E. Has the condition for the monopsonist's optimal choice of L changed? After the union influence, the level of employment will be
and workers will be paid $
. When the union insists on at least $4.79 then, relative to the monopsony outcome, employment is
(Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower)
and worker pay is
(Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower). When the union insists on at least $4.79 then, relative to the competitive outcome, employment is
(Enter "1" for higher, "0" the same, "-1" for lower) and worker pay is
(Enter "1" for higher, "0" for the same, "-1" for lower). Do you think the union can
insist on a wage higher than $4? Write down what you think determines the minimum wage insisted on by the union.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning





Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax